Name the three main parts of the brain stem?
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
What is the primary function of the reticular activating system (RAS)
The RAS is a network of neurons in the brainstem that acts as a central control system for regulating wakefulness, arousal, and attention
Where is the cerebellum located?
back of the brain, below the cerebrum and above the brainstem
What is the primary function of the corpus callosum?
main communication pathway between the left and right cerebral hemispheres

Name the part of the brain that is shaded red
cerebellum
Which involuntary functions are regulated by the brainstem?
Heart rate, breathing, blood flow, and levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood.
How does the RAS helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle?
RAS is more active when awake, promoting alertness by activating the cerebral cortex.
RAS is less active when asleep, allowing the brain to transition to a state of reduced consciousness
What’s the difference between the cerebellum and cerebrum?
cerebellum - small part of brain located at the bottom near the back of your head
cerebrum - largest part of brain and includes parts above and forward of the cerebellum
What is the corpus callosum composed of?
It is made of millions of densely packed myelinated axons.

Name the part of the brain that is shaded blue
Brainstem
What are the functions of the three parts of the brainstem?
Midbrain - visual and auditory processing, eye movement
Pons - regulates breathing, sleep, and facial sensations
Medulla Oblongata - controls autonomic functions like heart rate, blood pressure, swallowing, and reflexes
What are two neurotransmitters involved in the RAS?
neurotransmitter in RAS include: acetylcholine, norepinephrine, serotonin, dopamine, histamine, orexin (Hypocretin)
What are some primary functions of the cerebellum?
How many axons does the corpus callosum contain?
200-300 million
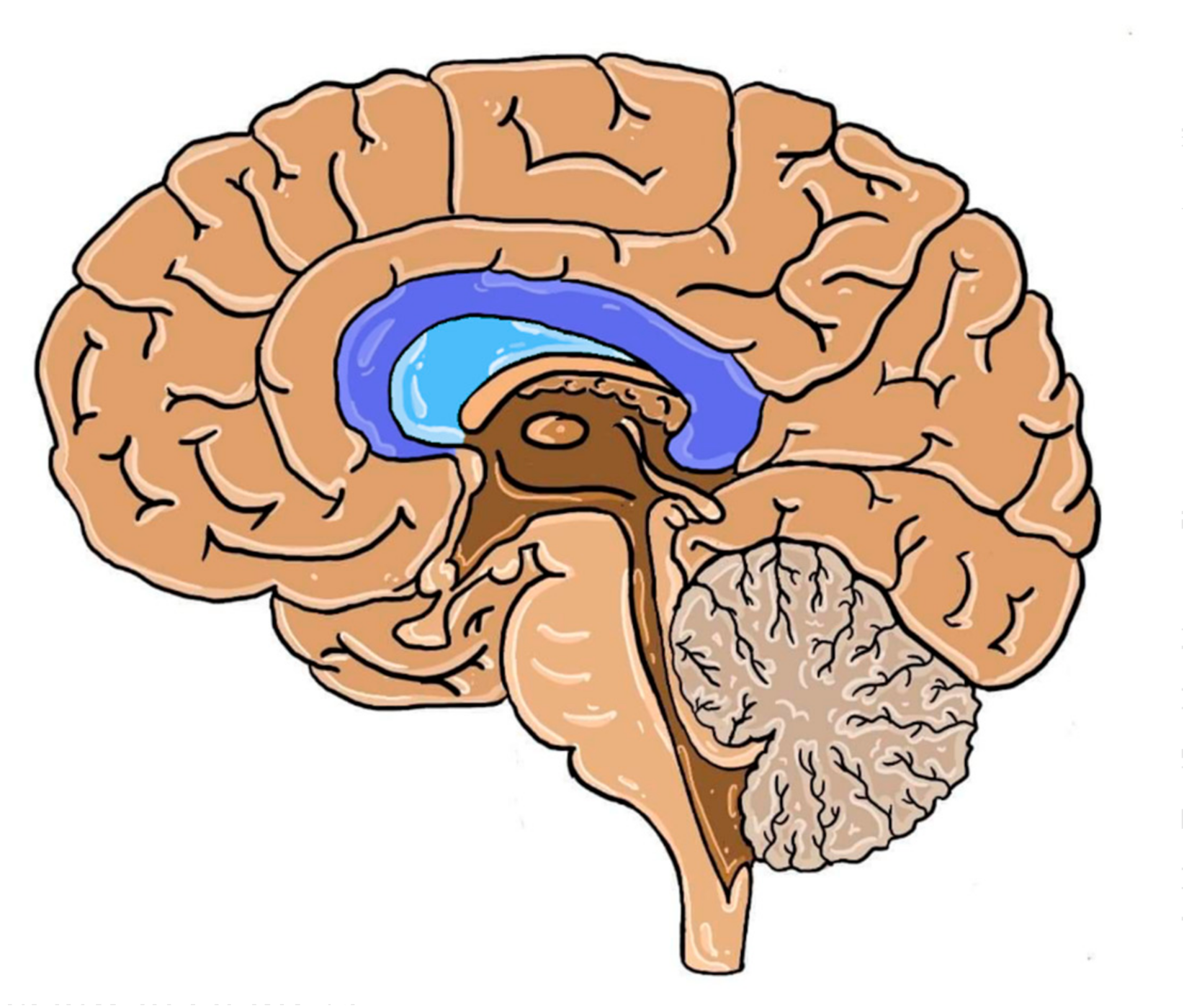
Identify the shaded part of the brain
Corpus callosum
What is the primary role of the brain stem in connecting the central nervous system?
Relaying information between the cerebrum and the spinal cord, and between the cerebellum and the rest of the brain
Where is the core location of the RAS?
brainstem (midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata)
What is the cerebellar role in non-motor functions?
Language processing and verbal working memory, Emotional regulation, Reward-seeking behaviors.
Is the corpus callosum made of gray or white matter?
white matter

What is the name of the part of this structure that is shaded gray?
Medulla Oblongata
Define what a brainstem reflex is
involuntary motor responses that you aren't concious thinking about. Brainstem automatically tells your body to do them.
What happens when the RAS is damaged?
Severe disturbances in consciousness and the sleep-wake cycle
True or False
Cerebellar damage can be caused by various factors; including multiple sclerosis
True
What would happen to information shared between the two hemispheres if the corpus callosum is severed.
Loss in the ability to communicate and share information (results in split-brain syndrome)

What is the name of the part of this structure that is shaded purple?
midbrain