The neurotransmitter of the neuromuscular junction
What is Acetylcholine?
The most important nerve of the forelimb, innervated the triceps as well as the digital extensors
What is the radial nerve?
The bone of the brachium
What is the humerus?
This muscle fills the subscapular fossa
What is the subscapularis muscle?
This group of muscles is collectively responsible for most of the propulsion when an animal runs
What are the Hamstrings?
(biceps femoris, semimembranosus, semitendinosus namely)
These structures in general help to stabalize unwanted movement of joints
This structure houses Calcium stores in the muscle
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
This nerve innervates the muscles on the plantar side of the hindlimb
What is the Tibial nerve?
This structure is acted on by the triceps brachi muscle in order to extend the elbow
Olecranon process
The main extensor muscle of the elbow
Triceps brachi
This muscle is the primary extensor of the tarsus
What is the gastrocnemius?
The stifle joint is made up of these bones
This receptor type is acted on at the NMJ to create an end-plate potential
What are Nicotinic ACh receptors?
This major nerve innervates most of the hip extensor muscles
What is the sciatic nerve?
This boney ridge houses the patella
This functional group of muscles originates on the lateral epicondyle of the humerus
Craniolateral group (extensors of the carpus and digits)
This head of the quadriceps femoris is the only one that originates in the hip
What is the Rectus femoris?
