•Fusiform, Uninucleated, No striations, &Involuntary
Found in walls of organs
What is Smooth Muscle
Synaptic vesicles are filled with this which will be released from the vesicle into the cleft once a signal reaches an axon terminal.
What is Acetylcholine (ACh)
States all the muscle fibers in a motor unit are stimulate at once.
What is the All- Or- None Law?
Fast-Acting process of forming energy that results in 2 ATP molecules and the buildup of lactate.
What is Fermentation?
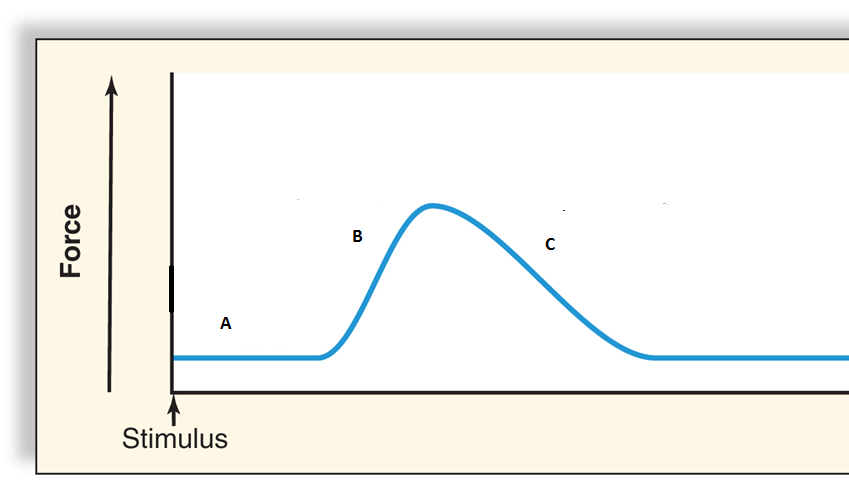
Explain B.
Contraction Period. This is where the myosin binding sites are exposed on the actin so the myosin is continually binding and pulling with the attachment of ATP and the release of ADP + P.
Branching chains of cells, Uninucleated, Striated, & Involuntary
What is Cardiac Muscle
Released from sacroplasmic reticulum which will then signal sarcomere contraction.
What is Calcium
Time between stimulation and initiation of contraction.
What is the latent period?
Slowest process, but most efficient. Produces several dozen ATP molecules and occurs in mitochondria.
What is Cellular Respiration.
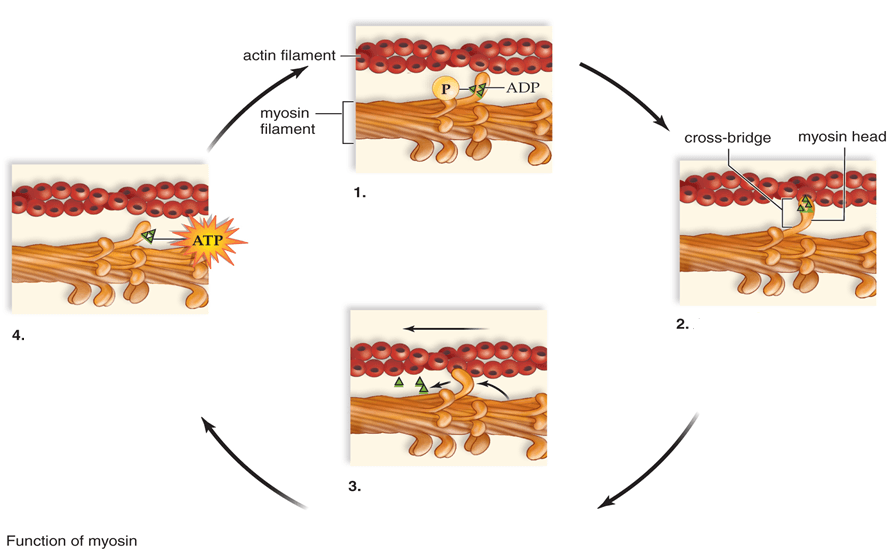
During which section would rigor mortis occur?
What is 3.
Cylindrical, Multinucleated, Striated & Voluntary
What is Skeletal Muscle
Thick myofilaments
What is Myosin
Cross-bridges broken, calcium returns to sarcoplasmic reticulum, and as a result the muscle returns to original state.
