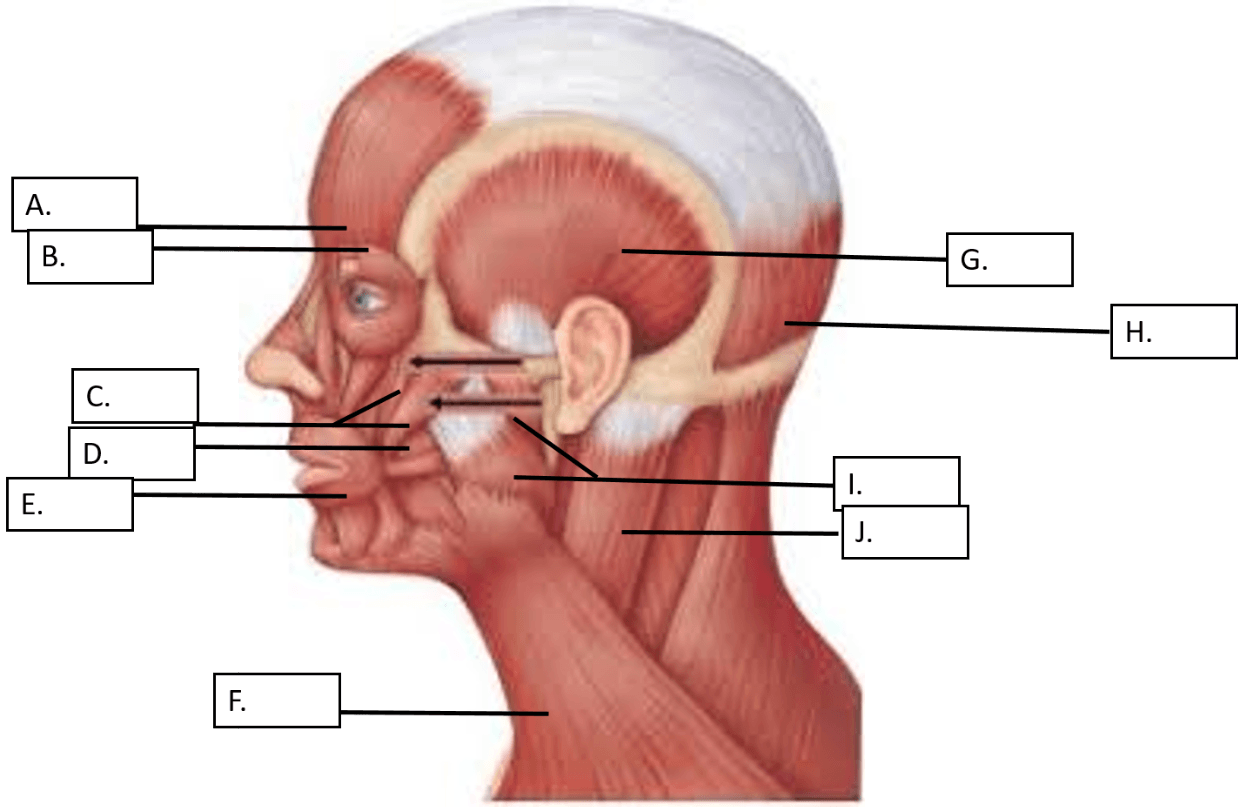
This muscle is indicated by the letter J in the diagram above
What is the Sternocleidomastoid
This muscle is responsible for raising the lateral corners of the mouth (smiling muscle)
What is the Zygomaticus
The tissue surrounding an individual muscle fiber
