Two carts of masses 1kg and 2kg travel together, as shown in Figure 1. At time t=2 s, a compressed spring inside the 2kg cart expands, and the carts separate. Figure 2 shows a graph of the carts’ velocities as a function of time. What is the magnitude of the change in linear momentum, if any, of the two-cart system between t=0 s and t=4 s?
a) 0kg⋅m/s
b) 0.5kg·m/s
c) 1.0kg·m/s
d) 2.0kg⋅m/s

a) 0kg⋅m/s
A block of mass 2.0 kg, starting from rest, is pushed with a constant force across a horizontal track. The position of the block as a function of time is recorded, and the data are shown in the table. What is the magnitude of the change in momentum of the block between zero and 4.0 seconds?

a) 0.8 kg⋅m/s
b) 1.2 kg⋅m/s
c) 1.6 kg⋅m/s
d) 3.2 kg⋅m/s
c) 1.6 kg⋅m/s
A 1000.–kilogram car traveling 20.0 meters per second east experiences an impulse of 2000. newton • seconds west. What is the final velocity of the car after the impulse has been applied?
1. 18.0 m/s east
2. 19.5 m/s east
3. 20.5 m/s west
4. 22.0 m/s west
1. 18.0 m/s east
An 8.00-kilogram ball is fired horizontally from a 1.00 × 103-kilogram cannon initially at rest. After having been fired, the momentum of the ball is 2.40 × 103 kilogram·meters per second east. [Neglect friction.]
Calculate the magnitude of the cannon’s velocity after the ball is fired. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth of a meter per second.
2.40 m/s
How does an air mattress protect a stunt person landing on the ground after a stunt?
a) It reduces the kinetic energy loss of the stunt person.
b) It reduces the momentum change of the stunt person.
c) It increases the momentum change of the stunt person.
d) It shortens the stopping time of the stunt person and increases the force applied during the landing.
e) It lengthens the stopping time of the stunt person and reduces the force applied during the landing.
e) It lengthens the stopping time of the stunt person and reduces the force applied during the landing.
A person of mass 60 kg sliding along level ice at a speed of 3.0 m/s collides with a second person who is initially at rest. Assume that friction is negligible. If the two people hold onto each other and their common final speed after colliding is 2.0 m/s, the mass of the second person is
a) 10 kg
b) 30 kg
c) 40 kg
d) 80 kg
e) 90 kg
b) 30 kg
Which situation will produce the greatest change of momentum for a 1.0-kilogram cart?
- accelerating it from rest to 3.0 m/s
- accelerating it from 2.0 m/s to 4.0 m/s
- applying a net force of 5.0 N for 2.0 s
- applying a net force of 10.0 N for 0.5 s
3. applying a net force of 5.0 N for 2.0 s
Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second. Compared to the inertia and magnitude of momentum of cart A, cart B has
1) the same inertia and a smaller magnitude of momentum
2) the same inertia and the same magnitude of momentum
3) greater inertia and a smaller magnitude of momentum
4) greater inertia and the same magnitude of momentum
4) greater inertia and the same magnitude of momentum
A 4 kg object moving to the left collides with and sticks to a 3 kg object moving to the right. Which of the following is true of the motion of the combined objects immediately after the collision?
a) They must be moving to the left.
b) They must be moving to the right.
c) They must be at rest.
d) The motion cannot be determined without knowing the speeds of the objects before the collision.
d) The motion cannot be determined without knowing the speeds of the objects before the collision.
An object of mass 5kg travels in the positive direction with a speed of 1m/s. The object collides with a second object that exerts an average net force over an interval of time such that the 5kg object comes to rest. Which of the following best predicts the change in momentum for the 5kg object?
a) The change in momentum is in the negative direction.
b) The change in momentum is in the positive direction.
c) The change in momentum is zero.
d) The direction of the change in momentum cannot be determined without knowing the value of the average force and time in which the force is exerted.
a) The change in momentum is in the negative direction.
An air bag is used to safely decrease the momentum of a driver in a car accident. The air bag reduces the magnitude of the force acting on the driver by
1. increasing the length of time the force acts on the driver
2. decreasing the distance over which the force acts on the driver
3. increasing the rate of acceleration of the driver
4. decreasing the mass of the driver
1. increasing the length of time the force acts on the driver
Derive the conservation of momentum equation for an explosion (using m and v)

A cart of mass 1kg travels along a horizontal, frictionless surface. A net force is applied to the cart. A graph of the net force applied to the cart as a function of time is shown. The initial and final direction of the cart and the direction of the net force exerted on the cart is unknown. The distance of one grid unit represents a change in velocity of 1 m/s. Which of the following diagrams could represent the direction and relative magnitude of the velocity of the cart before the force is applied and after the force is applied? Select two answers.

A & D
Block X of mass 4M travels at a speed 5vo toward block Y of mass M, which is initially at rest. After block X elastically collides with block Y, block X has a speed of 3vo in the same direction as before the collision. What is the speed of block Y immediately after the collision?
a) 1.2vo
b) 3vo
c) 8vo
d) 20vo
c) 8vo
A 3.0-kilogram object is acted upon by an impulse having a magnitude of 15 newton•seconds. What is the magnitude of the object’s change in momentum due to this impulse?
- 5.0 kg•m/s
- 15 kg•m/s
- 3.0 kg•m/s
- 45 kg•m/s
2. 15 kg•m/s
Derive the conservation of momentum equation for an inelastic collision. (using m and v)
A person applies an impulse of 5.0 kg∙m/s to a box in order to set it in motion. If the person is in contact with the box for 0.25 s, what is the average force exerted by the person on the box?
a) 1.25 N
b) 2.00 N
c) 12.5 N
d) 20.0 N
e) 200 N
d) 20.0 N

Which of the following choices lists the measuring tools necessary to determine the initial momentum of the system before the collision takes place?
a) Mass balance
b) Mass balance and meterstick
c) Mass balance, meterstick, and stopwatch
d) Mass balance, meterstick, stopwatch, and force probe
c) Mass balance, meterstick, and stopwatch
The diagram below represents two masses before and after they collide. Before the collision, mass mA is moving to the right with speed v, and mass mB is at rest. Upon collision, the two masses stick together.
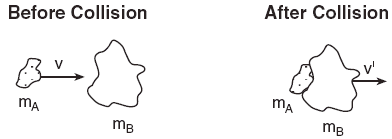
Which expression represents the speed, v', of the masses after the collision? [Assume no outside forces are acting on mA or mB.]

4)
Derive the conservation of momentum equation for the an elastic collision. (using m and v)