This ligament on the dorsal aspect of the hind limb is responsible for tarsal flexion
What is the peroneus tertius?
ADP and Phosphate are removed from myosin
What is the cause of the power stroke?
This bundle of nerves is responsible for the innervation of the forelimb
What is the brachial plexus?
The main weight-bearing bone of the distal hindlimb (distal to stifle, proximal to tarsus)
What is the tibia?
This muscle covers a large area on the craniodorsal aspect of the animal, and contains a cervical and thoracic portion (separated by the spine of the scapula)
IM injections in horses are typically given in this/these muscle(s)
What are the semimembranosus and semitendinosus muscles?
This ligament, in horses, helps to support the head and neck but is largely absent in dogs and cats
What is the Nuchal ligament?
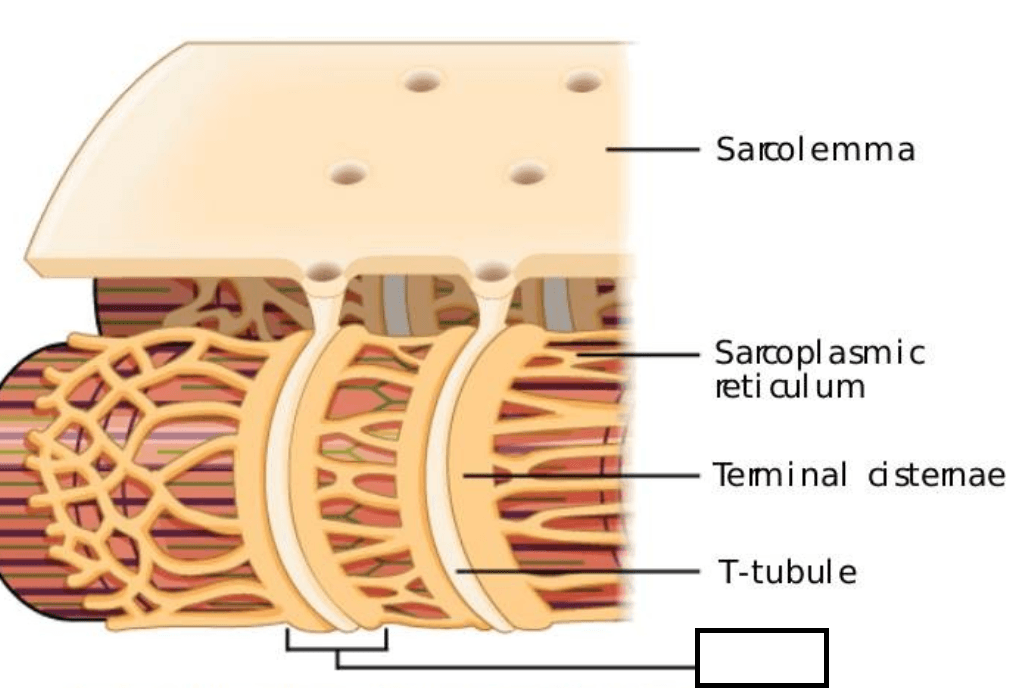
Triad
This nerve innervates the cranial tibial muscle
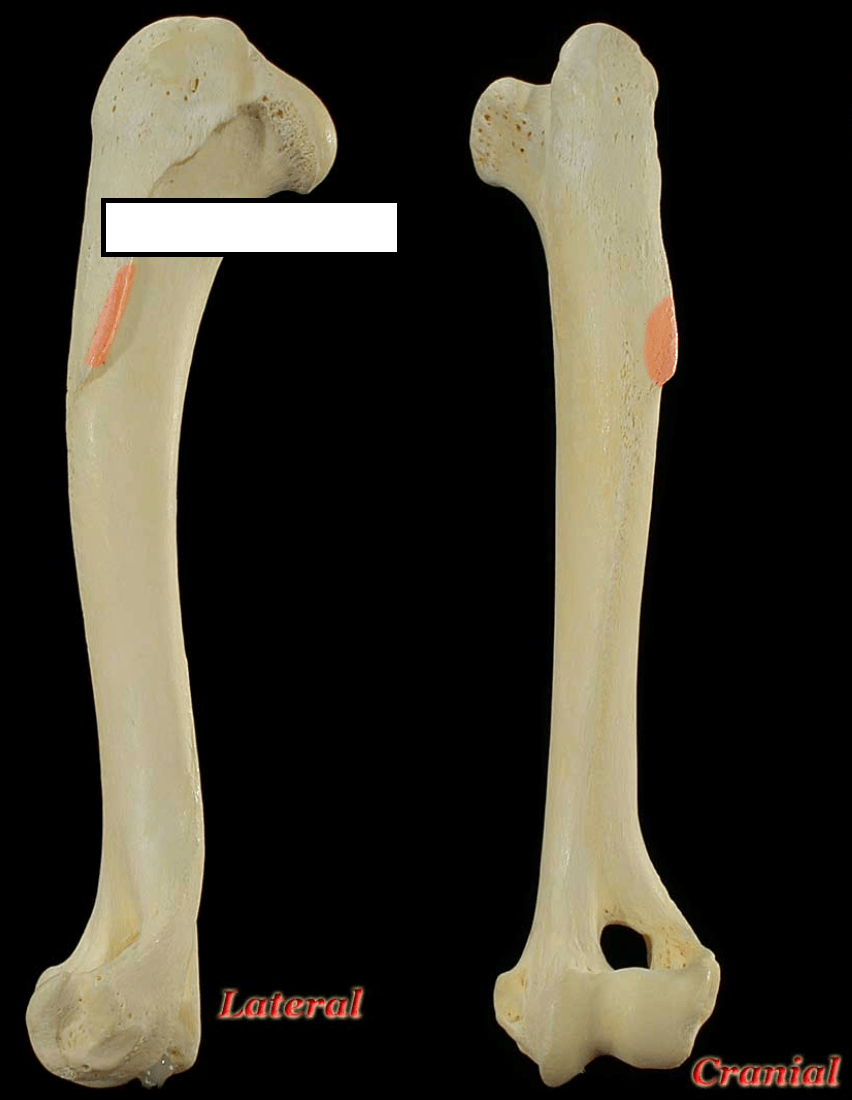
Deltoid tuberosity
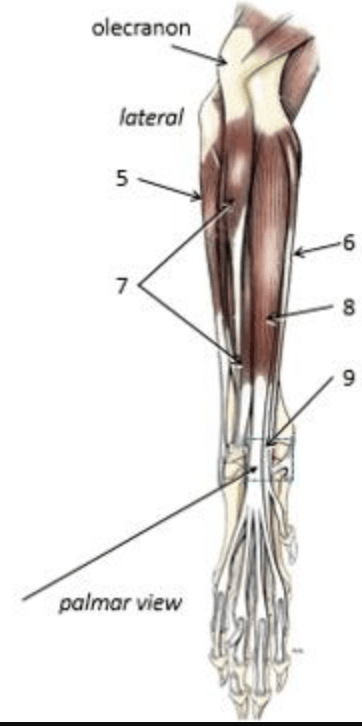 What muscle is shown by #8?
What muscle is shown by #8?
Superficial digital flexor
This group of muscles typically lay on the craniolateral aspect of the crus
Tarsal flexors/digital extensors
These structures help absorb the impact in the stifle joint
What are the Menisci?
Calcium acts on this protein in order to initiate muscle contraction at the level of the sarcomere
Troponin
This bone is incomplete in most horse hind-limbs
What is the fibula?
The adductor muscles of the forelimb
What are the pectorals?
