T or F the Volume of Distribution for water-soluble drugs is higher in an adult than in a child.
False children have a higher VD for water soluble drugs
but have lower VD in fat-soluble drugs
Better in Children or adults? C or A
1. Bioavailability of basic drugs -
2. Max volume of injection 5 mL -
3. Higher concentration of free drug -
4. Has a higher GFR -
Better in Children or adults? C or A
1. Bioavailability of basic drugs - C (A has higher bioavailability of acids) this is due to infants having a lower pH when born and getting more acidic as they become adults.
2. Max volume of injection 5 mL - A (C has a 1 mL max and neonates have a 0.5 mL)
3. Higher concentration of free drug - C has less plasma proteins than A so increased risk of toxicities
4. Has a higher GFR - A (Children are born with a GFR of 26)
What components does premature infant formula contain to improve premature infant's nutrition? (5)
Increased caloric density: (24 kcal/oz)
Increased calcium, phosphorus, and proteins
Increased MCT --> improves digestion
Examples: Enfamil or Similac
The patient is currently down to 7 kg from the 8.5 kg baseline after being sick on the weekend. Calculate the % dehydration and the fluid deficit.
% dehydration = (Pre-illness wt - illness wt)/ (pre-illness wt) x 100
8.5-7kg = 1.5 kg / 8.5 kg = 0.1764 x 100 = 17.6 %
Fluid deficit = 10 ml/kg x % dehydration x pre-illness wt
10 ml/kg x 17.6% x 8.5kg = 1496 mL
The T in Torch stands for Toxoplasmosis which is most likely acquired due to undercooked meat, unwashed veggies, and kitty litter. Normal symptoms impact the vision, CSF, and intracranial calcification. What is the maternal and neonatal treatment (drugs)?
Maternal: Spiramycin decreases transmission to child if confirmed fetal infection add Pyrimethamine-sulfadiazine AND Leucovorin
Neonate treatment:
Pyrimethamine-sulfadiazine AND Leucovorin for 1st year of life
Way to Remember song by Brittany Spears "Toxic" - "With the taste of your lips"
If the baby gets a taste of the Toxoplasmosis then it needs to take the drugs LiPS
Leucovorin the I is a plus sign Pyrimethamine-sulfadiazine.
Brittany also states "Your toxic, I'm slipping under" which we are gonna pretend is the baby in the mom getting closer to infection so needs the s in slipping before the baby reaches lip the mom takes Spiramycin to prevent infection.
What 2 medications are the first line for early onset sepsis? (empiric treatment)
Ampicillin and gentamicin
Please give the age definition for each category:
Premature infant
Term infant
Infant
Neonate
Child
Adolescents
Bonus if you can name which test is used in which category Fenton, CDC, and WHO growth charts
• Premature infant: < 37 weeks gestational age (GA)
-GA "time from the first day of the last menstrual period to birth"
• Term infant: 37-42 weeks GA
• Neonate: Birth – 1 month
• Infant: 1 month – 12 months
• Child: 1 – 11 years
• Adolescent: 12 – 21 years
Fenton growth chart if a premature infant
• WHO growth chart if ≤ 2 yrs old
• CDC growth chart if > 2 yrs old • Age and gender-specific • Assess BMI for age
• Toddler: 12 months – 35 months
• Preschooler: 3 – 5 years
• Adolescent: 12 – 21 years
Calculate the CrCl for the following peds case: (Schwartz)
25 wk DOL 10
Length 12 inches
SCr 0.7 mg/dL
K values based on age:
Premature < 1 year: 0.33
Term < 1 year: 0.45
Child and adolescent female: 0.45
adolescent male: 0.7
What would be different for Beside Schwartz? When would this be used?
1 inch = 2.54 cm
12 in x 2.54 = 30.48 cm
Equation = k x L / sCr
(0.33 x 30.48)/0.7 = 14 mL/min/1.73 m2
Beside Schwartz - use 0.413 for K only for age 1-18
Whole milk contains high amounts of calcium and vitamin D, which formula for 9-36 months also contains the same or more than whole milk. Which 3 other vitamins does the formula for 9-36 months of age contain that also help with nutrition?
Vitamin C, E and iron
Whole milk also has too much protein, sodium and potassium
For oral hydration is a patient is mildly dehydrated what is the oral regimen for aliquots?
Moderate?
Severe?
