Which two scientists were the first to recognize that both plants and animals are both made of cells?
Schleiden (plants) and Schwann (animals)
What is the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell?
Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus and eukaryotic cells do.
In which type of cell can you find a nucleus?
What do chloroplasts help accomplish in a plant cell?
Photosynthesis
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of life?
Growing, Reproducing, or Breathing
Breathing
Which scientist discovered cells by looking at a wine cork through a microscope for the first time?
Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
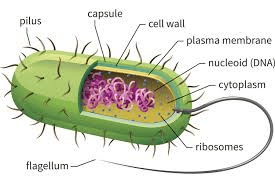
Prokaryote
In which type of cell can you find a large central vacuole? In which can you find small vacuoles?
Large is plant cell
Small is animal cell
What do mitochondria provide to the cell?
Cell energy in the form of ATP.
Which of the following is an abiotic factor?
Apple, banana, water
Water
Which scientist finished the modern-day cell theory by discovering that cells come from pre-existing cells?
Rudolf Virchow
Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
Eukaryote
In which type of cell can you find a lysosome?
Animal Cell
Which cells have an organelle that determines what can enter and leave the cell?
Plant and animal cells have a cell membrane that regulates what can enter and leave the cell
Which of the following do organisms need to survive and grow?
Biotic factor, nutrition, oxygen
Nutrition
Which is not part of the cell theory?
A. Cells are the building blocks of life.
B. Cells are the smallest unit of life.
C. Cells come from pre-existing cells.
D. Cells are formed by spontaneous generation.
D. Cells are formed by spontaneous generation.
Name 4 things about a prokaryotic cell that are not the same of eukaryotic cells.
No membrane-bound organelles
Unicellular (simple organisms)
DNA free-floats in the cells
Example: Bacteria
In which type of cell can you find a chloroplast and cell wall?
Plant Cell
Label the following: 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 10, 11
2: Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
3: Mitochondria
4: Nucleus
7: Lysosome
8: Rough Endoplasmic
10: Golgi Body/ Golgi Apparatus
11: Ribosome
Today in PE it was sweltering hot. As you were sweating, you noticed it was hard to catch your breath and cool down. What does this scenario represent in regards to living things?
Homeostasis or stimulus
Homeostasis
What did Anton van Leeuwenhoek name the tiny creatures he saw in the pond water sample?
Animalcules
Name 5 things about a eukaryotic cell that are not the same of a prokaryotic cell.
Membrane-bound organelles
Can be multicellular or unicellular organisms (simple or complex)
Includes plants, animals and fungi
DNA is found in the nucleus
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus
In which type of cell can you find cytoplasm, cell membrane and mitochondria?
Both plant and animal cells
Which organelle is considered the brain of the operation of the cell?
Nucleus because it houses the cell's DNA which are the cell's instruction manual on how to function.
Otters rely on both biotic and abiotic factors in their environment to survive. Select which abiotic factor supports the otter's survival.
Trees, moss, water, sea urchins
Water