The patella. The patellar ligament then connects the muscle to the tibial tuberosity
These ligaments prevent "drawer" movement of the stifle (cranial to caudal movement)
Actin is often referred to as the ______ filament
Thin
The medial bone of the antebrachium
Radius
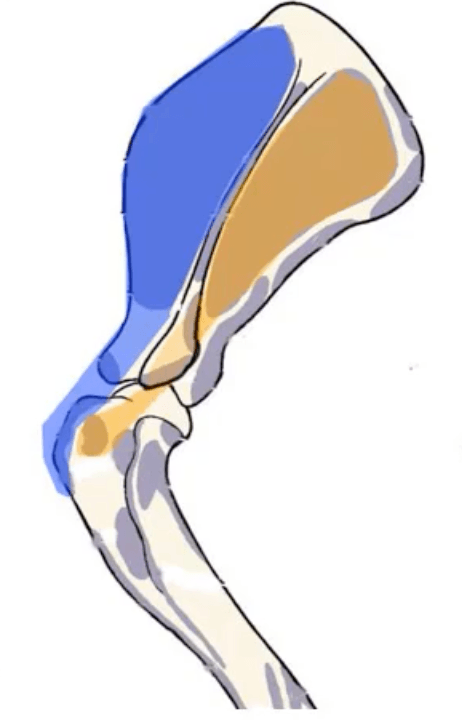
What muscle is shown in blue in this LATERAL view of the shoulder?
Supraspinatus
These two muscles cover most of the medial surface of the hindlimb
What are the gracilis and sartorius muscles
This GAG is the most common found in synovial joint fluid and assists with viscosity, shock absorption, and reduction of friction
What is hyaluronic acid?
This structure is what causes striations in skeletal muscle
What are Z-discs
This nerve innervates the quadriceps femoris
A structure on the equine and bovine femur that is absent in smaller animals
What is the third trochanter?
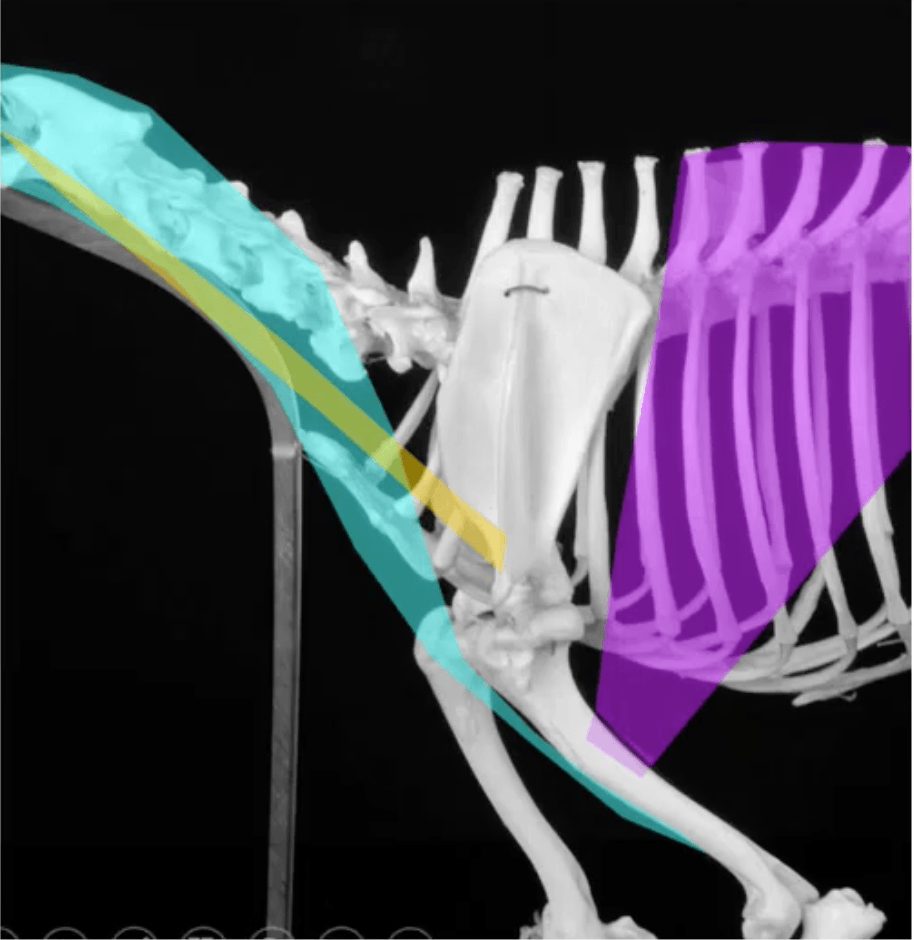
What is the magenta-colored muscle?
