The long thoracic nerve innervates which of the following muscles?
A. Levator scapulae
B. Serratus anterior
C. Subclavius
D. Supraspinatus
E. Latissimus dorsi
B. Serratus Anterior
A 65-year-old male with a history of liver cirrhosis has been examined for hepatitis A, B, and C viruses. In an attempt to attain a blood sample from the patient’s median cubital vein, a health care specialist accidentally procures blood from an artery. The blood most likely comes from which artery?
A. Brachial
B. Common interosseous
C. Radial
D. Superior ulnar collateral
E. Ulnar
A. Brachial
A patient injures his radial nerve where it courses through the lateral intermuscular septum of the arm. Which of the following deficits may be observed in the patient due to the injury?
A. Loss of elbow flexion
B. Paresthesia of the lateral forearm
C. Inability to abduct the fingers
D. Weakness of thumb adduction
E. Paresthesia of the lateral dorsum of the hand
F. Inability to oppose the thumb
E. Paresthesia of the lateral dorsum of the hand
Identify the structure indicated by the yellow asterisk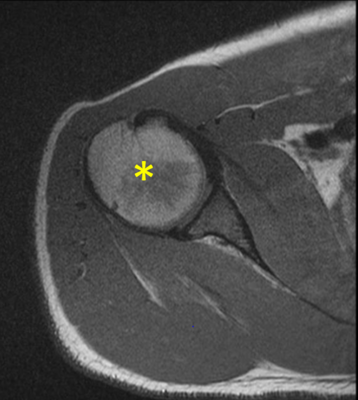
Humerus
What is a genetically determined state of hypersensitivity to common environmental allergens, mediated by IgE antibodies?
Atopy
Which upper limb compartment(s) would be affected if the ulnar nerve was lesioned?
A. Anterior arm and flexor forearm
B. Extensor forearm and hand
C. Extensor forearm only
D. Flexor forearm and hand
E. Hand only
D. Flexor forearm and hand
A 65-year-old male with a history of liver cirrhosis has been examined for hepatitis A, B, and C viruses. In an attempt to attain a blood sample from the patient’s median cubital vein, a health care specialist accidentally procures blood from an artery. During the procedure, the needle also hits a nerve sitting medial to the artery. Which of the following nerves is most likely hit?
A. Axillary
B. Median
C. Musculocutaneous
D. Radial
E. Ulnar
B. Median
A 27-year-old man with cubital tunnel syndrome complains of numbness and tingling in the skin of the ring and little finger and medial hand. Assuming this patient has a nerve injury resulting in these cutaneous symptoms, which of the following muscles is most likely to be paralyzed as well?
A. Flexor digitorum superficialis
B. Opponens pollicis
C. Pronator teres
D. Supinator
E. Medial two lumbricals
E. Median two lumbricals
Identify the specific region indicated by the yellow asterisks
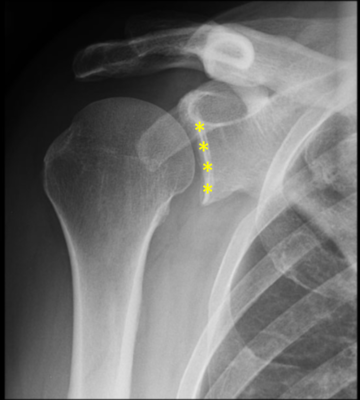
Glenoid fossa
This is the glenoid fossa of the scapula.
You have various landmarks to know that you are looking at the region of the shoulder complex. The head of the humerus is very distinct and lets you know the area articulating with it is the glenoid cavity.
Note: you may notice that the system grades you incorrect for any answer that is not exact. For example, you may have written "glenoid cavity" or "glenoid fossa of scapula". These are all correct answers. On a real assessment, these are graded by a human (Dr. Funk), so these answer choices will be considered correct.
Give the mechanism and an example of Type II hypersensitivity.
Mechanism: IgG, IgM activating complement or ADCC1 to kill cells
Ex. hemolytic anemia, Pemphigus (autoimmune disease of the skin)
Which nerves contribute the most to distributing the C8 dermatome to the skin?
A. Lateral antebrachial cutaneous and medial antebrachial cutaneous
B. Median and ulnar
C. Posterior antebrachial cutaneous and radial
D. Radial and median
E. Ulnar and medial antebrachial cutaneous nerves
E. Ulnar and medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve
Which nerve would most likely be damaged by an avulsion fracture at the medial epicondyle of the humerus?
A. Axillary
B. Median
C. Musculocutaneous
D. Radial
E. Ulnar
E. Ulnar
Make an OK sign with your thumb and index finger.
Which of the following is a correct pairing of muscles and nerve that is allowing you to bring the tips of your thumb and index finger together?
A. Flexor digitorum profundus - ulnar nerve
B. Flexor pollicis longus and flexor digitorum superficialis - radial nerve
C. Flexor digitorum profundus and flexor pollicis longus - anterior interosseous nerve
D. Pronator quadratus and flexor pollicis longus - anterior interosseous nerve
E. Flexor digitorum profundus and flexor digitorum superficialis - anterior interosseous nerve
C. Flexor digitorum profundus and flexor pollicis longus - anterior interosseous nerve
Identify the major group of muscles surrounded by the yellow circle.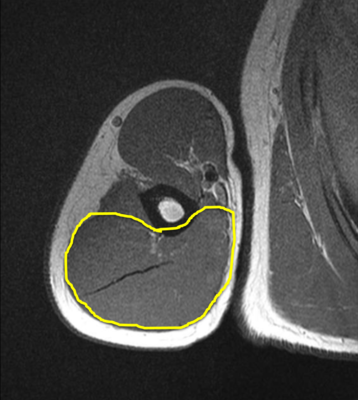
Triceps brachii
This is the posterior arm compartment - major muscles include the triceps brachii
A research scientist was screening natural molecules and found that compound X binds to the Fc region of human IgE molecule exclusively. Which of the following experimental results would suggest this molecule is a candidate for an anti-allergy medication?
