Which allele is ALWAYS expressed?
Dominant
Green (G) is dominant to brown (g) for anole lizards. What is the genotype of a brown lizard?
gg
What are 3 examples of a phenotype?
Physical characteristics- Hair color, Fur texture, eye color, height, etc...
Teacher will check!

What percent of the offspring are heterozygous?
50%
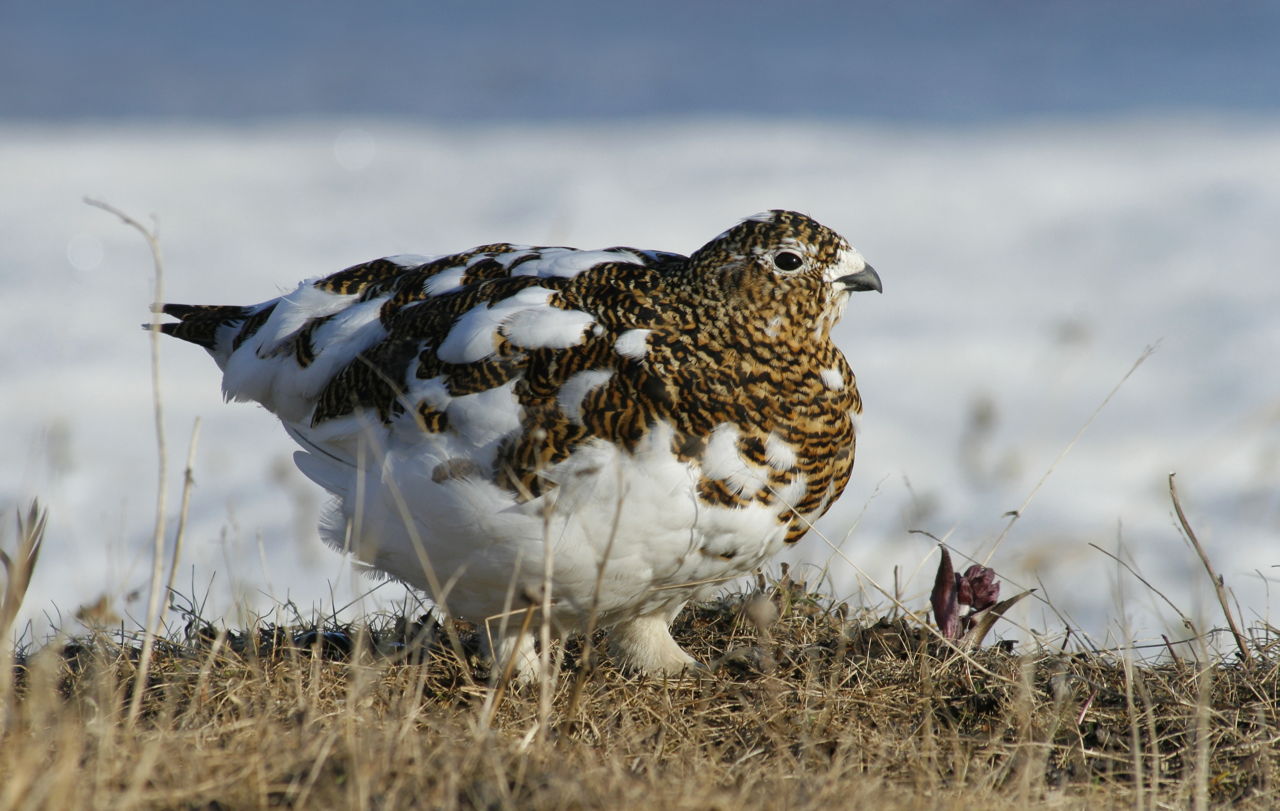

When both alleles are expressed, this is an example of-
Codominance
Which allele is only expressed in a homozygous state?
Recessive
Non-waxy corn kernels (N) is dominant to waxy corn kernels (n). A heterozygous non-waxy corn kernel is crossed with a homozygous waxy corn kernel. What are the parents genotypes?