Latissimus dorsi
Muscles that extend the tarsus do this to the digits of the hindlimb
Flex the digit
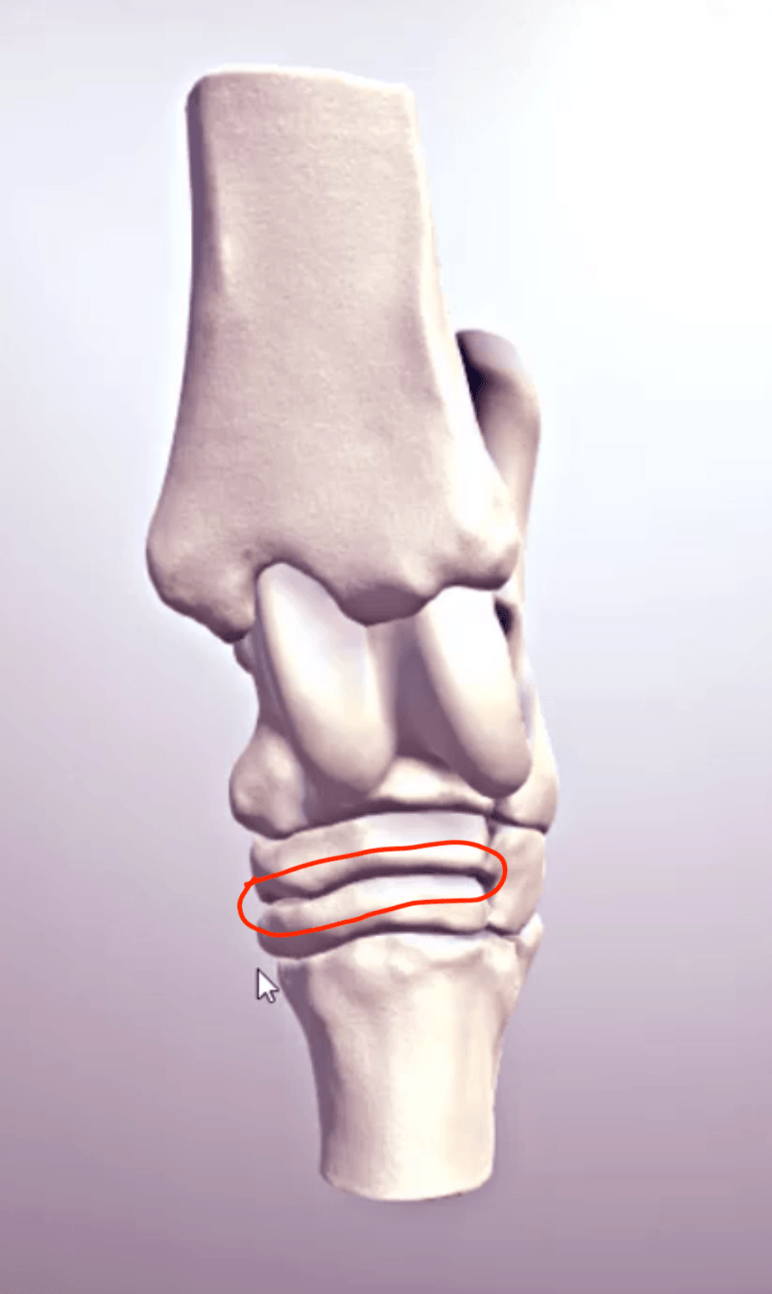 Shown is a dorsal view of the tarsus. The joint highlighted in red is the ________ joint
Shown is a dorsal view of the tarsus. The joint highlighted in red is the ________ joint
Distal intertarsal joint
Compare and contrast the muscle fibers in terms of
1. speed of contraction
2. main energy production method
3. amount of myoglobin
Type 2x- fastest (glycolytic) [no myoglobin]
Type 2a- fast (oxidation or glycolytic) [low myoglobin]
Type 1- slow (oxidative) [high myoglobin]
Commonly referred to as the "splint" bones in a horse
Metatarsal 2 and 4
This muscle antagonizes the triceps brachi
Biceps brachi
This muscle acts on a large flat sheet of fibrous tissue that covers most of the craniodorsal aspect of the hind limb
What is the tensor fascia latae?
The 3 types of joints are.....
Fibrous
Cartilaginous
Synovial
Describe the events following an action potential that lead to muscle contraction in pictures! (roughly 15 events... do not include relaxation of muscle... most complete answer wins!)
