The respiratory system has two major subdivisions. What are they?
The two subdivisions of the respiratory system are the pulmonary apparatus and the chest wall.
Where is the respiratory system located?
It is located within the torso and is in two subdivisions: the pulmonary apparatus and the chest wall.
These are a pair of cone-shaped structures that are porous and spongy and are considered the organs of breathing. What are they called?
The lungs
What muscle has a complex origin that includes the upper surface of the coxal bone, lumbodorsal fascia, and inner surfaces of the costal cartilages of ribs 7 through 12?
The Transversus Abdominis Muscle
These are the five functions of the respiratory system.
Pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, internal respiration, causing vibration, and olfaction.
Explain how the pulmonary apparatus and chest wall are linked and how this linkage affects their resting sizes.
The pulmonary apparatus and the chest wall are linked by the pleural membranes, forming a single functional unit known as pleural linkage. This linkage allows the respiratory system at an intermediate resting size. When the pulmonary apparatus is removed from the chest wall, it collapses and contains little air, resulting in a smaller resting size (Hoit et al., 2022). Because of this linkage, when the chest wall expands, the pulmonary apparatus expands with it.
What are the five main functions of the respiratory system ?
Inhalation and Exhalation Are Pulmonary Ventilation provides day to day breathing
External Respiration Exchanges Gases Between the Lungs and the Bloodstream
Internal Respiration Exchanges Gases Between the Bloodstream and Body Tissue
Airflow Causes Vibration of the Vocal Folds to Create Sound
Airflow over sense organs results in Olfaction, or Smelling (Is a Chemical Sensation)
This forms the convex floor of the thorax and the concave roof of the abdomen. It also separates them and is considered to be “the fence between.” What structure is this?
The Diaphragm
This muscle contracts and pulls the lower ribs downward and forces the front and side of the abdominal wall inward. What is this muscle called?
The External Oblique Muscle

This function of the respiratory system allows airflow to cause vibration of the vocal folds, creating sound. What is it called?
Phonation
Name the four abdominal wall muscles and explain how their activity and internal pressure affect the respiratory system.
The abdominal wall muscles include the rectus abdominis, external oblique, internal oblique, and transversus abdominis, which surround the torso on the front, back, and sides. At rest, the lower abdominal wall is distended because pressure within the abdomen is greater (Hoit et al., 2022). Inward movement of the abdominal wall causes it to flatten, while outward movement results in protrusion, influencing respiratory movements.
During one respiratory cycle, how do passive forces influence inspiration and expiration?
Passive forces arise from elastic recoil of tissues, surface tension of alveoli, and gravity. When the respiratory system contains more air than its resting level, passive recoil causes expiration (Hoit et al., 2022). When it contains less air than its resting level, passive recoil causes inspiration. The farther the system is displaced from its resting size, the greater the passive recoil force.
This framework includes the thoracic segments of the vertebral column,the ribs, the costal cartilages, and the sternum. Additionally, it surrounds the lungs and is shaped like a barrel. What part of the respiratory system is this?
The Rib Cage
Known to be a broad, thick, structure positioned on the front and side of the neck, this muscle originates in two subdivisions, one at the top and front of the sternum, and the other at the top of the sternal end of the clavicle. What muscle is this?
The Sternocleidomastoid Muscle
This is the type of intervention for respiratory conditions impacting speech production that speech pathologists can provide
Breathing exercises and respiratory muscle training
Describe the two main types of rib cage wall movements during respiration and how each one changes the size of them.
One type of movement is a vertical excursion of the front of the ribs, where the ribs move upward and forward during inspiration and downward and backward during expiration. This changes the front-to-back diameter of the rib cage and is similar to a pump-handle movement (Hoit et al., 2022). The second type of movement occurs along the sides of the rib cage, where the ribs move upward and outward or downward and inward, changing the side-to-side diameter of the rib cage in a different way. These movements occur together to increase or decrease the overall size of the rib cage.
Why does movement of a respiratory structure not always mean that the structure caused its own movement?
A respiratory structure does not always move itself. For example, outward movement of the rib cage wall may be caused by activation of inspiratory rib cage muscles, or it may result from increased abdominal pressure pushing the rib cage outward. Likewise, the abdominal wall cannot move outward on its own because it has no inspiratory muscles and may instead be moved by forces generated by the diaphragm or rib cage wall(Hoit et al., 2022) . Therefore, observing movement alone does not identify the source of the force.
This structure provides oxygen to the cells of the body and removes carbon dioxide from them. It is the air containing. air conducting, and gas exchange of the respiratory system. What is this structure?
The Pulmonary Apparatus

Considered a “ribbon like structure” located on the front of the flower rib cage wall and abdominal wall just off the midline. It arises from the upper, front edge of the coxal bone and runs upward vertically to insert into the outer surfaces of the fifth, sixth, and seventh costal cartilages and lower sternum. What muscle is this?
The Rectus Abdominis Muscle
This is the type of intervention for respiratory conditions impacting speech production that speech pathologists can provide:
Breathing exercises and respiratory muscle training
Describe how the skeletal framework, chest wall, and pulmonary apparatus are structurally connected to form a single functional unit of the respiratory system.
The respiratory system is supported by a skeletal framework of bone and cartilage that includes the vertebral column, rib cage, and costal cartilages (Hoit et al., 2022). The chest wall (includes the rib cage wall, diaphragm, and abdominal wall) and its purpose is to surround and protect the pulmonary apparatus. The pulmonary apparatus consists of the lungs and airways and is linked to the chest wall by pleural membranes, forming a pleural linkage. This structural connection allows the chest wall and pulmonary apparatus to function together as a single unit during respiration.
