What is activation energy?
The minimum amount of energy required for a reaction to occur
Does increasing the molarity of a solution make it more concentrated or more diluted?
concentrated
What is the molarity of a solution with 3 moles of solute and 6 liters of solution?
0.5 M
What happens to the reaction rate as you increase the temperature of the reaction?
Reaction rate increases
In sugar water, is sugar a solute, solvent or solution?
Solute
What is the molarity of a solution with 8 moles of solute and 2,000 mL of solution?
4 M
Since I want my chicken to cook faster, I decide to cut it into chunks. Does that make the surface area of the chicken increase or decrease?
Increase
What is considered a concentrated solution?
A: A solution with a high molarity (like 2.0 M).
B: A solution with a low molarity (like 0.1 M).
A: A solution with a high molarity (like 2.0 M).
Determine the molarity of a solution containing 2.5 g of CuCl2 in 1,000 mL of solution.
0.02 M
How does adding a catalyst affect the activation energy of a reaction? 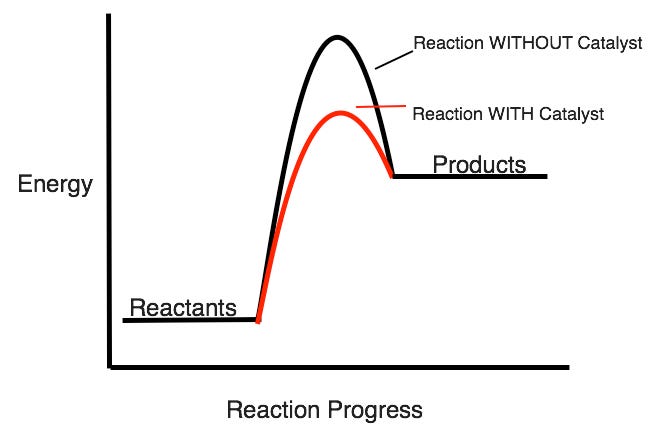
Lowers it
Which solution would lead to the fastest reaction rate? Assume all of the compounds are the same.
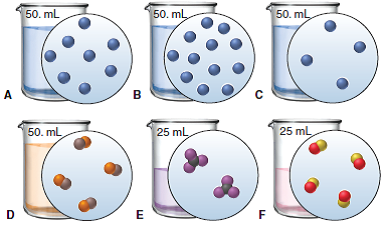
B
How many grams of NaCl are needed to create 320 mL of a 5.0 M solution.
94 g NaCl