The units for momentum and impulse
kg m/s or N-s
Calculate the momentum of 14 kg sloth moving at a velocity of 2.0 m/s to the right.
28 kg m/s to the right
True or False: Momentum is a scalar.
False, momentum is a vector!
In order for a 45 kg person to leave as a human cannonball from a cannon, a 1600 N force must be exerted on the person for 0.68 seconds. Find the speed with which they leave the cannon.
24 m/s
A marble of mass 0.1kg falls off a bed with a height of 1.2m. What is the impulse on the marble as it hits the ground?
0.49N-s
Calculate the velocity of 10 kg koala bear that has a momentum has the same momentum as a 68 kg kangaroo moving at 19.2 m/s to the right.
130.6 m/s to the right
This is proportional to the square of velocity.
kinetic energy
A 35 m tall statue has a mass of 1.00 x 10^6 kg. If the statue is to be moved by a 12.5 kN force from a speed of 0.0 m/s to 0.20 m/s, calculate the time it will take.
16 seconds
Impulse is synonymous to this.
Change in momentum.
A roller-skater skates at a speed of 40.3 km/h. If the skater's momentum is 660 kg m/s, calculate his mass.
59 kg
Momentum and kinetic energy are conserved for this type of collision.
Elastic Collision
A giant earthworm is 12.0 kg. Suppose one is picked up by an eagle, and is dropped from a height of 40.0 m. By skillfully using its muscles, the earthworm manages to extend the time during which it collides with the ground to 0.250 s. Find the force that acts on the earthworm.
1344 N upwards
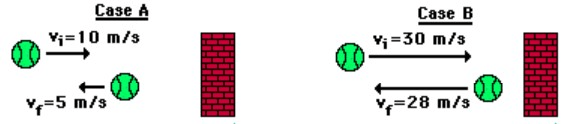
This case has the largest impulse
Case B
Two pop cans are at rest on a stand. A firecracker is placed between the cans and lit. The firecracker explodes and exerts equal and opposite forces on the two cans. Assuming the system of two cans to be isolated, the post-explosion momentum of the system ____.
a. is dependent upon the mass and velocities of the two cans
b. is dependent upon the velocities of the two cans (but not their mass)
c. is typically a very large value
d. can be a positive, negative or zero value
e. is definitely zero
e. is definitely zero
Two different arrows are shot.
Arrow 1: m = 2 kg, v = +10 m/s
Arrow 2: m = 1 kg, v = -20 m/s
Compare momentum and kinetic energy.
Momentum is the same in magnitude and opposite in direction. Arrow 2 has a greater kinetic energy.
A car with mass m1 and initial velocity v1 strikes a car of mass m2, which is at rest. If the two cars stick together after the collision, what is the final velocity?
(m1v1)/(m1+m2)
In 1994, a tower 22.13 m tall was built out of LEGO blocks. Suppose a 2.00 g block is dropped from the top of the tower. Neglecting air resistance, calculate the block's momentum at the instant the block hits the ground.
0.042 kg m/s downwards
The only way to determine if a collision is elastic or inelastic is
To determine if kinetic energy is conserved for the system before and after the collision
Two bumper cars at an amusement park collide as one approaches the other directly from the rear. The car in front (Car A) has a mass of 550 kg and the car behind it (Car B) has a mass of 450 kg. Car A in front was traveling at 3.70 m/s before the collision and 4.4 m/s after the collision, while the car behind hit him with a velocity of 4.50 m/s. What is the final velocity of Car B after the collision?
+3.6 m/s