Why is communication important according to TeamSTEPPS?
Because ineffective communication leads to mistakes which makes patients less safe.
Who is the primary source of patient data?
The patient

A H. pylori infection causes this disease.
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
The most common cause of Cystitis inside a hospital is what?
Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infections (CAUTIs)

Joint disease with systemic symptoms: fever, weight loss, fatigue and anemia
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)

What stage of a pressure injury has intact skin and nonblanchable erythema?
Stage 1
• BUN
• PSA (prostatic-specific antigen)
• Ultrasound
• Bladder Scan (to determine if retention is occurring)
• Biopsy
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
• Alpha-blocking-tamsulosin (Flomax)
• 5-alpha reductase inhibitor-finasteride (Proscar)
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
• DMARD therapy - methotrexate
• Corticosteroids - methylprednisolone (short term
• NSAIDS - ibuprofen (possible side effect of gastric ulcers)
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
What does SBAR Stand for?
Situation, Background, Assessment, and Recommendations

Name a secondary source of patient data.
family and/or medical record (EMR)
If a patient has had diarrhea for 3 days is it chronic or acute?
chronic because acute is defined as 1-2 days
These factors put a patient at risk for what?
• Bedrest, Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
• Decreased bladder tone, Calculi
• Some medications, Post operative effects
Urinary retention
An injury to the ligaments and tendons that surround a joint, caused by twisting or hyperextension. (common locations ankles, knees, and wrists)
Sprain
*Bonus 100 pts f you can explain what a strain and contusion is.
What is the scoring mechanism used to predict risk of pressure injuries?
Braden score
• CBC (Hgb, Hct, WBC, Platelets)
• Albumin
• Total Protein
• BUN and Cr
• Liver function
• Wound cultures
Wounds and Pressure Injuries
• Colchicine
• Probenecid
• Allopurinol- interrupts the breakdown of purines before it can form uric acid.
• NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen)
• Corticosteroids (methylprednisolone, prednisolone (Prednisone))
Gout
• Antacids (ex. calcium carbonate)
• H2 receptor antagonists (ex. famotidine (Pepcid))
• Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) (ex. pantoprazole (Protonix))
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
What is Call-Out and Check-Back?
Call-Out - informs all team members of important info simultaneously during emergency situations
Check-Back – repeating what was said back to the person who said it so there isn't a miscommunication
There are 3 types of nursing diagnoses: Health promotion, Risk diagnosis, and problem focused. They may contain a NANDA Label, a r/t, and an AEB.
What does the Risk diagnosis contain?
Health promotion (1 part): just a NANDA label
Risk Diagnosis (2 part): NANDA label and r/t only
Problem focused (3 part): NANDA label, r/t, and AEB
Non-GI symptoms of what disease: Fatigue, Weakness, Depression, Numbness of the hands and feet, Migraines, Osteopenia
Celiac Disease

Emptying without needing to pee is what kind of urinary incontinence?
Reflex
Osteogenic sarcoma could lead to what happening?
Amputation
What makes a wound unstageable?
wound covered in slough so you can't see how deep it is
*Bonus 100 points: correctly describe a deep tissue injury
Dual energy X Ray absorptiometry (DEXA)
Osteoporosis
*Bonus 100 pts if you can remember what is measured in a DEXA scan as it relates to Osteoporosis
Antibiotics (Bacterial infection)
or
Antifungals (Fungal infection)
Cystitis
Cyclobenzaprine
Lower Back Pain
Name 3 barriers to effective communication (there were 15 in the lecture).
Inconsistency in Team Membership
Lack of Time
Lack of Information Sharing
Hierarchy
Defensiveness
Conventional Thinking
Complacency
Varying Communication Styles
Conflict
Lack of Coordination and Followup with Coworkers
Distractions
Fatigue
Workload
Misinterpretation of Cues
Lack of Role Clarity
What is the greatest priority for a newly admitted patient?
Safety concern, Issues delaying client discharge, Has client expressed it as a priority, Are there several AEB, Breathing or circulation, Psychosocial concerns?
Breathing and circulation are the primary concerns

