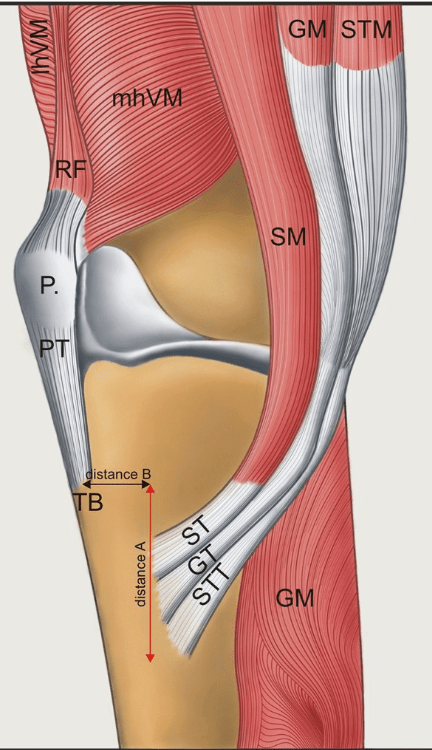
What tendons form the Pes Anserine?
"Say Grace before Tea"
- Satorius
- Gracilis
- SemiTendinosus
What artery supplies the anterior circulation of the Circle of Willis?
Internal Carotid
Patient is getting worked up for a medial meniscal tear to the right knee. Which part of the meniscus is poorly vascularized? What is the treatment?
Inner ⅔; Tx with surgical resection
A patient seen in the stroke recreational unit is told to draw a clock. After examining his illustration, you note that all the numbers of the clock are written and squeezed to the right side. Where do you suspect his lesion?
Right Middle Cerebral Artery . . . patient has left sided neglect
What is the name of the therapeutic treatment for patient’s with Broca Aphasia?
Melodic Intonation Therapy . . . by singing your speech, you recruit the right brain to help with speech production.
Which hip flexor is innervated by the Obtruator and Sciatic (Tibial Division) nerve?
Adductor Magnus (L2, L3, L4, L5, S1)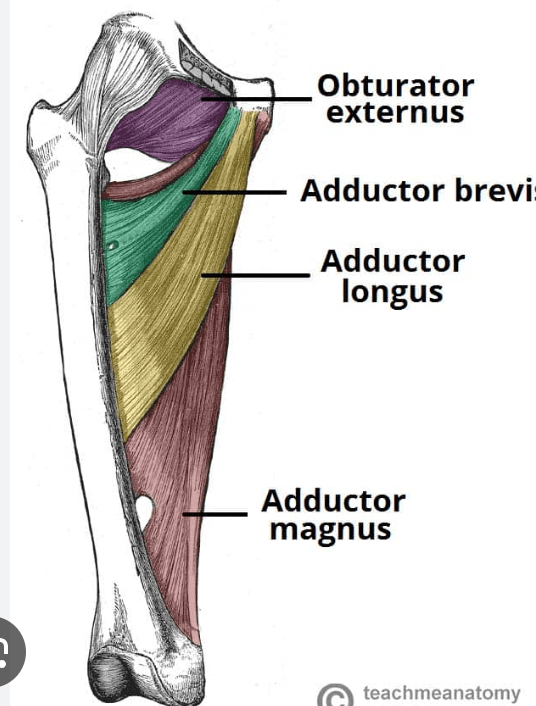
Stroke survivor presents with spatial neglect. What artery is responsible and on what hemisphere?
Nondominant Middle Cerebral Artery infarct
70 y.o. Female was walking her dog, and fell on an outstretched hand. X-ray finding here. What do you see on x-ray?
Colles Fracture . . . distal radius fragment is dorsally displaced
You are consulted for a 61 y.o. Female who is 6 weeks after a new-onset stroke. She is still having difficulty swallowing and requires evaluation for a feeding tube. Where do you think her stroke was located?
Brainstem
Patient underwent a total shoulder replacement several weeks ago. What are 2 exercises that patients should complete with Phase 2?
Vigorous isometrics
Progressive isotonics (ex: elastic tubing exercises)
Active-assisted ROM and active ROM past 90 degrees
2-handed ADLs encouraged
What medial branches innervate the L4-L5 facet joint?
