What are the four main things that patients may mean when complaining of fatigue?
1) fatigue ("apathy" or "lack of energy") refers to a subjective lack of physical or mental energy during the day interfering with usual activities
2) increased sleepiness ("drowsiness" or "hypersomnia") refers to the inability to maintain alertness and wakefulness during the day
3) weakness refers to lack of muscle strength, usually not associated with mental dysfunction
4) Dyspnea with exertion or lack of endurance
What are the three types of hyperparathyroidism and name a common cause of each?
Primary - Adenoma
Secondary - CKD, Dietary vitamin D deficiency
Tertiary - Renal failure
What diagnostic testing is required to make a diagnosis of Asthma in a patient presenting with shortness of breath?
No tests are required. But you may order viral testing or a chest x-ray depending on the patient's presentation and time of the year.
No further workup is required if 8/8 PERC are met, that essentially rules out a PE.
What is the first line treatment for a hemodynamically unstable patient (hypotensive, declining mental status, unresponsive) with this EKG?
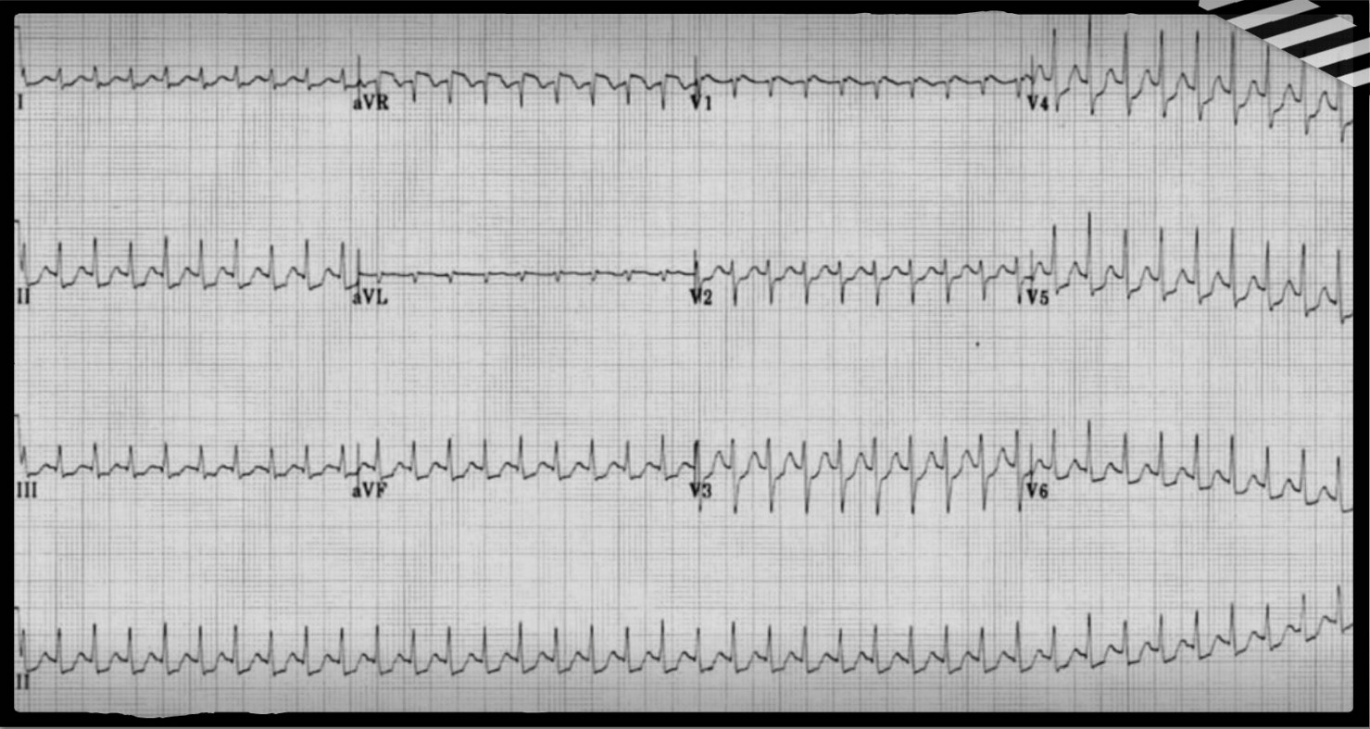
Electrical cardioversion 50-100J x 3 shocks, if they then don't convert - initiate ACLS protocols.
In a patient with suspicion for DKA, when is a VBG acceptable instead of an ABG?
If the patient is hemodynamically stable and does not have respiratory failure.
What are some can't miss causes of fatigue?
Tumor, Infection (such as HIV), renal failure, liver failure
Name three possible triggers of DKA.
Poor metabolic control or missed insulin doses
Medications (Steroids, antipsychotics, beta blockers, thiazide diuretics, fluroquinolones)
Illness/Infection
Drugs and alcohol
Define community acquired and nosocomial pneumonia.
CAP: acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma acquired outside of the hospital
Nosocomial: Hospital acquired PNA - acquired >= 48 hours after hospital admission.; Ventilator associated PNA - acquired >= 48 hours after endotracheal intubation.
Describe the four types of heart blocks (how they appear on an EKG tracing).
