What happens to a metal atom when forming an ionic bond?
It loses electrons to form a cation
What do the three dots on the Lewis dot diagram indicate?
Valence electrons
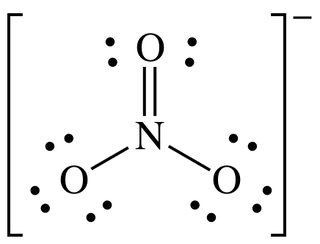
What is the lewis structure of nitrate?
What is an orbital
a region of space where an electron is most likely to be found
Do isotopes change part of the atom?
yes
What is the chemical bond that is between oppositely charged ions?
Ionic bond.
What happens to bond energy when there is an increase in bond length?
It decreases
What is molecular geometry?
Three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule
The three fundamental particles that make up an atom
Proton, electron and neutron
Atomic mass represents ___
the total number of protons and neutrons
What molecule would be expected to have a non-polar covalent bond?
It is F2
Who created the lewis dot structure?
Gilbert Lewis Newton
Trigonal planar
three atoms and no electron pairs
Like charges repel ___________
Opposites attract
A chemical formula tells us ___
how many of each atom make up a molecule
What is a covalent bond largely made up of?
Organic compounds
What does the lewis structure show?
The valence shell electrons in a molecule
Tetrahedral
four atoms and no electron pairs
Do isotopes separate easily from one another?
No
Law of mass conservation states
Matter cannot be created or destroyed, it can only change form
How many elements make up the compound MgSO4?
3 elements
How many dots does nitrogen have?
2 dots
Square pyramidal
five atoms and one electron pair
Definition of isotope
atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
A covalent bond does not conduct ___
electricity