
What is Aliasing
Bonus question worth $50:
What can be done to reduce or eliminate this artifact?
Increasing FOV ___________ spatial resolution.
What is reduces or lowers?
It's the number of gradient coils in an MRI system
what is 6?
It's the fundamental equation in MR
What is the Larmour Equation?
It's the advantage to using Phased Array coils
What is to increasing SNR

What is cross talk or cross excitation?
Bonus question worth $300:
What can be done to reduce this artifact?
Decrease slice thickness from 5mm to 3mm results in this.
Decreasing spatial resolution
It is the hardware component that reconstructs the image Fourier Transformation
What is the Array Processor?
This has a very long T1 time
What is Cerebral Spinal Fluid?
What is a thinner slice
 You do this to reduce or eliminate this artifact
You do this to reduce or eliminate this artifact
What is increase phase and/or frequency encoding
You can do this to increase spatial resolution by increasing this without increasing scan time.
It's what happens when you increasing the amplitude of the frequency encoding gradient.
What is making the FOV smaller.
It's the pulse sequence that starts with a 180 degree RF pulse
What is Inversion Recovery?
This can result in partial voluming effects
What is slices that are too thick?

What is di-electric artifact?
Bonus question worth $200.
This artifact is often seen in this situation?
Decreasing this always increases spatial resolution
What is decreasing voxel size
This describes the number of water-bound protons per volume of tissue.
What is Proton Density
It's an advantage of resistive or electro magnet MRI systems
What is turning "off" the magnet?
What are shim coils.

Parallel Imaging: FOV too small or Factor too high
It's the reason decreasing slice thickness decreases SNR
What is sampling fewer water-bound protons?
It's what unit of measure of the B0 homogeneity.
What is ppm... Parts Per Million
It's the dephasing caused by susceptibility effects
What is T2' (prime)?
It's the structure circled.
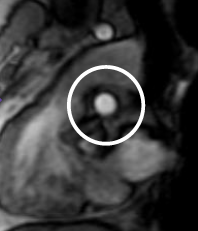
What is the pulmonary artery?

Moire or "zebra-stripe" artifact
Bonus question with $200:
Name a possible solution to this artifact.
All other factors remaining the same, what is the effect of changing the FOV from a square FOV to a rectangular FOV. (Think it through)
No change
The phase encoding gradient is turn on at this time
Immediately after slice excitation
Bonus question with $300
What does the phase encoding gradient dephase?
It controls the amount of spins placed into the transverse plane in a gradient echo sequence
What is flip angle?
Bonus question worth $500
What is the signal intensity of a tissue that is heavily saturated by RF?

The brachiocephalic artery