What is the endomysium
The region that is shown below: 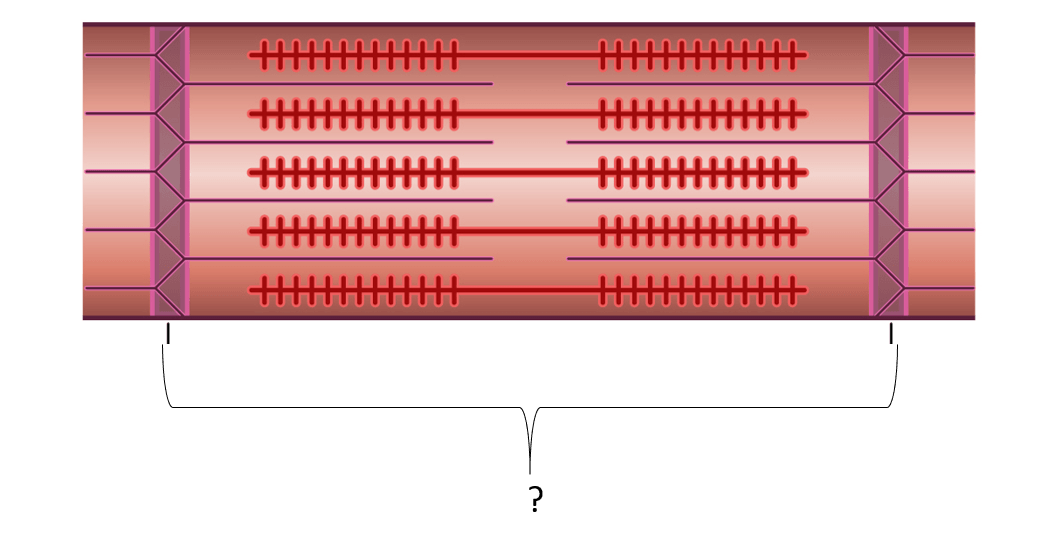
What is the sarcomere
An isotonic contraction where the muscle shortens.
What is a concentric contraction
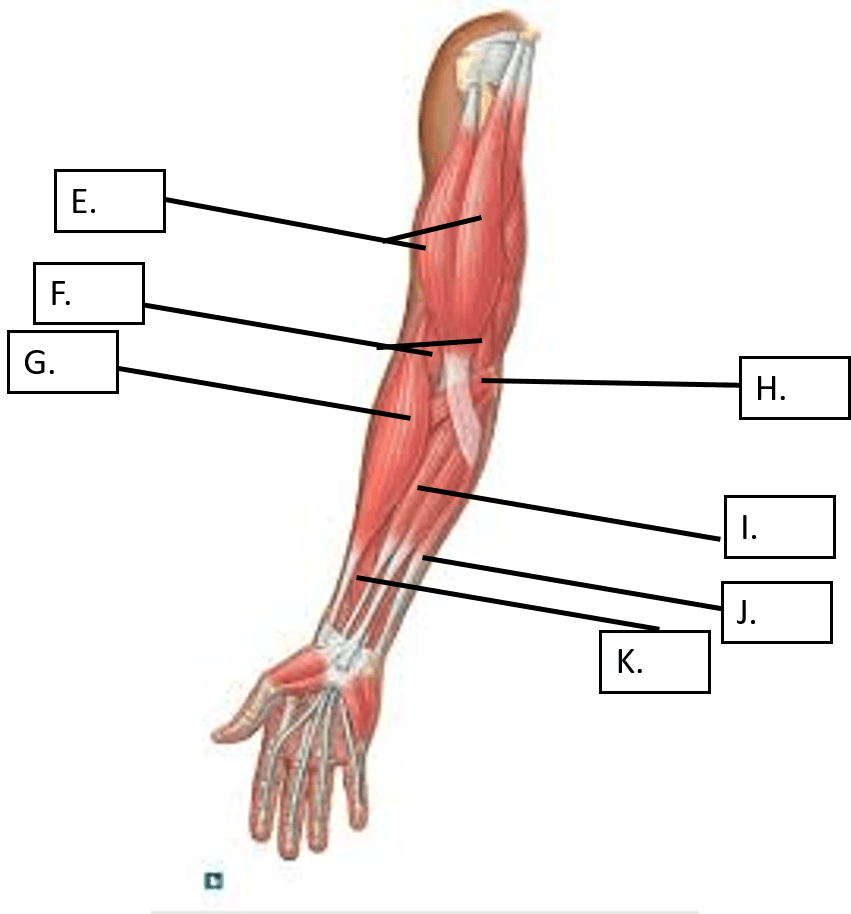
This is the muscle indicated by the letter G in the diagram above.
