What is the formula for momentum?
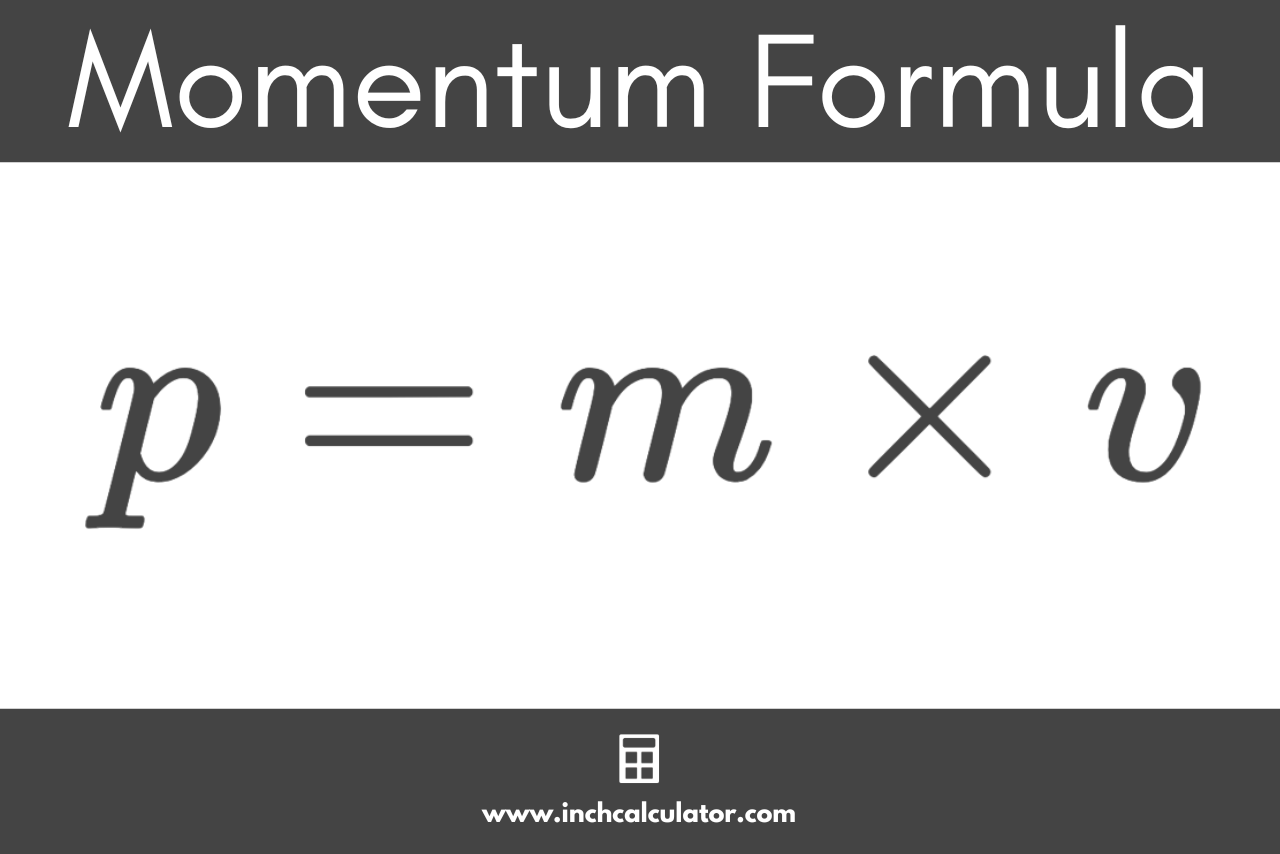 P = m•v
P = m•v
Impulse is = to what change in physical quantity?
Change in momentum
What must be conserved in all collisions?
Momentum
A 2kg object moves at 3 m/s, what is its momentum?
6 kg•m/s
Why do athletes follow through when swinging?
What are the units of momentum?
Kg•m/s
What is the formula for impulse?
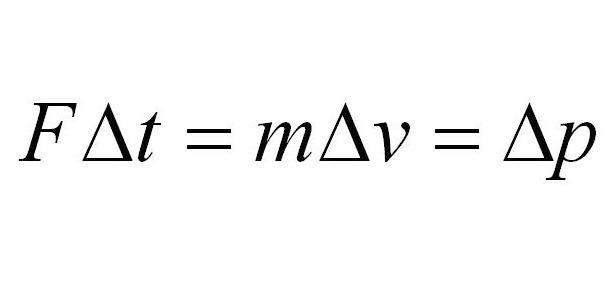
A collision in which objects stick together is called what?
Inelastic collisions
A 1 kg ball at 4m/s hits a 2 kg ball at rest. Find the total momentum before collision.
4 kg•m/s
Why are crumple zones used in cars?
To increase collision time and reduce force
If velocity doubles, what happens to momentum?
It also doubles
Increasing the impact time does what to the force?
It reduces the force.
A collision that conserves both momentum and kinetic energy is called what?
Elastic collision
A force of 20 N acts for 0.5 seconds, what is the change in momentum?
10 N•s
A rocket moves forward by conservation of what?
Momentum
What quantity is momentum?
A vector
If airbags protect you from something, what do they protect you from?
From collision time.
True or false: kinetic energy is always conserved?
False
A 5 kg cart is moving at 2 m/s hits a 1 kg cart at rest, they stick together. Find the velocity?
1.67 m/s
Why does a heavier truck take longer to stop then a small car?
The truck has more momentum
What must change for an object to change its momentum?
Its velocity or mass
If a force of 10 N acts for 5 seconds, what is the impulse?
50 N•s
In an inelastic collision, what type of energy is often lost?
Mechanical kinetic energy
A 50 g bullet (0.05kg) is fired at 200 m/s. What is its momentum?
10 kg • m/s
Why does a gun recoil backward when fired?
Because of conservation of momentum.