You see this on the monitor and go to the patients room. What should you do immediately?

You should immediately assess your patient for pulse.
..Often a lead can fall off or equipment malfunction can cause abnormal readings. Pt assessment can indicate a problem.
How can you tell that a patient is unstable when assessing the patient?
Pt has low HR, BP, significant signs of decreased perfusion (low cap refill, cool to touch abnormal color), altered mental status, unresponsive.
Upon hearing this common phrase I will stop CPR and immediately move away from the patient. WHY??
"stand clear" or " you're clear, i'm clear, we're all clear"
...the patients is about to recieve a shock of electricity.
I am typically given to a rhythm that is classified as symtomatic bradycardia.
Atropine
....If the drug doesn't work what will usually come next...Pacemaker
Your patient just came froma simple procedure in the OR. You are recovering them in PACU and see the rhythm below. What can you identify and how would you treat this?
Unifocal PVCs and it should be treated with O2.
...lack of oxygen is the most common reason you will see and PVC. Making administration of oxygen a priority.
The patient is in the following rhythm. You have given 2 doses of adenosine with no change. The patient is SOB, and having CP. The patients BP is 68/50 and just went unresponsive. What is the next action?
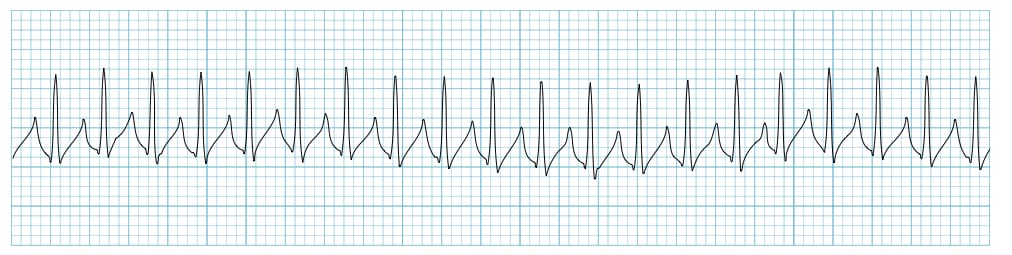
Synchronized cardioversion
...You do not defibrillate because the patient is not dead. They still have a pulse and BP at this point.
You see the following rhythm on the monitor. You assess the patient and determine there is no pulse and no breathing. What are your next actions?

You should start CPR and defibrillate early to convert the rhythm. Remember early defibrillation is key to survival.
** you have already assessed you patient.
What is this a visual representation of?
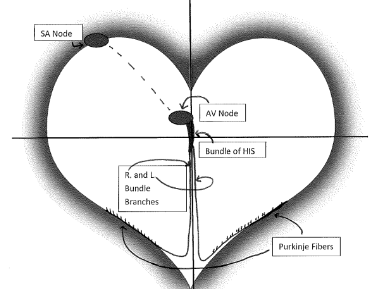
The conduction pathway of the heart.
The patient is in the following rhythm; Complaining of Palpiations and Shortness of Breath. I was given to the patient in an effort to convert the rhythm.

What is Adenosine?
...Rapid push, patient should be attached to the monitor, MD and codecart at the bedside.
...What is the dosage? 6 mg then 12 mg
Looking at the wave form below. The area highlighted can have a different form and is often related to a specific electrolyte. It can be inverted or peaked, depending on the electrolyte abnormality. What is the name of the wave and electrolyte abnormality?
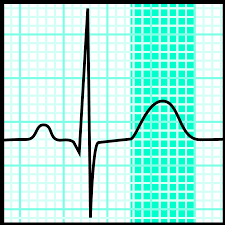
A peaked t-wave can be indicative of hyperkalemia
A inverted t-wave can be due to hypokalemia.
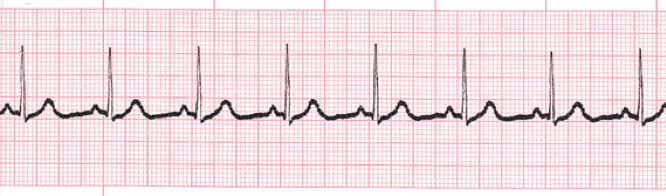
You see the following rhythm. During assessment you identify altered mental status, gerneralized weakness and BP 105/76. What should you immediately report to the provider? Identify the rhythm.

This is a third degree block. You should immediately report altered mental status.
...What are the symptoms associated with a heart block?
Your patient is unresponsive. You identify the following rhythm on the monitor. After further assessing the patient, they are pulseless and apneic. What should you do next?