Mild: 50 mL/kg over 4 hours
Moderate: 100 mL/kg over 6 hours
Severe: Contraindicated --> go to hospital
The O in Torch is other so how do you treat the following maternal and neonatal:
Some symptoms to watch are rashes, deafness, and development delay but most are asymptomatic.
Maternal:
Neonatal:
Maternal: Penicillin benzathine 2.4 million international units IM given weekly for 2-3 doses
Remember that B stands for Before baby is born (triple B)
Neonatal: Penicillin G 10 days, but only if the infant is symptomatic, delivery within maternal therapy or maternal therapy didn't include penicillin.
Which of these regimens are correct for late onset sepsis? (not high risk)
A. Nafcillin + Vanco + Acyclovir
B. Cefazolin + Gentamicin
C. Fluconazole + Gentamicin
D. Vanco + Cefazolin
E. Cefepime + Gentamicin + Vancomycin
B is correct
When does a baby lose the tongue reflex? (Age) Why is this important?
When can a child use an inhaler with a spacer/mask?
4-6 months - allows them to more easily take oral meds
2 years
Use the information below to do G_ P_ (_,_,_,_)
You are collecting a patients history and this is what they tell you:
Jess is currently pregnant and this will be her 5th pregnancy. She has 3 living children (1 set of twins) - the twins were born preterm, but her other child was kept to term. One of her pregnancies was a miscarriage and one was an abortion.
G5 P2 (1,1,2,3)
G - # of pregnancy
P - # of births
T - term births
P - preterm births
A - Number of abortions or miscarriages
L - number of living children
These are all term infant formulas listed below please name one key point of each. Which category does this formula belong (Nutramigen)
Cow’s milk based
Lactose-free products
Soy based (milk-free, lactose-free)
Protein hydrolysate/Semi-elemental
Cow’s milk based - cheap, can add rice to decrease spit-up
Lactose-free products - still contain milk proteins
Soy based (milk-free, lactose-free) - not recommended for premature infants, good for milk allergy
Protein hydrolysate/Semi-elemental contains • Nutramigen® as one of the formula, good for milk and soy allergy very expensive
What is the go-to regimen for peds in Emergencies?
Normal IV hydration solution for Peds vs Neonates?
What is the go-to regimen for peds in Emergencies?
LR or NS 20ml/kg (max 2L) Bolus
Peds D5 0.9% + 20 mEq/L of KCl (K depends on renal function)
Neonates D10 0.2% NaCl
The R in TORCH stands for Rubella with symptoms of deafness, cataracts, thrombocytopenia, and purpuric skin lesions (blueberry muffins). How do you prevent Rubella?
Vaccination before childbearing years, test all pregnant women
Immune globin can be an option to help, but no cure if infection
What major points should a physician ask a patient at the one and two-month visit? (7 points)
Sleeping
Eating
Stool
Crying
Awake
Response
Control
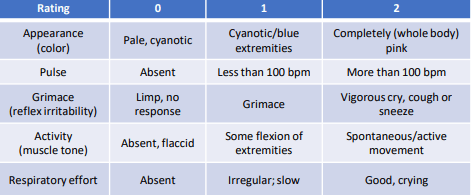
Patient is Blue with a pulse of 120 bpm crying with a lack of motion and light flexing, and showing no response to painful stimuli.
A - 1 blue
P - 2 120 bpm
G - 0 No response to painful stimuli
A - 1 Some flexing
R - 2 crying
Total = 6
Bag and mask assistance (4-6)
Which age should children start on supplemental food? What type of food is best to start with?
4-6 months, best is single ingredient food
Based on this information, is the patient mild, moderate, or severely dehydrated?
The patient is 16 months old weighing 25 lbs normally with a current weight of 22lbs after being ill for the past 3 days.
25 lbs = 11.4 kg
22 lbs = 10kg
11.4kg - 10kg = 1.4kg/11.4kg = 0.1228 x 100 = 12.3%
Patient is severely dehydrated
Infant 5%, 10%, 15%
Child 3%, 6%, 9%
The most common of TORCH is C which stands for Cytomegalovirus (CMV) - 90% asymptomatic if symptomatic then common symptoms include:
•Hepatosplenomegaly
• Petechiae/thrombocytopenia
• Elevated direct bilirubin
• Small-for-gestational age (SGA, < 10th percentile on growth chart)
• Intracranial calcifications
• Later → hearing loss, seizures, mental retardation, and developmental delay
What are prevention techniques and a treatment option?