Explain how the diaphragm, rib cage wall, abdominal wall, and pulmonary apparatus work together during one respiratory cycle to change thoracic volume.
During one respiratory cycle, the diaphragm, rib cage wall, abdominal wall, and pulmonary apparatus function together as a one system. When the diaphragm contracts, it moves downward and elevates the lower ribs, which increases thoracic volume. At the same time, the rib cage wall moves through vertical excursion and rotation, which in turn expands both the front-to-back and side-to-side dimensions of the rib cage. Then, the pulmonary apparatus expands with the chest wall due to pleural linkage (Hoit et al., 2022). As the diaphragm relaxes and abdominal pressure increases, thoracic volume decreases, allowing expiration to happen.
These constitute a complex network of flexible tubes through which air can be moved to and from the lungs and between different parts of the lungs. It is known to be referred to as the “pulmonary tree.” What is this?
The Pulmonary Airways
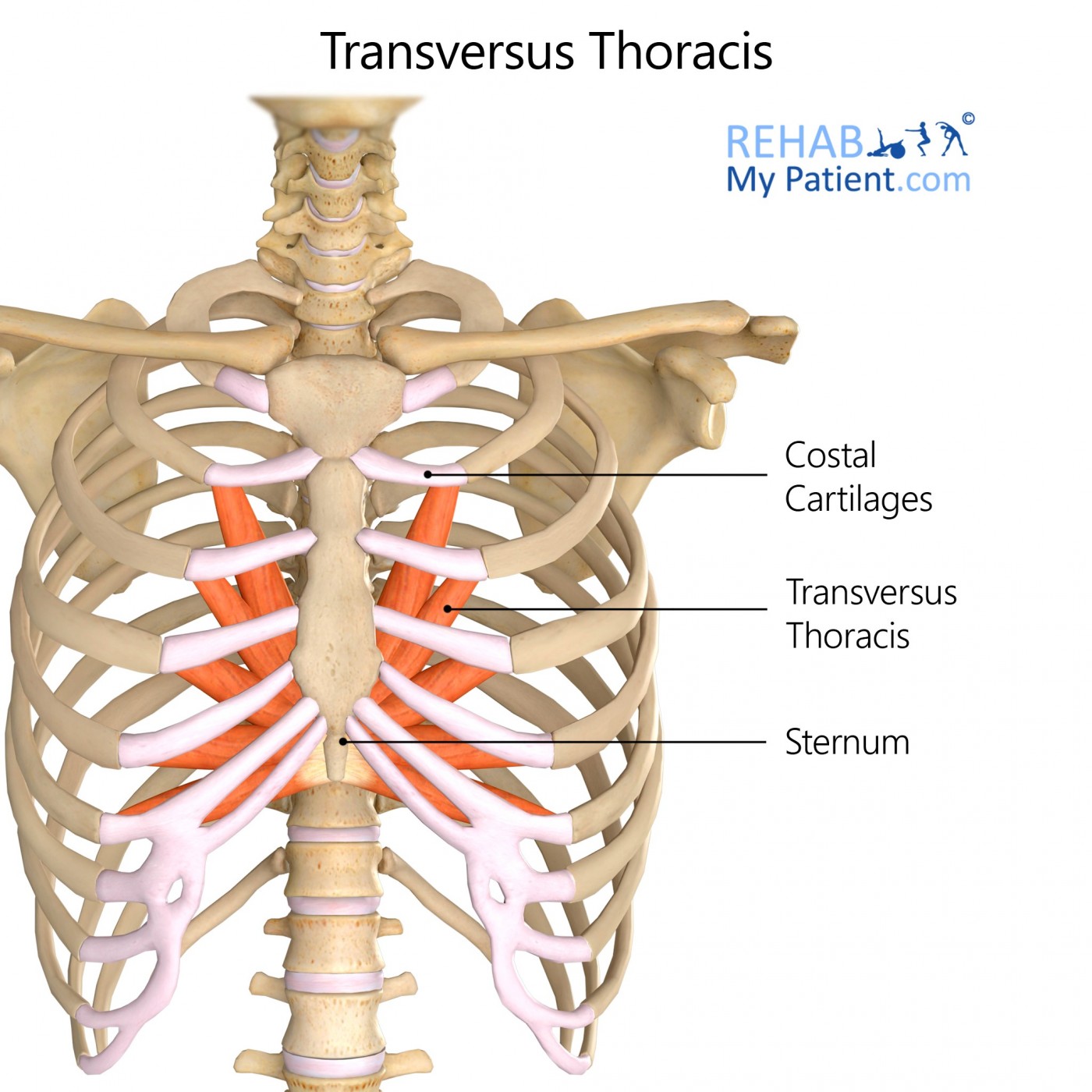
This is a “fan shaped structure” located on the inside, front wall of the rib cage. It originates at the midline on the inner surface of the lower sternum and fourth or fifth through seventh costal cartilages. From there, it fans out across the rib cage and inserts into the inner surface of the costal cartilages and bony ends of the second through sixth ribs. What muscle is this called?
The Transversus Thoracis
Both oral intubation and a tracheostomy prevent normal speech mainly by altering airflow through this structure, which also interacts with multiple subsystems. What are they called?
Vocal folds