What are the four structures that all cells have
What are the
Cell membrane , Genetic material, Cytoplasm, and Ribosomes
 Identify the organelle pictured to the right and include 3 things it does for the cell.
Identify the organelle pictured to the right and include 3 things it does for the cell.
Golgi apparatus
1 receives vesicles with proteins from the ER
2. Processes and sorts proteins
3. Ships them where needed
Categorize the following types of organisms as eukaryotes or prokaryotes.
Plants - Fungi - Bacteria - Protist - Animals
Eukaryotes = Plants, Fungi, animals, protists
Prokaryotes = bacteria
Match the macromolecule on the left to its main role in the cell membrane on the right.
Carbs Main component of bilayer
lipids Transport
Proteins Structural support
Carbs -> structural support
Lipids - > main component of bilayer
Proteins -> Transport
Which organelle is responsible for transporting proteins the cell makes to be processed, shipped out, and/or used?
Vesicles
Distinguish between cilia and flagella
Cilia are shorter and more numerous and move fluids across cell surface.
Flagella are longer, only 1-3 per cell, and move the entire cell
White blood cells protect the human body agains invaders and infectious diseases. What organelle(s) do you think play a critical role in them doing their job?
Lysosomes for breaking down invading bacteria
Identify which macromolecule is considered the " information molecule " and where it is stored in a eukaryotic cell vs. a prokaryotic cell
Information molecule = nucleic acids (DNA and RNA ) which hold the instructions for making proteins.
It is stored in the nucleus in a eukaryote and floats in the cytoplasm in a prokaryote.
Sperm cells must travel a long distance through the male and female reproductive systems in order to reach an egg to fertilize. Which organelle(s) would most help a sperm cell achieve this long journey?
Flagella since it moves the entire cell
List the 3 organelles unique to plant cells and explain why each one is important for plant cells but animal cells wouldn't need them.
Central vacuole - allows for tons of storage of water and nutrients which is especially important because plants make their own food.
Chloroplasts - converts light energy into chemical energy in glucose, which plants need to make their own food.
Cell wall - extra structure that keeps plants upright, whereas animals have skeletons
Muscle Cells require a lot of energy to contract and produce movement in the body. What organelle(s) do you think they have more of than other cells?
Mitochondria so they have access to enough energy for movement.
List two differences between the smooth and rough ER
Rough ER has ribosomes, smooth ER does not.
Rough ER hugs the nucleus, smooth ER does not.
Rough ER makes proteins, SMooth ER makes lipids
Define " organelle" in your own words
specialized structures within the cell that work together for one main purpose -> to make proteins
Describe the purpose of ribosomes and why they are so essential for the cell.
Ribosomes make proteins, and proteins run just about everything!

The cell pictured is a eukaryotic animal cell because it has a nucleus (defining characteristic of eukaryotes) and does NOT have a cell wall, central vacuole, or chloroplasts (organelles specific to plants).
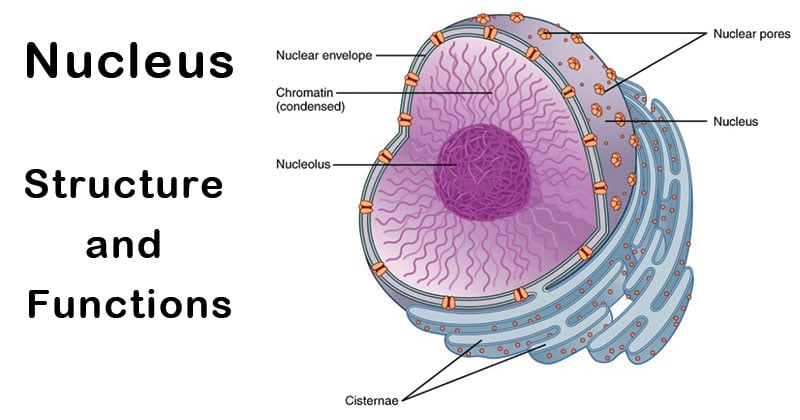
Draw the nucleus and Label the following parts: the nuclear membrane, nucleolus, and chromatin.
Explain why cellular respiration is a necessary process for living things. Include what organelle it occurs in.
Cellular respiration is critical because the cell can't use chemical energy directly from food - it has to be broken down during cellular respiration into a usable form called ATP. This occurs in the mitochondria.
fat cells specialize in storing energy. to do this, one organelle takes up nearly 90% of the cell, with all other organelles pushed to the sides. What organelle do you think it is?
A large vacuole for storage.
not the Central vacuole because this is't a plant cell
______________ organisms are made of one single cell, whereas ___ organisms are made of many cells that are organized into tissues, organs, and organ systems
Unicellular -- organisms are made of one single cell, whereas multicellular organisms are made of many cells that are organized into tissues, organs, and organ systems.
Consider a disease that results in a lack of energy. Which organelle(s) do you predict would most likely be impacted? which macromolecule(s) do you think the person would struggle to use?
The mitochondria would be impacted greatly by an energy deficiency. The person would most likely struggle to adequately use carbohydrates or lipids, which provide energy to the cell.