The nurse can only get this if the patient speaks the same language as the nurse and the nurse knows the patient fully understands the risks and benefits of the procedure.
What is Informed Consent?
This common food can cause toxoplasmosis if consumed during pregnancy.
What are Deli Meats?
These are assessments done at every visit.
What are blood pressure, urine dip for protein, weight, ketones, and Fetal Heart tones?
Discharge teaching.
What is no intercourse until following, follow up in 4-6 weeks, limits stairs and lifting for three weeks, and proper peri-care (do not wipe front to back use the peri bottle and pat dry)?
This can keep a person from dilating in labor by interfering with the fetal head's ability to push on the cervix.
What is a full bladder?
Bonus: Prevent this by having the patient urinate often and insert a foley once the patient has an epidural.
Abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and a rigid board-like abdomen indicate this complication.
What is abruption?
Normal fetal rate.
What is 110-160?
listen to the apical HR for 1 full minute.
This is the difference between a cephalohematoma and caput succedaneum.
What is cephalohematoma does not cross the suture line and caput does?
This condition causes pain in menstruation that is not helped with NSAIDs.
What is Endometriosis?
These STI can be cured with medications.
What are syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, BV, and trichomonas?
Getting an infant's temp this way is contraindicated.
What is rectal in fear of perforation?
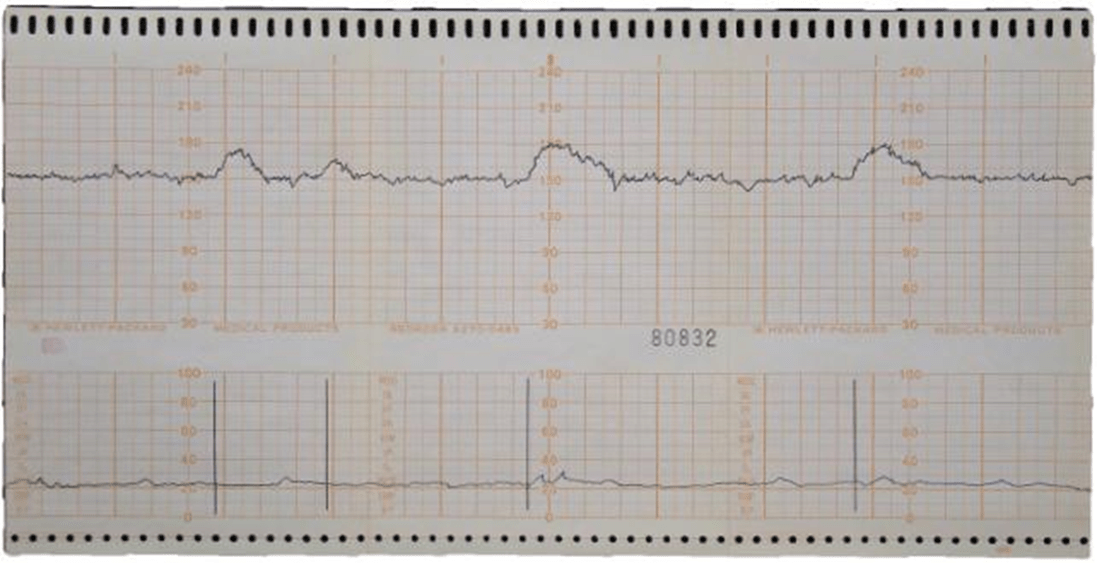
What are accelerations?
A nurse should do this if she does not know what to do in any giving situation.
What is checking the hospital's policy and procedures?
Smoking in pregnancy can cause this.
What is intrauterine growth restrictions because smoking causes vasoconstriction?
Determine the due date for a patient whose LMP is January 20, 2023, using the Naegele method.
When is October 27, 2023?
Mastitis teaching
Baby can have the milk, take all medications, apply a warm compress before feeding, and ensure the breast is empty?
After an epidural is administered the RN should closely monitor this,
What is the patient's blood pressure?
Most labor dystocia are caused by this condition in the infant.
What is Macrosomia?
Normal RR of a newborn.
What is 30-60?
listen to the lungs for 1 full minute.
Infants born to mothers with DM have this complication.
What is macrosomia?
A patient who has had several STIs in the last year should not use this birth control method.
What are IUDs?
PID.
Pelvic inflammatory disease. What is a complication of STIs that can lead to infertility?
What are erythromycin (prevent eye infections) and vitamin K (promote clotting)?
An infant born one minute ago has a HR of 110, a strong cry, and some flexion in the extremities. The infant's hands and feet are blue, but the truck is pink. The infant has a good grimace in response to suctioning the nose and mouth. What would the APGAR be?
HR-2
Strong cry- 2
some flexion: 1
acrocynosis- 1
Grimace- 2
What is 8?
This is the race that is most at risk for OB health disparities.
What are black Americans?
Changes in vaginal and cervical coloration, abdominal enlargement, and a positive pregnancy test are these types of pregnancy signs.
What are probable signs?
A patient who receives a Rubella should not get pregnant for this number of weeks.
What is 4?
DVT Management.
•Bed Rest
•Elevate Extremity
•Change positions
•Warm Most Compress
•Avoid Massage
•Leg Circumferences
•Administer Medications (Heparin & Warfarin)
Early decelerations are a sign of this.
What is labor progression and may mean the patient is ready to deliver?
This is the first action by the nurse is she notices a prolapsed cord.
What is elevating the presenting part of the infant off the cord?
this is how we treat polycythemia in a newborn.