Nn x nn
What are 3 examples of a genotype? BE SPECIFIC (think names)
Homozygous Dominant (HH)
Heterozygous (Hh)
Homozygous Recessive (hh)
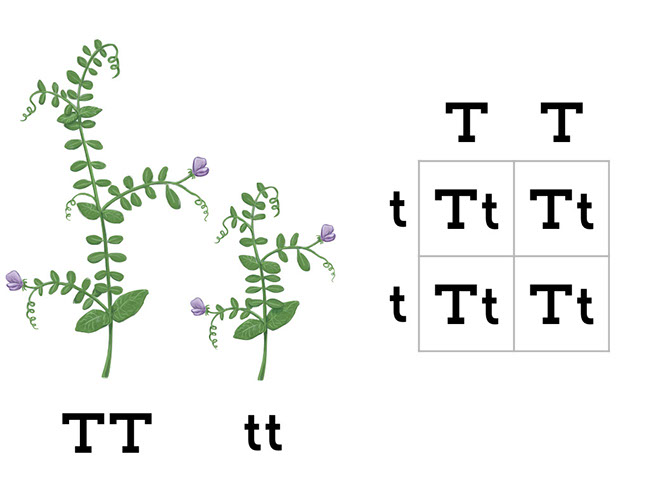
Tall is dominant to short. What percent of the offspring are tall?
100% tall
A man with heterozygous B blood marries a women with AB blood. What percentage of the offspring will have A blood type?
25% A
What is the genotype made of different alleles?
heterozygous
White fur is dominant to gray fur for arctic rabbits. A heterozygous white fur rabbit is crossed with a gray rabbit. What percent of the offspring will be homozygous recessive? (use the letter F)
50% ff or gray fur
Dark colored beaks are dominant to light colored beaks in chickens. A chicken with light colored beak is crossed with a homozygous dominant dark colored beak chicken. What percent of the offspring with have dark colored beaks?
100% dark colored beaks
Pointed leaves are dominant to round leaves. Two heterozygous pointed leaves are crossed. What percent of the offspring will be heterozygous for the trait? (use the letter L)
50% Ll
In horses, the chestnut coloration is incompletely dominant to cremello(white) coloration. Palomino (tan) is the heterozygous phenotype. If a chesnut horse is crossed with a palomino horse, what fraction of the offspring will be palomino?
2/4=1/2 palomino
What is the genotype made of the same alleles?
homozygous
Tongue rollers are dominant to non-tongue rollers. Two heterozygous tongue rollers are crossed. What fraction of the offspring will be heterozygous for the trait? (use the letter T)
2/4 or 1/2 Tt
Having a widow's peak is dominant to a straight hairline. Someone who is homozygous dominant is crossed with a heterozygous widow's peak. What fraction of the offspring will be homozygous dominant? (use the letter H)
1/2 HH
Pointed leaves are dominant to round leaves. Two heterozygous pointed leaves are crossed. What are the phenotypic probabilities (%)?
75% pointed leaves and 25% round leaves
The ABO blood group has three different alleles: IA, IB, and i. The genotypes and phenotypes (blood types) for different combinations of the three alleles are shown in the table.
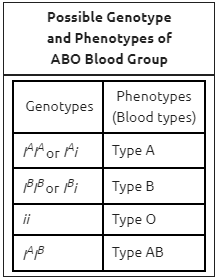
What are the phenotype probabilities of a cross between a heterozygous Type A parent and a Type AB parent?
50% A blood
50% AB blood
What is a specific characteristic that is controlled by genes?
Trait
Curly hair is dominant to straight hair in poodles. Two heterozygous curly haired poodles are crossed. What percent of the offspring will be homozygous dominant? (use the letter H)
25% HH
Having dimples is a dominant trait. Someone who is heterozygous for dimples is crossed with someone who has no dimples. What are the phenotypic fractions?
2/4=1/2 Dimples: 2/4=1/2 no dimples
Red tomatoes are dominant to green tomatoes. A heterozygous red tomato is crossed with a green tomato plant. What are the percentages of each phenotype?
50% Red
50% Green
In leopard geckos, no pigment (NN) is codominant to pigmented (PP) coloration. Leopard geckos that express both traits are will have spots of pigment and no pigment (NP)
When you cross a pignmented leopard gecko with a spotted leopard gecko, what phenotypic and genotypic percentages would occur in the offspring?
50% pigmented and 50% spotted
50% PP and 50% NP