What is the Brachioradialis
This muscle's action is pronation of the forearm.
What is the Pronator Teres
The tissue surrounding a group of muscle fibers
These two myofilaments are the main protein filaments responsible for muscle contraction
What are myosin and actin
A neuron and all the muscle cells it stimulates make up this
What is a motor unit
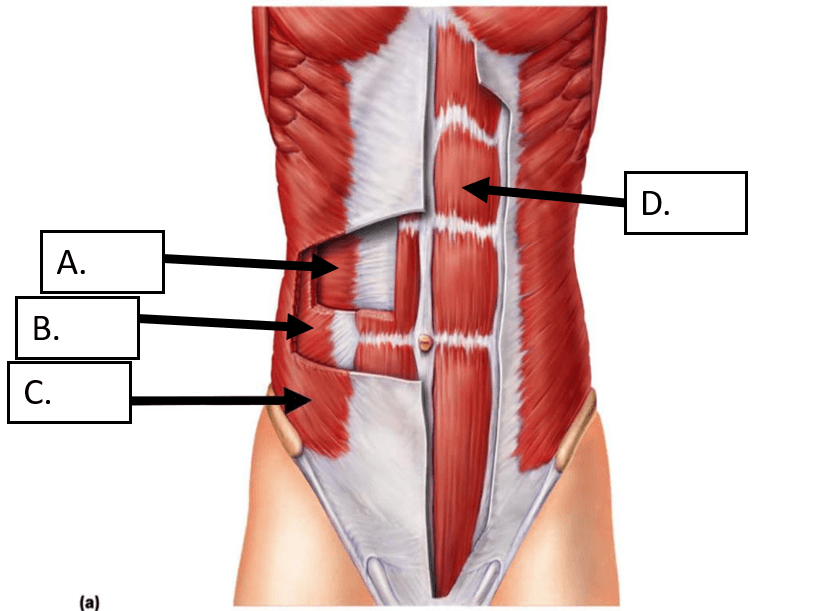
This is the muscle indicated by the letter D. in the image above
What is the rectus abdominis
This posterior muscle of the forearm extends and abducts the wrist
What is the Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
The epimysium is a layer of connective tissue that surrounds the muscle and forms ___________ which connect the muscles to the bones.
What are tendons
This is the neurotransmitter that is released from the axon terminal into the synaptic cleft in a neuromuscular junction.
What is acetylcholine
single contractions of muscle fibers caused by single threshold stimulus; rare
