Amount of air that can be inhaled above TV
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
The primary muscle during inhalation
The diaphragm
Is alveolar pressure negative or positive during exhalation?
Positive
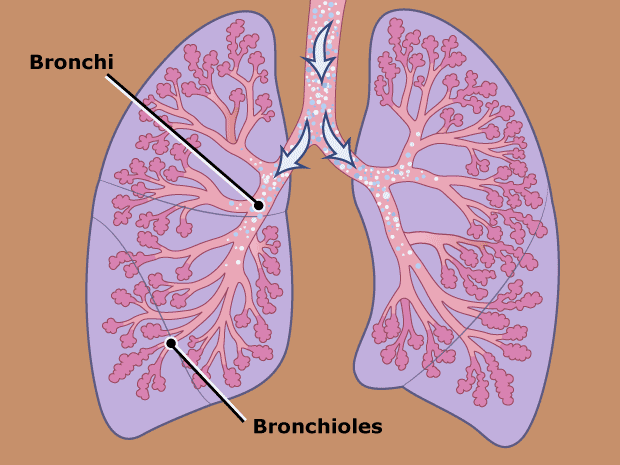
What is the difference between bronchi and bronchioles?
The bronchi is the primary airway which later divides into smaller and smaller passages which are the bronchioles, the tiniest airways.
The function of the muscles of the abdomen
Contract to decrease the volume of the thoracic cavity
Total amount of air the lungs can hold
Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
The lung volume __ during inhalation and the intrapulmonary pressure ___.
increases, decreases
When exhalation occurs does alveolar pressure increase or decrease?
Increases
To which anatomical structure do the nasal cavity, oral cavity, and pharynx belong?
Upper respiratory system
The internal intercostal muscles __ the rib cage
Depress
Air remaining in the lungs after a maximum exhalation
Residual Volume (RV)
40%
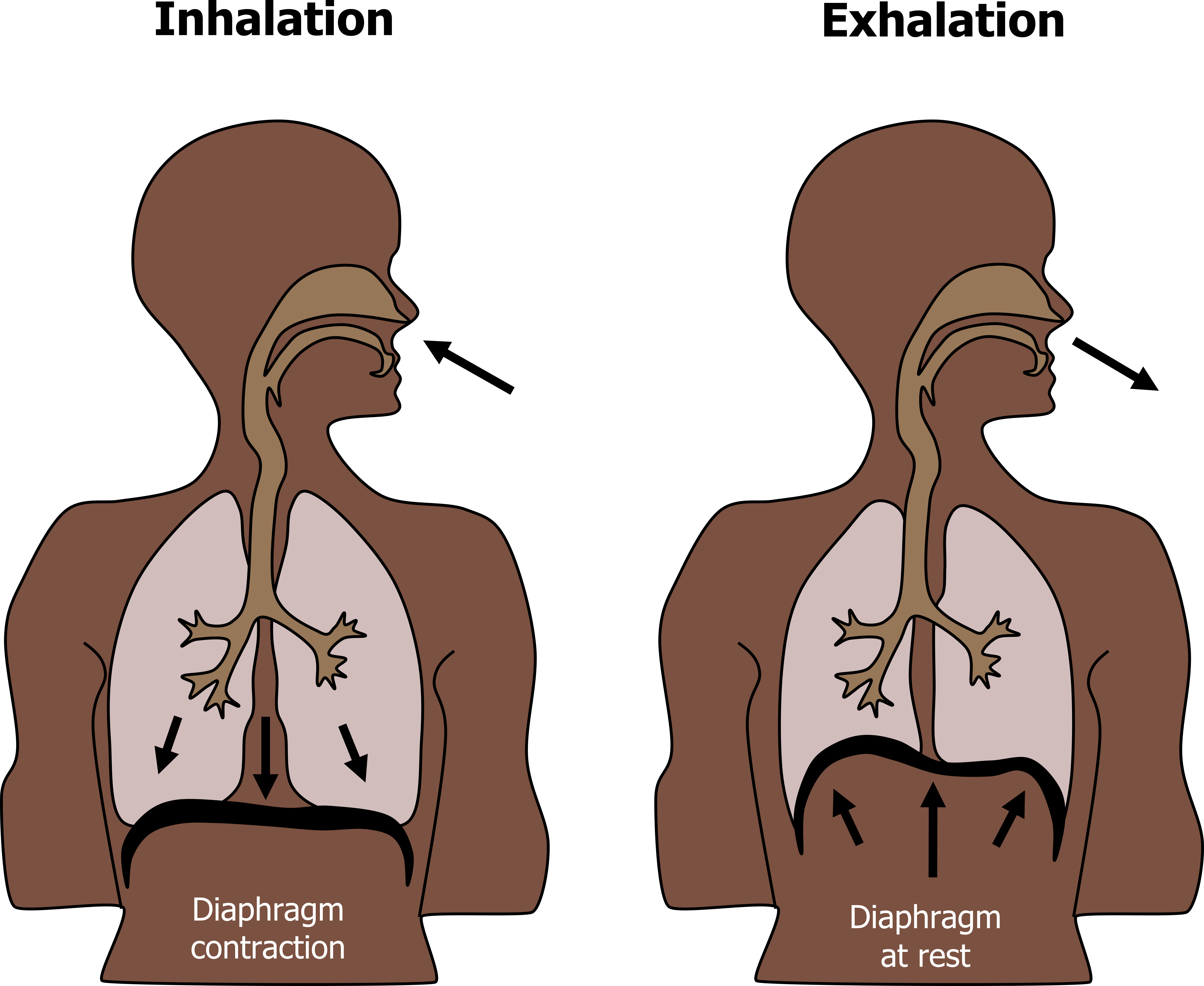
How does the volume of the thoracic cavity change during exhalation?
Decreases as the diaphragm relaxes
When the diaphragm contracts, does the volume of the thoracic cavity increase or decrease?
When the diaphragm muscle contracts, what happens?
By pulling the central tendon downward and forward, the diaphragm expands the thorax vertically. It can also widen the thorax by lifting the lower six ribs.
State of equilibrium in the respiratory system
Resting Expiratory Level
What is the force that causes air to flow into the lungs
Changes in lung pressure
What is the difference between exhalation and inhalation?
Inhalation depends on active muscle forces and exhalation is passive and no active muscle force is required

What is the primary function of the diaphragm?
To help you inhale and exhale. Contracts and flattens when inhaled and relaxes and returns to its dome shape when exhaled.
Muscle activity for exhalation is __ for life and __ for speech
Passive, Active
Maximum amount of air that can be exhaled following a maximum inhalation
Vital Capacity

The pressure relative to atmospheric pressure during inhalation is
Negative (lower than atmospheric pressure)
In what way does exhalation contribute to the production of speech?
Supplying the airflow needed to vibrate the vocal cords, which produces the sound of speech.
What is the role of the alveoli in gas exchange during respiration?
Tiny sacs in the lungs where oxygen moves into the blood and carbon dioxide moves out of the blood to be exhaled.

What happens when the external oblique muscle contracts?
It draws the lower ribs downward and compresses the front and sides of the abdominal wall inward.