A. it also upregulates mast cell degranulation
B. it crosslinks IgE molecules
C. the compound enhances binding of IgE to C1 complement protein
D. when added to human IgE, no binding to FcεR is observed
D
Mast cell degranulation is triggered by IgE molcules that are bound to the FcεR on their surface binding the allergen at their antigen binding site and crosslink the FcεRs. See slides 9 and 10
A 64-year-old male with lymphoma begins to develop swollen lymph nodes in the axillary fossa. He reports to his physician complaining of paresthesia radiating down the posterior surface of his arm, forearm, and lateral hand. The physician suspects that the axillary lymph nodes are beginning to compress nerves within the axillary fossa. Based on the sensory deficits in this patient, the physician is able to determine which nerve may be injured. Using this information, which of the following muscle groups may demonstrate weakness due to the nerve injury?
A. Biceps brachii
B. Flexor forearm muscles
C. Intrinsic hand muscles
D. Shoulder abductors
E. Triceps brachii
E. Triceps brachii
A patient presents with weakness of flexion and supination of the forearm at the elbow. Further examination also reveals paresthesia along the lateral forearm. Which of the following is a correct location where an injury could have occurred to cause these signs/symptoms?
A. Anterior arm compartment
B. In the cubital fossa
C. Near the spiral groove of the humerus
D. In the cubital tunnel
E. Near the surgical neck of the humerus
A. Anterior arm compartment
A 47-year-old female presents with pain that she reports primarily in the third metacarpophalangeal joint. The patient is determined to have developed gout in this articulation. The impaired joint is which of the following types?
A. Symphysis
B. Synchondrosis
C. Synovial, ball and socket
D. Synovial, condyloid
E. Synovial, hing
D. Synovial, condyloid
The red arrow in the image is pointing to a fractured bone. What is the fractured bone?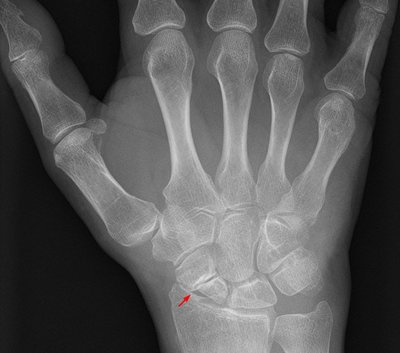
scaphoid
This is the most frequently fractured carpal. It is the scaphoid.
Landmarks - you first need to know lateral/medial. So, you can use either the distinct appearance of the distal radius or the thumb.
The most lateral bone in the proximal row of carpals = scaphoid
A 17-year-old female who recently emigrated from south Asia has a positive PPD skin test for
tuberculosis. The results of this test are due to
A. activated CD4+ T cells, macrophages, and their cytokines
B. a Th17 mediated immune response
C. an IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reaction
D. an IgM/IgG-mediated hypersensitivity reaction
E. inflammation triggered by the needle insertion
A.
The PPD test is a DTH ot Type IV hypersensitivity reaction. See slides 28 and 31.
Which of the following muscles is innervated by a branch of the medial cord?
A. Deltoid
B. Flexor carpi ulnaris
C. Latissimus dorsi
D. Serratus anterior
E. Triceps brachii
B. Flexor carpi ulnaris
Which structure would be spared if the medial intermuscular septum were to be lacerated in the mid-brachium?
A. Median nerve
B. Brachial a.
C. Ulnar n.
D. Radial n.
Young Johnny was playing on the playground at school when he fell and struck his arm against the swing set. He ran to the school nurse, complaining of which of the following conditions as a result of injuring the radial nerve in the spiral groove of the humerus?
A. Inability to extend the hand
B. Inability to oppose thumb
C. Numbness over the medial side of the forearm
D. Weakness in abducting the arm
E. Weakness in pronating the forearm
A. Inability to extend the hand
The attached image is cut in which plane of section?
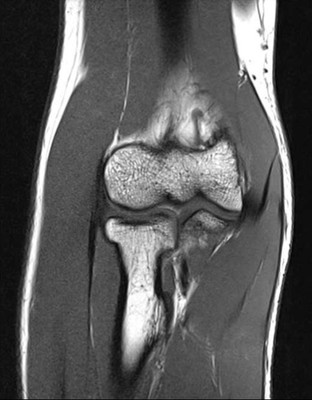
Coronal
A 19-year-old female complains of stiff joints in her hands, constant fatigue, and a rash over her face. The rash seems to worsen after exposure to sunlight. Examination revealed confluent symmetrical macular erythema over the malar eminences, with tenderness and swelling in peripheral joints. Laboratory tests revealed high titers of anti-nuclear antibody (ANA) and proteinuria. What type of hypersensitivity is the patient demonstrating?
Type III