1st degree: PR-prolonged
Wenchebach: PR-interval gets longer, longer longer, until a complex is dropped.
Mobitz II: No QRS for every P wave
3rd degree: the P and QRS complexes have no consistent relationship
....If the R is far from P, then you have a first degree. Longer longer longer drop, then you have a Wenchebach. When some P's just don't go through, then you have a Mobitz II. When the Ps and Qs just don't agree - then you have a third degree. ...
When might a patient having s/sx of an NSTEMI need urgent cardiac catheterization?
Persistent chest pain and/or hypotension
We have used VINDICATE-P to help us form differentials this semester. What do the letters stand for?
V - Vascular
I - Inflammatory / Infectious
N - Neoplasm
D - Degenerative / Drugs
I - Idiopathic / Iatrogenic
C - Congenital
A - Autoimmune
T - Traumatic
E - Endocrine/Metabolic
P - Psychiatric
Name two screening tools and how you may use them in working a differential for fatigue.
1) Epworth Sleepiness Scale - when considering sleep apnea on the differential for a patient.
2) PHQ-9 - used as part of a screening for depression.
What organs and or body parts are involved in the calcium homeostasis system?
Parathyroid glands
Bones
Kidneys
GI Tract
What factors may warrant inpatient management in a patient diagnosed with COVID-19? (Name three)
Oxygen requirement
Significant dyspnea or increased respiratory rate (>30/min)
Significant infectious sequelae (myocarditis, pulmonary embolism, hypercarbia, AKI, etc)
Frequent falls
Unable to care for themselves at home.
Provide two possible diagnoses for each of the following: 1) a narrow complex QRS, regular tachyarrhythmia; 2) a widened complex QRS, irregular tachyarrhythmia
1) Sinus tachycardia, SVT, A flutter, junctional tachycardia, AVNRT, AVRT, SANRT (and others!)
2) WPW, ventricular fibrillation, polymorphic VT (inc. torsades), AF, atrial flutter, focal AT with aberrant conduction (and others!)
Name two major contraindications to thrombolytic therapy:
Hemorrhagic stroke
Severe hypo- or hyperglycemia
Uncontrolled severe hypertension
Significant bleeding conditions
Your patient is presenting with a headache with nausea and vomiting, of gradual onset, worse in morning. You have a high suspicion for a brain tumor because of the patient's age and presentation. Name two physical examination findings that may be present with that diagnosis?
Papilledema
Cognitive difficulties
Focal neurological deficits
Name four laboratory studies and how they may work the differential for fatigue.
TSH: evaluate thyroid function (hypo-, hyper-)
Glucose and/or HgbA1C: considering DM or level of glucose control
BMP/CMP: Lytes, Cr, LFTs
B-NP: Heart failure
CBC: Anemia, infections (must include differential)
HIV, ESR: May utilize to r/o can't miss diagnoses
If a patient has a high PTH level, what is the most likely cause?
Primary hyperparathyroidism
Name three physical examination findings that may be found in a patient with an acute aortic dissection?
Pulse deficit (checking peripheral pulses)
New heart murmur
Focal neurological deficit (chest pain + any neurological symptom)
Hypotension
Syncope
What are the EKG findings that occur in hypo- and hypercalcemia?
Hypocalcemia: QTc prolongation primarily by prolonging the ST segment
Hypercalcemia: shortened QT, ST segment elevation (Osborne waves), biphasic T waves, and prominent U waves.
What is the first line outpatient treatment for CAP in a patient without significant comorbidities or lung problems and no allergies?
Amoxicillin 1g three times daily PLUS a macrolide (i.e. Azithromycin, doxycycline)
Name four conditions in which a D-Dimer may be elevated.
DVT
PE
Pregnancy
DIC
Sepsis
Recent MI
Recent surgery...
Name four of the red flags for fatigue.
1) Recent onset in a previously well patient.
2) Unintentional weight loss
3) Abnormal bleeding
4) Shortness of breath
5) Unexplained lymphadenopathy
6) Fever
7) Recent onset or progression of GI, CV, neuro, or rheumatological symptoms.
What are the five diagnostic criteria for DKA?
Glucose > 250 mg/dL. (Rarely patients with DKA have near normal blood glucoses [euglycemic DKA]. This is more common in pregnant patients and patients taking SGLT2 inhibitors.)
pH ≤ 7.3
HCO3− ≤ 18 mEq/L
Positive serum ketones
Anion gap > 10 mEq/L
What are three signs of hemodynamic instability? (there are many!)
Hypotension
Narrow pulse pressure (<20mmHg)
Altered mental status (restless, combative, confused, lethargic)
Diminished or absent peripheral pulses
Cool extremities
Prolonged capillary refill
In the workup of a patient with a suspected stroke, what is the preferred imaging?
CT of the head without contrast
You started your newly diagnosed atrial fibrillation patient on warfarin (Coumadin) and asked them to have an INR repeated in 7-10 days. What is the therapeutic goal of the INR for atrial fibrillation?
2-3
Interpret this ABG:
pH 7.6
PaO2 120 mm Hg
PaCO2 31 mm Hg
HCO3 25 mmol/L
Respiratory Alkalosis, Uncompensated