L3 and L4 medial branches innervate the L4-5 facet joint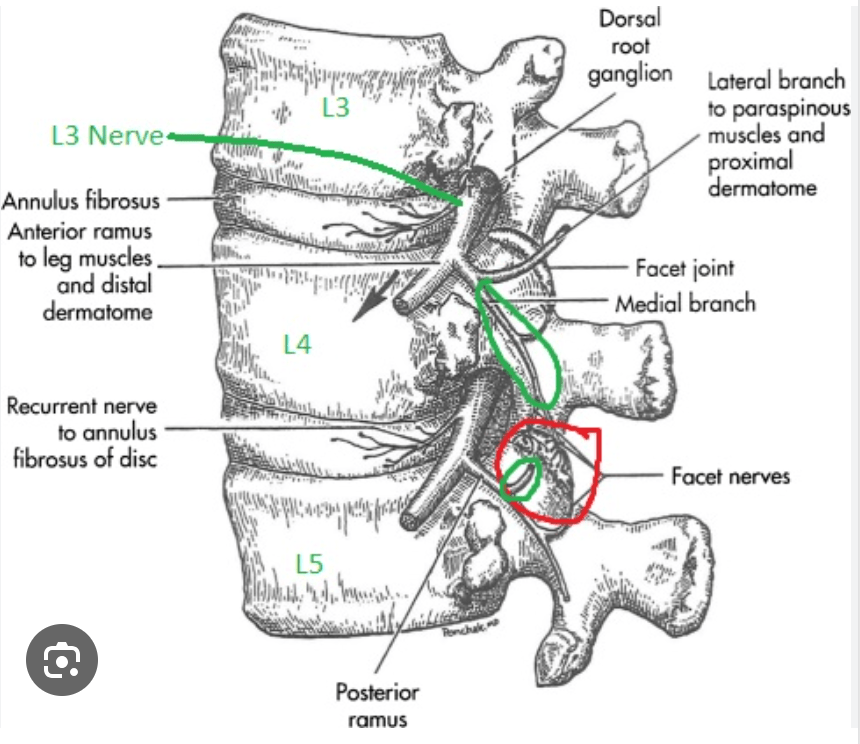
What tracts may get affected by basilar artery strokes?
Corticospinal and corticobulbar tract
What X-ray view shows Bankart lesions the best?
West Point Lateral Axillary view
For this variant of the AP view, the patient lies prone, arm in 90 degrees of abduction and elbow hanging over the edge of the examination table. The beam has an approximate 25 degrees anterior and medial tilt to demonstrate the anteroinferior glenoid rim. This view is difficult to obtain in noncooperative patients and in acute dislocation because of pain. The West Point view is also helpful in the workup of suspected glenoid bone loss because it provides an excellent view of the anterior glenoid rim.
Patient presents after stroke in your rehab. Patient is not fluent, unable to comprehend, and can’t repeat. What is the type of aphasia and what artery is most likely involved?
Global aphasia is affected by the Middle Cerebral Artery
Name 3 precautions that patient’s must maintain during phase 1 post-op for rotator cuff repair.
No weight-bearing
No active ROM above table level
Sling or immobilizer at all times except exercise
Avoid arm adduction across body and internal rotation; avoid shoulder extension and external rotation as dictated by surgeon
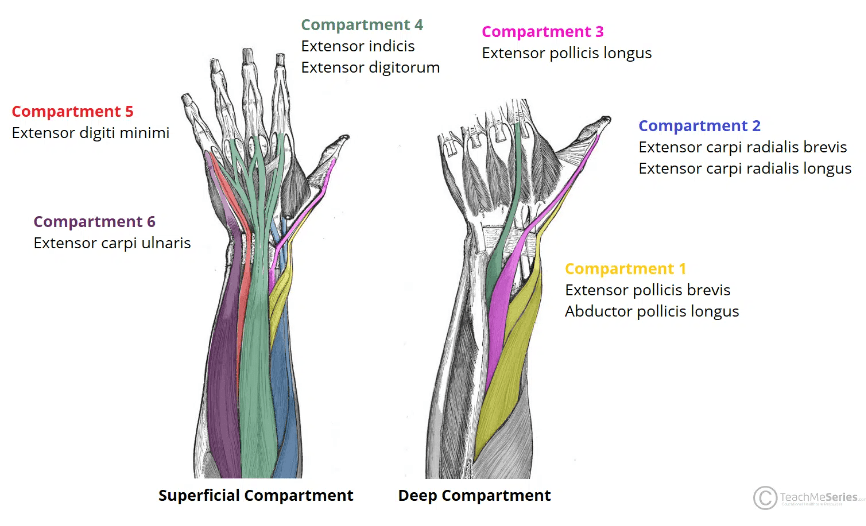
What tendons pass through the 4th extensor compartment of the wrist?