These are complications of what:
Syncope, hypotension, and bradycardia due to vagus nerve compression
Constipation

Diagnostics ordered for what problem:
non-contrast CT scan
24-hour urine test to measure amount of calcium, uric acid, creatinine, sodium, pH, and total volume.
Urinary and Kidney Stones (Calculi)
Clinical manifestations:
• Numbness or tingling
• Increased edema
• Decreased pulses and capillary refill
• If identified notify provider immediately as this may lead to disability or loss of the extremity.
compartment syndrome

What stage(s) of pressure injuries require analgesics and how many minutes before do they need they be administered?
Stages 3 and 4 (before debridement) and 30 minutes prior
• Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP)
• ESR an CRP (used to detect inflammation)
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
*Bonus 100 pts if you can explain what else commonly needs to be monitored with RA medication administration
• Calcium and Vitamin D supp.
• Bisphosphonates
• estrogen agonists/antagonists
• RANKL inhibitors improve BMD
Osteoporosis
• Aminosalicylates (sulfasalazine (Azulfidine)
• Antibiotics (metronidazole (Flagyl) and ciprofloxacin (Cipro))
•Corticosteroids (Prednisone)
• Immunomodulator medications Anti-Tumor necrosis factor medications
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Chron's and Ulcerative Colitis)
Name the 4 standards of communication for TeamSTEPPS.

Complete
Clear
Brief
Timely
For planning SMART care, the plan should be what?
Specific
Measurable (objectively measurable)
Attainable
Realistic
Timely (needs to be soon)
s/s:
Feeling of fullness in chest with pain laying down
• Chest pain and/or heartburn
• Frequent belching
• Dysphagia
Hiatal Hernia
Surgery for BPH is called what?
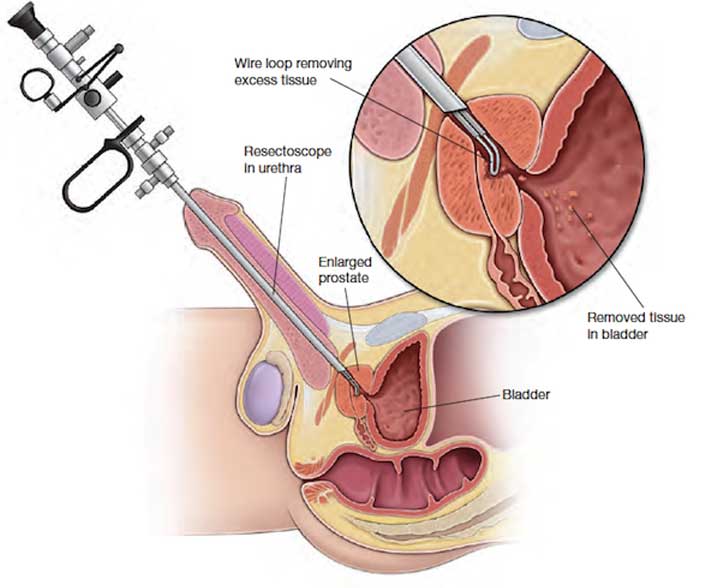
TURP – transurethral resection of the prostate
Nursing interventions:
• Apply cool/moist heat 20-30 min 4 times daily
• Fowler position with moderate hip/knee flexion
Lower Back Pain (Acute lumbosacral strain)
Why is the nurse specialist that can assist with wound care?
Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nurse (WOCN)

• Ambulatory PH monitoring
• PPI trial
• Endoscopy/barium swallow
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
• Antacids
• H2 Antagonists
• PPIs
• Antibiotics for H. Pylori infections
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
• acetaminophen (Tylenol)
• NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen)
• Corticosteroids (methylprednisolone, prednisolone (Prednisone))
• Tramadol
• Topical NSAIDs (diclofenac sodium (Voltaren))
Osteoarthritis (OA)