Prevention:
• Seronegative women should avoid the urine and saliva of toddlers
• ~70% of daycare children aged 1-3 years infectious
• Initiative from Institute of Medicine for vaccine
Treatment
Ganciclovir/valganciclovir may be used in symptomatic infants to reduce the severity of hearing loss
• Considered teratogenic
• Previously 6 weeks of therapy, now 6 months to decrease the incidence of increase in developmental delays
Explain the importance of each of these resources:
Lexi-Comp’s Pediatric and Neonatal Dosage Handbook
Extemporaneous Formulations for Pediatric, Geriatric, and Special Needs Patients
The Harriet Lane Handbook
Neofax
Red Book
The Teddy Bear Book: Pediatric Injectable Drugs
KIDs List
Lexi-Comp’s Pediatric and Neonatal Dosage Handbook
- Drug dosing and preparation recipes
Extemporaneous Formulations for Pediatric, Geriatric, and Special Needs Patients
- Data sheets for each formulation
The Harriet Lane Handbook
- Peds diseases low info of drug dosing
Neofax
- Drug dosing, monitoring, some info for neonates
Red Book
- disease and treatment not much drug dosing
The Teddy Bear Book: Pediatric Injectable Drugs
- dosing, IV, concentration
KIDs List
As one ages what happens to these vital signs:
Heart rate:
Blood pressure:
Respiratory rate:
Name the A, B, and D's we are watching for in vital signs
Heart rate: Decreases
Blood pressure: Increases
Respiratory rate: Decreases
A - Apneas - pause longer than 20s
B - Bradycardia HR less than 90
D - oxygen saturation less than 85%
The patient weighs 20 kg and is receiving Resource Just for Kids 1.5 45 mL/hr.
What is the caloric content:
Amount:
Delivery:
Calculate fluids:
What is the caloric content: 1.5 kcal/mL
Amount: 45 mL/hr
Delivery: Continuous
Calculate fluids: 45 mL/hr x 24 hr = 1080 mL/day
Rehydration:
The patient is severely dehydrated with a fluid deficit of 2200 mL.
What would be the fluid regimen for rehydration without the MIVPs?
1/2 fluid deficit is 1100 mL
Over the first 8 hours 1100mL so 137.5 mL/hr
Over the next 16 hours the next 1100 at a rate of 68.75 mL/hr
The H in TORCH stands for Herpes Simplex (HSV) - shown by symptoms of skin lesions can also spread to becomes systematic and cause shock, pneumonia, hepatitis as well as serious CNS effects. What is the prevention if active lesions?
What is the treatment and must-know dosing?
Prevention: C section as baby won't be exposed to lesions
Treatment: If suspected acyclovir 20 mg/kg/dose IV every 8 hours
14 days if local
21 days if CNS disease
Followed by suppression therapy for 6 months
Sally comes into your pharmacy to ask what dose of Children's Tylenol to give her 6 yo son. He currently weighs 130 lbs and is taking the liquid Tylenol as he can't swallow pills yet. Sally stated she lost the package dosing, so she doesn't know how much to give. You look up a dosing calculator and see that 130 lbs gets 25 mL of solution. Additional information is given below:
Dosing: 130 lbs = 59 kg
59 kg
10 kg - 2.5 mL
10-20 kg - 5 mL
20-30 kg - 7.5 mL
30-40 kg - 10 mL
40 + kg - 15 mL Max Adult Dose
What's your recommendation?
Can't go over max adult dose so give the patient 15 mL
Word bank - (less than 1 year of age) ( 1-3 years of age)
(older than 3 years of age) (Older than 8 years of age)
Which scale is used
FACES, Numeric rating scale, CRIES, FLACC
CRIES - less than 1 yo
FLACC - 1-3 yo
FACES - 3 yo or older
Number scale - older than 8 yo
The patient weighs 2.0 kg and is receiving Similac Special Care 25 45 mL q3hrs.
Formula -
Caloric content:
Amount:
Delivery:
Calculate fluids:
Calculate calories:
Per weight fluid:
Per weight calories:
Formula - Similac Special Care
Caloric content: 25 kcal/oz or 25 kcal/30 mL
Amount: 45 mL
Delivery: q3hr or 8 times a day
Calculate fluids: 8 times x 45 mL = 360 mL
Calculate calories: 360 mL x 25 kcal/30 mL = 300 kcal
Per weight fluid: 360 mL / 2 kg = 180 ml/kg/day
Per weight calories: 300 kcal/ 2 kg = 150 kcal/kg/day
Calculate the MIVFs for a 20kg patient:
1000 mL/day + 50 mL/kg/day x 10kg = 1500 mL/day /24hr = 62.5 mL/hr
Neonatal conjunctivitis - caused by 2 different bacteria
• Chlamydia trachomatis: what is the systematic treatment?