1. Action potential
2. Calcium release in terminal of axon
3. Acetyl choline release into synapse
4. Acetyl choline binding to nicotinic ACh receptors
5. Graded potential
6. Sodium voltage gated channels open, causing action potential down the muscle fiber
7. DHP receptor changes configuration to stimulate Ryanodine receptor
8. Sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium
9. Calcium binds to troponin
10. Tropomyosin moves to reveal myosin-binding site
11. Myosin acts on actin, shortening sarcomeres
(specifics of 11 are that myosin binds[11], ADP+Pi are removed: which causes the power stroke[12]. ATP binds, releasing myosin from actin[13], ATP is hydrolyzed to prepare myosin for next cycle[14])
Injecting a local anesthetic into the _____ nerve at the level of the _____ will result in loss of sensation to most of the hoof (forelimb)
Palmer digital
Fetlock
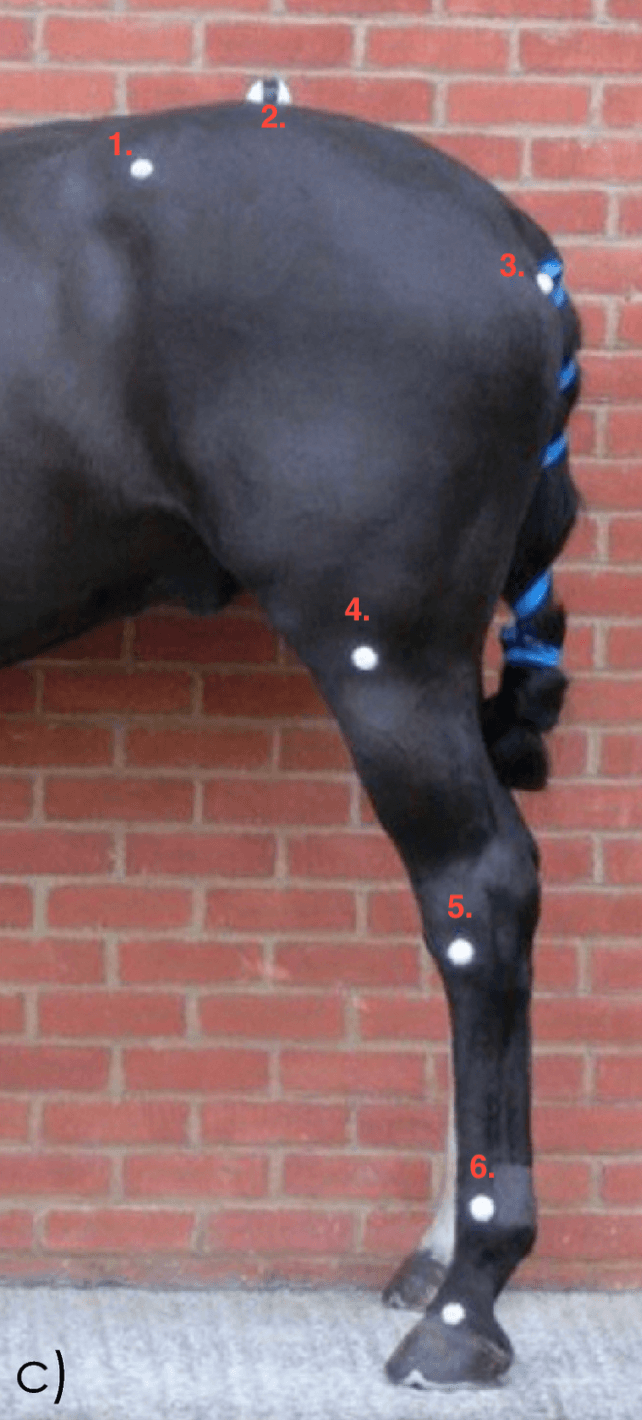
1. Point of the hip (Tuber coxae)
2. (Tuber sacralae)
3. Point of the buttock (Tuber ischia)
4. Stifle joint (femur, patella, tibia)
5. Hock (Tarsus)
6. Fetlock (Metatarsophalyngeal joint)
List the points of insertion for the superficial and deep digital flexors and illustrate the interaction between the two tendons of insertion
Deep inserts on the flexor tubercle of P3
Superficial inserts on proximal aspect of P2
if you got more than 10 right= 1000 points
100 points deducted for each wrong/incomplete answer under 10
Describe the arrangement of fibers in articular cartilage and name the different layers