The most common element used for cryogens in MRI.
What is Helium?
The most commonly used clinical magnet.
What is superconducting MRI unit?
Padding should be placed here.
What is between any skin-to-skin contact?
This zone is open for the general public.
What is zone I
What is MR conditional?
The loss of magnet superconductivity with sudden boil off of helium.
What is a quench?
The name of the little boy that was killed during an MRI because an MRI unsafe oxygen tank entered the room.
Who is Michael Colombini?
This kind of burn often comes from skin-to-skin contact.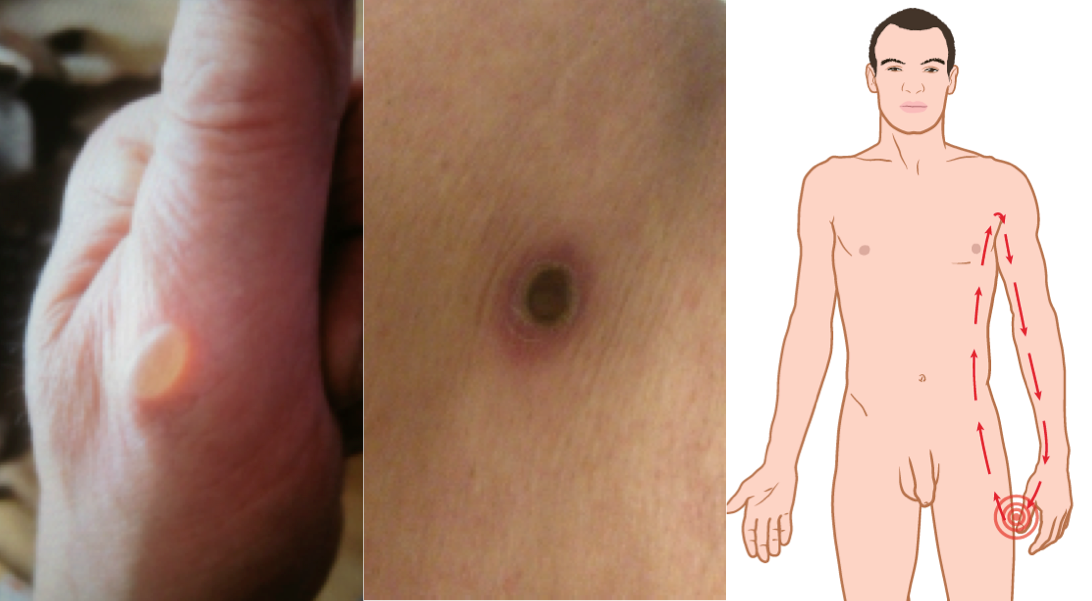
What is a kissing burn?
Entrances to this zone should be identified with signage denoting it's space. It should state "Caution", "Restricted Access", "Screened MRI Patients and Personnel only."
What is zone III
The three formal MR safety roles and responsibilities for facility management of MR safety.
What is MRSO, MRSE, and MRMD?
This may appear suddenly around or above the MRI scanner during a failed quench.
What is fog or clouds?
These are flashing lights induced in the retina due to changing magnetic fields.
What is magnetophosphenes?
Account for 59% of all MRI-related injuries.
What is burns?
This is the zone that patients should be changed into a site-supplied gown and given a locker for their belongings.
What is Zone II
The three independent magnetic fields that create MRI safety challenges.
What are the Static Magnetic Field, the Time-Varying Radiofrequency Field, and the Time-Varying Gradient Magnetic Field?
This device expels dangerous gases.
What is a Quench Vent/Quench Pipe?
The layering of flux lines or magnetic fields of different strengths.
What is the Spatial Magnetic Gradient?
The amount of time it can take a burn to come to the surface of the skin after MRI.
What is 24 hours?
Shielding must be built into this zone to contain the fringe field.
What is zone IV
Screening by FMDS is recommended prior to entering this zone.
What is zone III and zone IV?
This condenses helium gas into a liquid and inserted into the top of the cryostat.
What is the Cold Head?
This law proves when conductive material moves through a magnetic field, an electrical current is produced in the material. When electrical current is produced, a magnetic field is produced 90* to this electrical current. This magnetic field that has been produced will now show opposition to the static magnetic field.
What is Lenz's Law?
This effect involves long conductive objects or wires that act like antennas that can emit power. At 1.5T 26cm and at 3T 13cm wires are most likely to create heating problems.
What is the Antenna Effect.
This zone is not routinely monitored by MR personnel. It is where potentially harmful gases escape during a quench.
What is the Cryogen Venting Zone?
This person is responsible for determining site-specific training that is necessary and appropriate for those individuals who will serve as level 1 and level 2 MR personnel.
Who is the MRMD?