• Neisseria gonorrhoeae: what is the Prophylaxis and treatment if exposed?
• Chlamydia trachomatis: what is the systematic treatment?
T - Systemic treatment with erythromycin or azithromycin
• Neisseria gonorrhoeae:what is the Prophylaxis and treatment if exposed?
P - erythromycin ophthalmic ointment for all infants at birth
T - If known exposure or confirmed microbiology, treat with IV/IM ceftriaxone
Main differences between Peds and Neonate vitals?
Potassium: Neonatal - 3.7 - 7.2 Infants 3.5 - 5.1
SCr Neonates: 0.3-1mg Infants: 0.3-0.7
Glucose Neonates 50-90 Infants 60-100
Calcium Neonates 7-10.9 Infants 8.8-10.8
Phosphorus N 4.2 - 9 mg I 3.2 - 5.8
Albumin N 1.8-3.9 I 3.5 - 5.6
The patient was previously on Similac Special Care:
Total Calories: 380 kcal/day
The patient is being switched to Similac Neosure 22 q4h. Find the regimen fluid for the patient.
Total calories 380 kcal per day x (30 mL/22 kcal) = 518 mL/day
518 mL/day / 6 feedings a day = 86 mL/feeding
Neosure 86 mL q4h
What is a serious toxicity concentration of elemental iron? (mg/kg)
What are the 3 serious side effects of high concentrations of Iron in the body?
What is one option for systematic iron toxicity? If you can name the main side effect of medication and dose
What is a serious toxicity concentration for EI? (mg/kg) above 40mg/kg
CNS (coma, seizures)
Hepatic injury (jaundice, increased INR, high bilirubin, hypoglycemia)
Cardiovascular shock (acute respiratory distress syndrome)
Acidosis and shock are partly correct also
GI is first but not considered serious
First few hours GI, 6 hrs acidosis and shock, serious side effects 24-36 hrs.
What is one option for systematic iron toxicity?
If x-ray shows many iron tabs whole bowel irrigation with polyethylene glycol
Deferoxamine for systematic iron concentration greater than 500mcg/dL - orange/red urine main side effect dose 15 mg/kg/hr, slow admin due to hypotension
12 hrs after patient is asymptomatic and urine returns to normal color or until serum iron concentration < 350 mcg/dL and approaches 150 mcg/dL
Bronchiolitis is most commonly caused by RSV, lower respiratory tract infection, and presents as cold-like symptoms lasting 8-15 days with a persistent cough for an up to additional 3 weeks. Severe disease can cause serious respiratory symptoms with a need for ECMO.
1.) When should the RSV vaccine be given to pregnant mothers at Gestational age?
2.) There are 2 prevention medications for RSV one is Palivizumab and the other is Nirsevimab.
a. What is the normal dose for Palivizumab?
b. When is palivizumab given over Nirsevimab?
c. Indications for Palivizumab and Nirsevimab?
3.) RSV once you have RSV - what 2 things?
1.) 32-36 weeks GA due to risk of preterm birth
2.)
a.) 15 mg/kg IM every month during RSV season (NovemberMarch) for max of 5 doses/season
b.)
• If 8-19 months, use palivizumab per AAP recommendations except in American Indian and Alaska Native infants
• Follow AAP recommendations for palivizumab-eligible infants aged <8 months when appropriate dose of nirsevimab not available
c. P is given for patients at high risk for severe disease with prophylaxis with P and N is given in first season or children up to 24 months that remain vulnerable to severe RSV disease in 2nd season.
3.) Hydration, Respiratory support (no inhaled ribaviran)
Croup -
Preschool children - 6 months to 5 years of age most common
There is distal airway obstruction which can give a child hypoxemia which can put children at risk of catastrophic cardiorespiratory arrest and requires safe transfer to ICU.
What is the dose of medication that should be given in moderate to severe patients?
Dexamethasone 0.6 mg/kg/dose PO
If patient is vomiting use IM dexamethasone or nebulized budesonide