Immediately start CPR for a pt that is pulseless. You should be prepared to defibrillate. Early defibrillation is key to survival.
You see are assessing your patient and see the following rhythm on the monitor. Your patient is unresponsive and does not have a pulse and is not breathing. What is the name of the rhythm you see? What is your immediate action?
Pulseless electrical activity... You should immediately start CPR since your patient does not have a pulse.
...remember that electrical activity can show on a monitor, but that does not mean that the heart is actually beating.
Your patient is complaing of palpitations, chest pain, and weakness. You find RR26, BP 98/68. What medication should you expect to be ordered? Identify the rhythm.
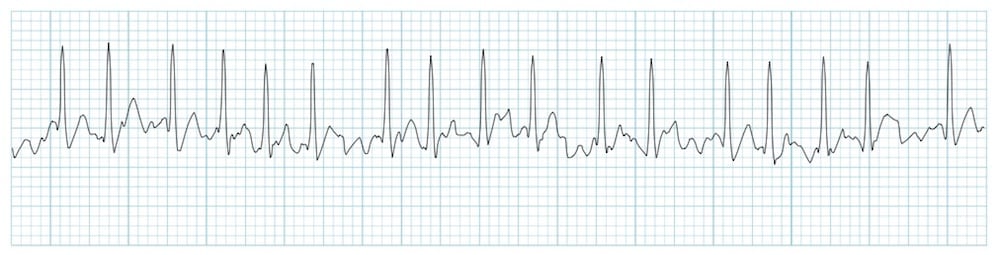
Ditiazem (Cardizem) should be ordered for this patient. This is A-fib with RVR.
...You could give adenosine to slow the rhythm enough to better determine what the rhythm is. However, this is temporary and treatment would be diltiazem.
***Daily Double ***
What looks abnormal in this ECG? (this is not a 6 second strip, it is 3 seconds)
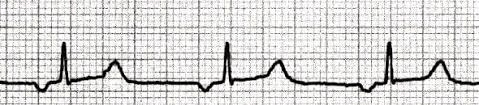
You should notice that the P wave is inverted. The HR is 60 and normal.
You identify the following rhythm. In order to treat the rhythm you should Identify underlying causes. List at least 3 underlying causes.
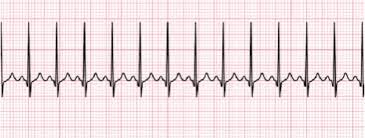
Drugs(cociane, meth)
Fever
Sepsis
Dehydration
Trauma
Hyperthyroid
ect.
You have a patient that is in v-fib. You have given 2 shocks, and given 3 rounds of CPR. What should you prepare to do next?
You should prepare to defibrillate again and administer epinepherine during the next pulse check.
What should you teach your patient after a pacemaker has been inserted?
they should take a daily pulse and blood pressure, Carry an info card about the pacemaker, Inform airport screeners of the pacemaker, reports any symptoms (including Hiccups) to MD, and inform medial staff (esp. MRI)
I am a front line drug used in cardiac arrest. You will give 1 mg to any client that does not have a pulse. It will be given every 4 minutes during CPR according to ACLS guidelines.
Epinephrine
What abnormality do you see in the following strip and should you be concerned?

PAC- premature atrial contraction
Generally, this is asymptomatic and you should not worry. Continue normal monitoring of pt.
When dealing with cardiac arrest it is important to identify possible causes. Name the Hs and Ts that you would identify in a cardiac arrest patient.
Hypovolemia
Hypoxia*
Hydrogen ion (acidosis)
Hyper-/Hypokalemia
Hypoglycemia
Hypothermia
Toxins
Tamponade (cardiac)
Tension pneumothorax
Thrombosis (coronary & pulmonary)
Trauma
What is this rhythm and how would you treat it?
Torsades de point- form of v-fib
Treated with magnesium sulfate
Name the 3 ways energy is delivered to a patient...
1)Transcutaneaous pacing-- used in the emergency setting.
Transvenous pacing
Permanant tansvenous pacing
2) Syncronized cardioversion
3)Defibrillation
You see the following rhythm on the monitor. When assessing the patient they complain of crushing chest pain, but have a pulse. You immediately place the patient on a defibrillator/ monitor. What would drug would be appropriate to give to the client? Identify the rhythm.
This is v-tach with a pulse.
You should administer 150 mg of Amiodorone IVP over 10 minutes.
**Sotolol and procainamide can also be used, however are not used as commonly as amiodorone.
What would you call what you see on the strip below?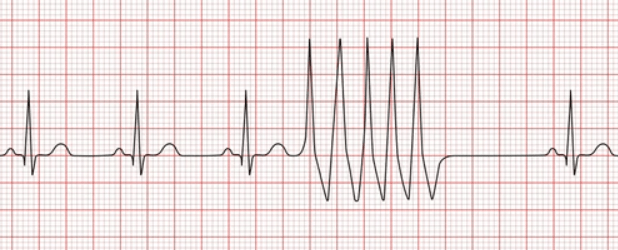
Sinus rhythm with a run of v-tach.