What is twitch
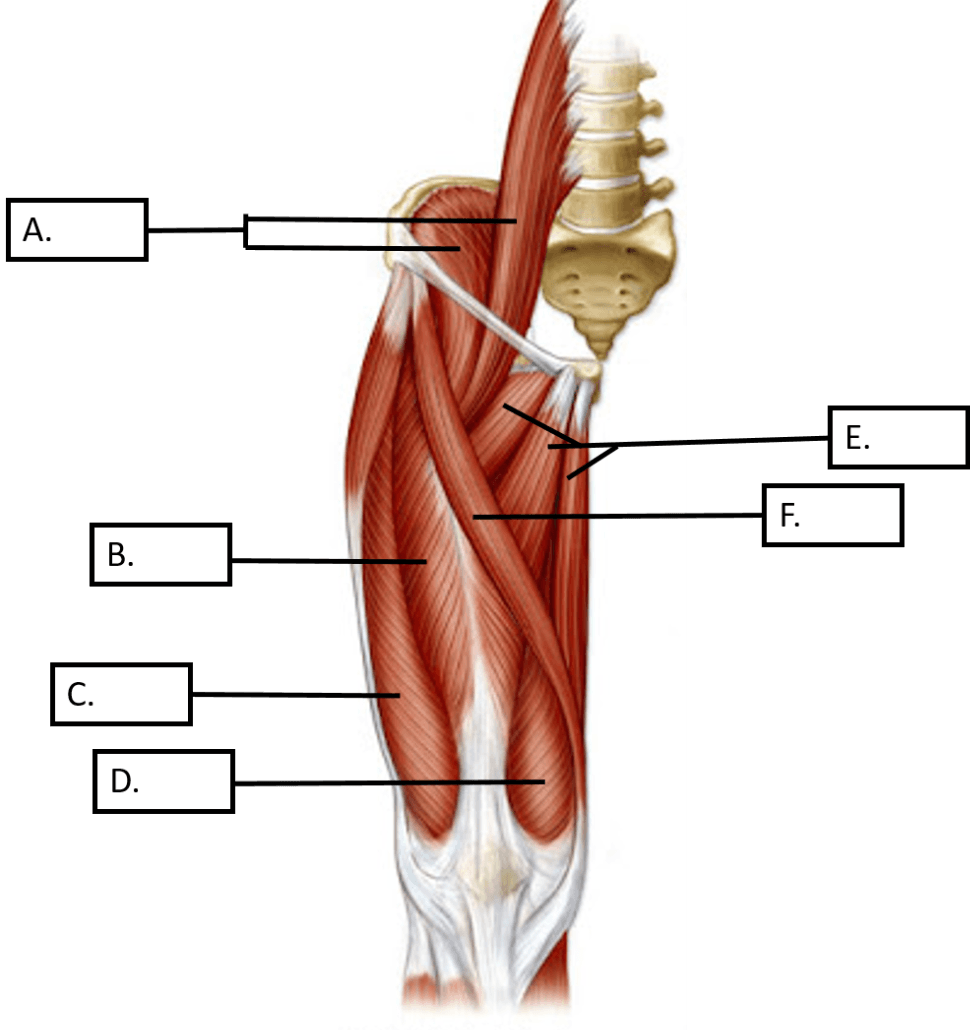
These THREE muscles are indicated by the letters B, C and D in the image above.
What are the Rectus Femoris, Vastus Lateralis and the Vastus Medialis
These two muscles work to elevate the mandible. (chewing)
What are the masseter and the temporalis muscles
Muscle fibers are made up of groups of these smaller pieces
What are myofibrils
In order for myosin to be able to reach out and attach to actin this molecule must be broken down into ADP + P. This energizes the myosin heads.
What is ATP
The minimal level of stimulation required to cause a muscle fiber to contract.
What is the threshold stimulus
These two muscles are indicated by the letters F and G in the diagram.
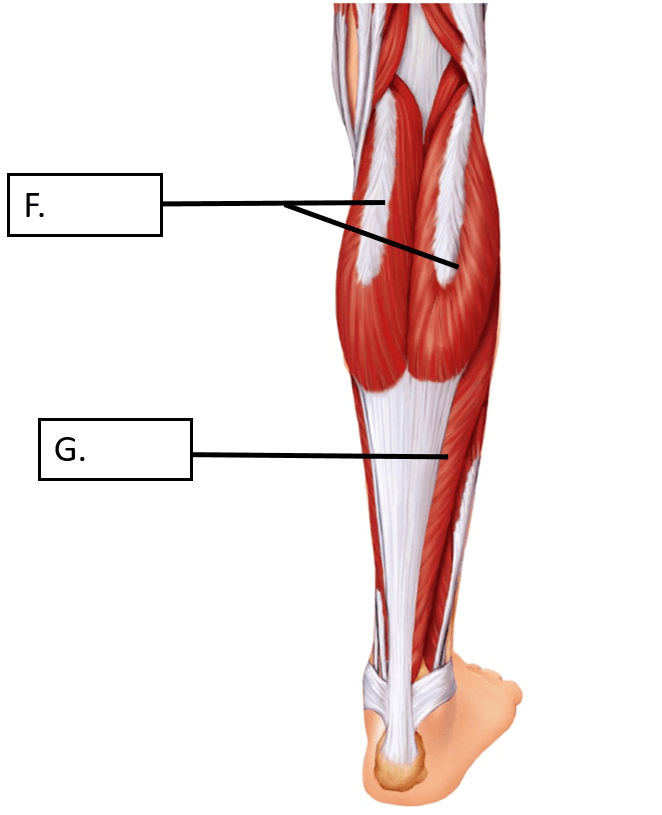
What are the gastrocnemius (F) and the soleus (G)
These THREE muscles of the thigh are responsible for adduction, medial rotation and flexion of the thigh.