Extensor digitorum, Extensor indicis
Patient presents with agraphia (inability to communicate with writing), acalculi (inability to process numbers and perform calculations), finger agnosia, and left-right disorientation after a stroke. Where is the location of the stroke?
Dominant Parietal Cortex
50 y.o. Male presents to your clinic after completing rehab following a stroke. Patient reports pain in his back and shoulder. You notice weakness to his right shoulder with abduction, forward flexion, and extension. You ask the patient to remove his shirt to assess his scapular motion, and you see the picture upon provocation.
What muscle is weak, and what nerve is involved?
Weak Trapezius, which is innervated by the spinal accessory nerve
A patient presents to the ED with ptosis, anhidrosis, and miosis on the left side of his face. He has difficulty walking and recently fell on his left side. On physical exam, there is decrease in pain and temperature sensation on the left side of his face and on the right side of his body. There is no muscle weakness. What is the diagnosis?
Lateral Medullary Syndrome (aka Wallenberg Syndrome, PICA Syndrome, or Vertebral Artery Syndrome)
What are 2 exercises that patients can start on post-op day 1 for Total Hip Arthroplasty?
Quadriceps isometric exercises
Gluteus muscle isometrics (depending on surgical approach)
Maintain hips in abduction
Active-assisted and knee flexion exercises as tolerated
What are the nerve roots, trunks, cords, and branches of the latissimus dorsi?
C 6,7,8 —> all 3 trunks → posterior cord → thoracodorsal nerve
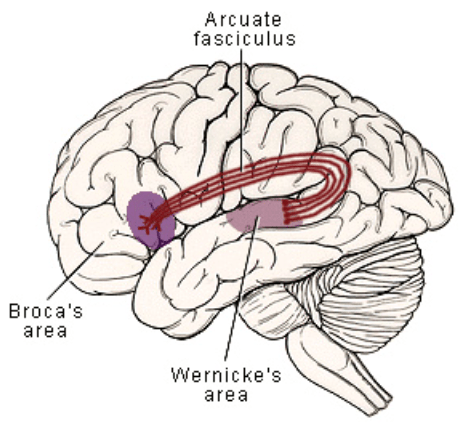
Patient presents with an aphasia. You notice the patient is fluent, can comprehend, but can’t repeat. Where is the location of this aphasia?
Conduction Aphasia → subcortical lesion in the arcuate fasciculus (an associated tract running beneath the cortex, connecting temporal and parietal lobes and carrying impulses between Wernicke’s and Broca’s area)
35 y.o. Female with no significant PMH complains right lateral thigh pain when running. Patient has pain when palpating the greater trochanter as well as a snapping sound when performing the log roll test. Patient has a positive Ober’s test as well as pain in her right lateral thigh with the FABERs test.
What most likely caused this presentation?
Diagnosis is External Snapping Hip due to a tight IT band subluxing/snapping over the greater trochanter
A patient presents to the ED with loss of muscle strength in his right upper and lower extremities. He has loss of proprioception and position sense on his right side and has left side tongue deviation. What does he most likely have?
Medial Medullary Syndrome
What is the Minimum Motor Criterion for someone to participate in CIMT (Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy)? (What are 3 things patients should be able to display in order to participate in CIMT?)
20 degrees of voluntary extension of the wrist
10 degrees abduction at the thumb
10 degrees of extension of 2 fingers in the affected hand repeated 3 times in 1 minute