What is partial Exchange tranfusion?
These are the s/s associated with NAS.
What are Prolonged high-pitched cry, Difficult to console, Tremors, Jittering, Yawning or Sneezing, Poor Suck Swallow, Vomiting, Diarrhea, Tachypnea, Tachycardia, Diaphoresis, Trouble Sleeping, Exaggerated Moro, Stuffy Nose, Hypertonia, Excoriation, Mottling, and Seizures.
These are the signs and symptoms of PCOS.
What are infertility, infrequent periods, weight gain, acne, and excess body hair?
STI with yellow-green or brown-gray discharge.
What is trichomoniasis vaginalis?
This infection can cause sepsis in a newborn if the mother is positive during labor.
What is GBS?
VEAL CHOP MINE
variable-cord-maternal positioning
Earl-head-indicate labor progression
Late-placenta-execute interventions
This protects nurses and the public by defining the scope of practice for nursing.
What are the Standards of Practice?
This is the difference between monozygotic and dizygotic twins.
What is: Mono-one sperm and one egg—Di- two sperm and two eggs.
A patient who is experiencing a spontaneous abortion may need this procedure.
What is a D&C or D&E?
DVT Prevention.
•Sequential Compression Device
•ROM exercises
•Ambulation
•Elevate Legs
•Avoid Crossing Legs
•Encourage Fluids
•Smoking Cessation
This is needed for labor to be true and not false.
What are cervical dilation and effacement, contractions that get stronger, walking make contractions stronger, and contractions that start in the back and work around to the abdomen?
If the intervention slows or stops the contractions it is false labor.
These are the interventions needed for shoulder dystocia.
What are McRobert's maneuvers, calling for help, and applying suprapubic pressure?
Sign of newborn distress.
What are retractions, nasal flaring, crackles, and grunting?
If a newborn is born and any part of the inside of the body is on the outside the nurse should do this.
What is cover it with a sterile saline-soaked dressing?
These methods of birth control can help with painful menstruation.
What are COCs?
Two STIs are commonly found together and can lead to blindness in newborns.
What are chlamydia or gonorrhea?
These are events that would make a patient a candidate for a c-section.
What are no progression in cervical dilation, late deceleration, or fetal intolerance to labor?
Contractions frequency.

What are contractions every 2-3 minutes?
Characteristics of family-centered care.
What is birth is a normal, healthy event, that affects the entire family, roles/relationships change, the family can make their own decisions, family members support each other, babies room in, and involve siblings?
We do not encourage epidurals, limit visitors, or prevent people from coming into the room.
These drugs are known to cause placenta abruptions.
What are "street drugs?"
Your patient is currently 39 weeks pregnant; she states she has had two children born at 37 and 35 weeks. She also stated that she suffered from three miscarriages all before 12 weeks.
G 6 T1 P 1 A 3 L 2
Fetal positioning.
If you can see or feel the fetal spine the infant is anterior if you can see the infant's face the infant is posterior.
if the infant is looking toward your left its left, right it's right.
What is an amniotomy and why would it be done?
What is artificial rupture of membrane, to speed up labor?
What is a cerclage?
The first thing a nurse does to prevent cold stress in newborns.
What is dry the infant?
temps below 97.7 can lead to cold stress. Temps over 99.5 can cause a brain bleed and can often indicate sepsis and need to be looked at promptly.
This is how additional damage is prevented after Asphyxia.
What is therapeutic hypothermia?
If an infant has TTN or RDS the nurse's priority is to maintain adequate oxygen levels.
A birth control patch can go anywhere except for this area.
What is the breast?
This STI is not more of an imbalance in vaginal PH than an STI and is diagnosed by a fishy odor.
What is bacterial vaginosis?
Fetal bradycardia.
What is a FHR less than 110? normal FHR is 110-160.
Bonus: Moderate variability is what we want to see.
A uterus that is bigger than expected for the current gestation could be this complication.
What is a molar pregnancy?
Cultural Considerations
What are Communication Patterns, Feeding Practices, Cultural Competence, and Cultural Sensitivity?
The week of pregnancy is when the patient begins to feel quickening.
What are weeks 18-20?
Patients who have pregnancies that are close together are at risk for this complication.
What is Iron deficiency anemia?
Bonus: what should the patient take with the iron pill?
What is orange juice?
Pushing when the cervix is not fully dilated can cause this complication.
What is cervical swelling? If the patient has the urge to push and the cervix is still present they need to focus on relaxation and breathing through the contration.
This procedure is done for infants in a breech position to allow for a possible vaginal delivery.
What is an External Cephalic Version?
Infants born to mothers with DM should be monitored for this complication.
What is hypoglycemia?
Bonus: What is the first intervention for hypoglycemia?
Feed the infant.
Signs of a congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
What are barrel chest, tachypnea, concave abdomen, bowel sounds heard in the chest, displaced heartbeat, and diminished bowel sounds?
This is the difference between Pals and NRP.
What is everything? NRP is only for infants 28 days or younger.
What are Swollen or Tender Breasts, Constipation or Diarrhea, Fluid Retention, Bloating, Cramping, Mood Swings, Social withdrawal, Confusion, Anxiety, Cravings, Nausea/ Vomiting, Headache, Fatigue, Backache, Sleep problems, and Depressed Mood.
This STI can go dormant for many years and then come back and make a person lose their mind.
What is syphilis?
The priority of the nurse after ROM.
What is FHR?
This medication is the first used to treat Postpartum Hemorrhage.
What is oxytocin?