two angles that add up to a right angle
What are complementary angles?
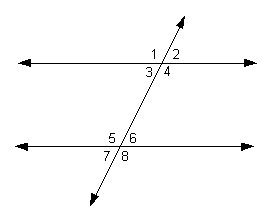
angle 4 and angle 6 are supplementary; this is stated by me
(this works backwards, too)
What is the same side interior angles postulate?
lines parallel to me have an undefined slope and lines perpendicular to me have a slope of 0
What is a vertical line?
 angle 1 and angle 5 are an example of these
angle 1 and angle 5 are an example of these
What are corresponding angles?
this is the equation of a line perpendicular to 3y+7x=12 that goes through (14, 9) written in slope-intercept form
What is y=3/7x-5?
a line that crosses two lines that will never intersect and have the same slope
What is a transversal?

angle 4 and angle 5 are congruent by this statement
What is the alternate interior angles theorem?
Ax+By=C
What is standard form?

angle 3 and angle 6 are an example of these

the relationship between angle 5 and angle 6
What is a linear pair?
when a transversal cuts through two parallel lines, these two are on different sides of the transversal and outside of the parallel lines
What are alternate exterior angles?

angle 1 and angle 5 are congruent by this statement
(this works backwards, too)
What is the corresponding angles theorem?
write the equation of a line (in slope-intercept form) given that m=3/4 and (8,2) lies on this line
What is y=3/4x-4?

given that the measure of angle 1 is 104˚, this is what the measure of angle 7 is equal to
this is the equation of a line perpendicular to a horizontal line and goes through (209, 37)
What is x=209?
two angles that add up to 180˚
What are supplementary angles?

this statement is used to prove the lines parallel when given that angle 3 and angle 6 are congruent
What is the converse of the alternate interior angles theorem?
y=mx+b
What is slope-intercept form?

given that angle GDB is 162˚, this is the measure of angle ADH
What is 162˚?

this image is an example of ______
What are parallel lines cut by a transversal?
two angles that are congruent to each other and are located across from each other
What are vertical angles?
if a point is equidistant from the ends of a segment, it lies on the ______ by this theorem
(this works backwards, too)
What is the Converse of the Perpendicular Bisector Theorem?
(x-x1)=m(y-y1)
What is point-slope form?

angle 2 and angle 3 are an example of this
What are vertical angles?
 C is equidistant to A and B due to this theorem
C is equidistant to A and B due to this theorem
What is the Perpendicular Bisector Theorem?