What is the relaxation period?
In weight loss you want to burn which energy source?
What are Plasma Fatty Acids.
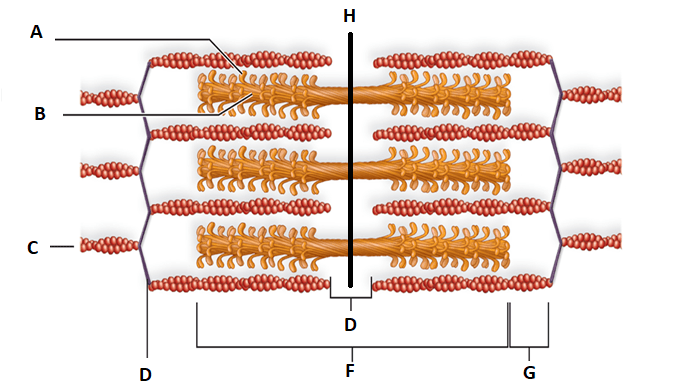
Myosin
Equals 1 muscle cell and is covered by endomysium.
Fiber
Bind to released Ca2+ which will lead to exposing myosin binding sites.
What is Troponin?
How many muscle fibers are associated per axon.
What is innervation ratio?
Explain why continual training is important for energy usage?
The more you train the more mitochondria. Which results in more use of cellular respiration for use and resulting in less soreness.
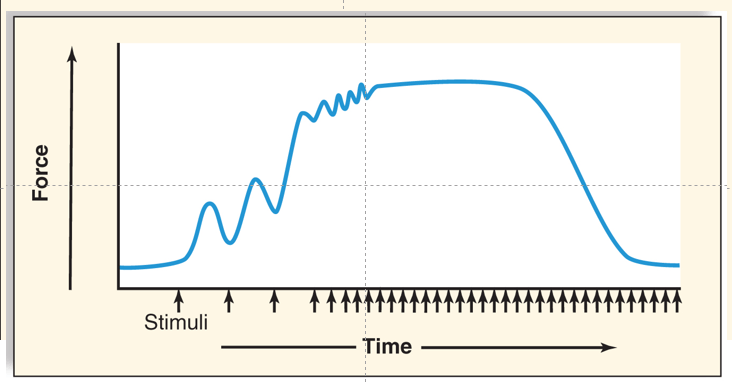 Explain the 3 parts to this chart and what it means about muscle contraction.
Explain the 3 parts to this chart and what it means about muscle contraction.
Summation- the muscle is not returning to orginal state but contracting further.
Tetanus- with continual stimuli it is at maximal contraction.
Fatigue- even though there is stimuli it does not have the energy to sustain contraction.
Used for Aerobic exercise with more stamina and steadier “tug”. Dark in color due to its numerous mitochondria.
What is Slow Twitch.
Released and the cross-bridges are bent causing the power stroke that pulls the actin filament.
ADP + P
Explain the importance of recruitment.
Cannot all go at once- all fatigue together. Some are contracting maximally while other are resting
Allows for sustainability
Allows for control of how much strength applied.
Which 2 forms of energy are stored in the muscles?
What are Glycogen & Triglycerides?
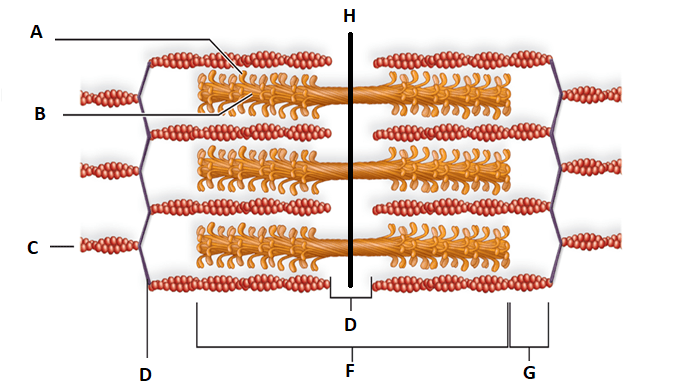
Identifiy F and which filaments does is include?
A band- Both Myosin and Actin filaments