Groups of muscle fibers surrounded by the perimysium make up these
What is a fascicle
These ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and help to move tropomyosin and troponin off of the actin myofilament.
What is Calcium or Ca2+
sustained, steady muscular contractions caused by a series of stimuli bombarding a muscle in rapid succession (not necessarily a maximal contraction)
What is tetanus
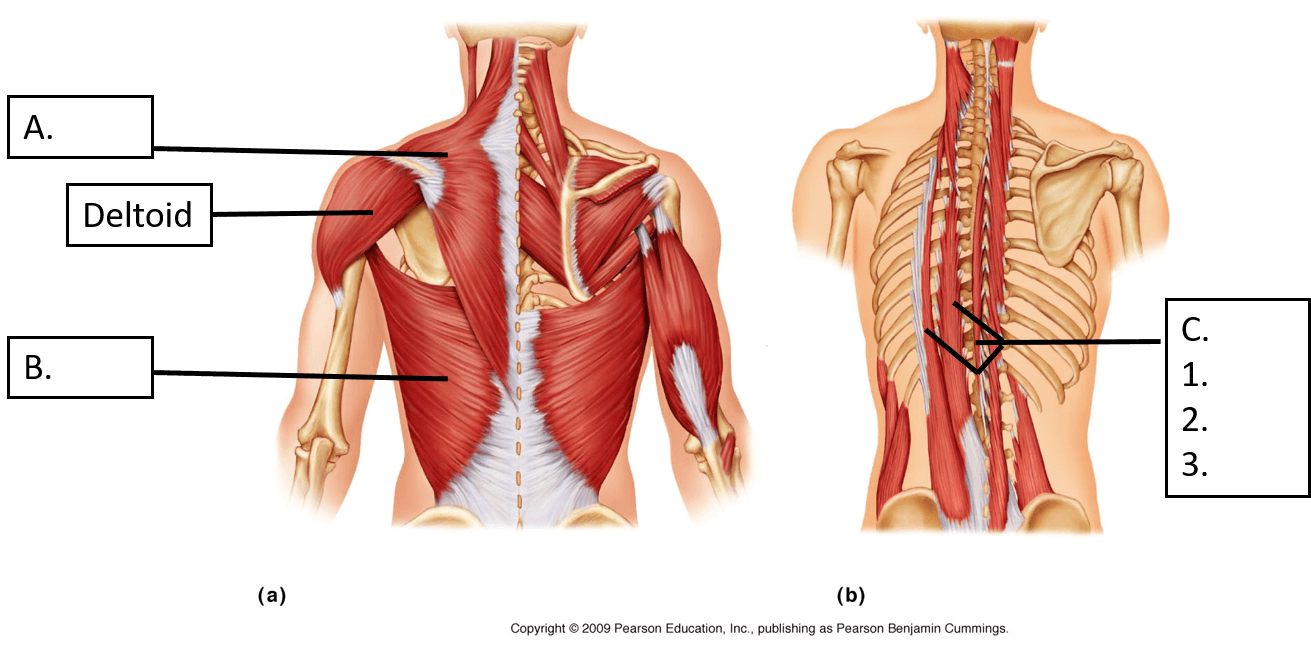
These three muscles make up the Erector spinae (1,2 and three in the image above)
What are the iliocostalis, longissimus, and the spinalis.
These three muscles work together to extend at the hip and flex at the knee.
What are the Biceps Femoris, Semitendinosus, and the Semimembranosus. (Hamstrings)
Muscle fibers have multiple ___________ and a plasma membrane called a _______________.
What are nuclei and sarcolemma.
Once the channel proteins on the sarcolemma are changed by the acetylcholine this allows for these two ions to rush in and out of the muscle cell causing depolarization of the motor end plate.
What are sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+)
Muscle contractions that do not produce movement.
What are isometric contractions