I bands, Z lines, A bands, H zone, and M line.
What are the parts that make up the striation pattern of skeletal muscle fibers?
The source of energy for skeletal muscle contraction for a short time
What is ATP?
Smooth, Cardiac, and Skeletal
What are the three types of muscle in the muscular system?
This action involves a muscle decreasing the angle between two body parts, such as when you bend your elbow.
What is flexion?
This muscle group extends the knee.
What are the quadriceps?
An organ of the muscular system made of skeletal muscle tissue, nervous tissue, blood, and other connective tissue.
What is skeletal muscle?
When exercising extensively lactate develops in the muscle fiber, this is the amount of oxygen that liver cells need to convert the lactate into glucose.
What is oxygen debt?
Both smooth and cardiac muscle move due to impulses not from choice.
What is involuntary movement?
When the forearm rotates so the palm faces upward, this action is referred to as this.
What is supination?
The main muscle stimulated when performing skullcrushers.
These threadlike parts in the sarcoplasm contain protein filaments such as myosin and actin and have a major role in muscle contraction.
What are myofibrils?
This is the term for the process in which the muscle fiber contracts after receiving an action potential, leading to the sliding of actin and myosin filaments.
What is sliding filament theory?
This protein, found in smooth muscle, forms cross-bridges with actin to produce force during contraction, similar to myosin in skeletal muscle.
What is myosin?
This term describes the muscle action that occurs when the body moves in a circular motion, such as when you rotate your shoulder.
What is circumduction?
This muscle, located in the upper back and neck, is responsible for moving the shoulder blades and extending the neck.
What is the trapezius?
This connective tissue layer surrounds each individual muscle fiber and plays a role in transmitting force during contraction.
What is the endomysium?
This occurs when a muscle is exercised strenuously for a prolonged period of time and there is an increased lactic acid production from anaerobic respiration and if pH drops sufficiently,muscle fibers may no longer respond to stimulation.
What is muscle fatigue?
Unlike skeletal muscle fibers, smooth muscle cells have this shape, which helps them contract in a more continuous, sustained manner.
What is a splindle shape?
This term refers to the process of a muscle working in opposition to the primary mover, helping control or slow down a movement.
What is an antagonistic action?
This muscle is responsible for flexing the wrist and fingers and is one of the primary muscles used when gripping objects.
What is the flexor digitorum superficialis?
This specialized organelle within muscle fibers stores calcium ions, which are crucial for muscle contraction and relaxation. This organelle is also a network of membranous channels that surround each myofibril and run parallel to it.
What is a sarcoplasmic reticulum?
This ion is crucial for the release of acetylcholine from the synaptic vesicles at the neuromuscular junction and for the propagation of the action potential in both the motor neuron and the muscle fiber.
What is calcium?
These specialized structures, located at the junctions between cardiac muscle cells, allow for rapid transmission of action potentials, coordinating contraction.
What are intercalated discs?
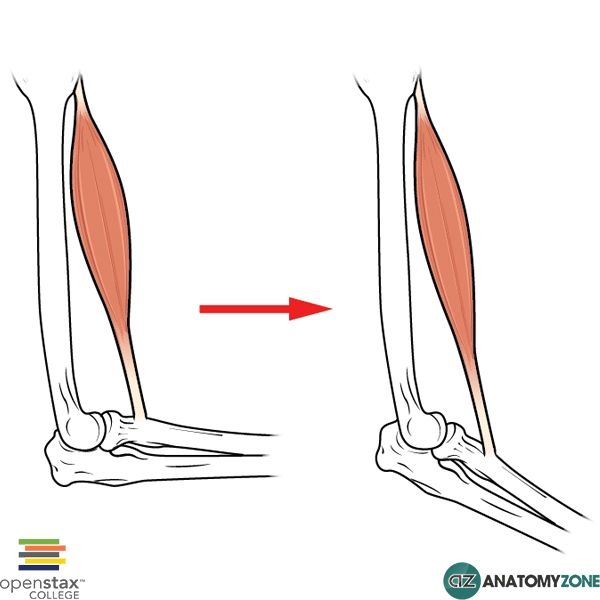
What is isotonic eccentric contraction?
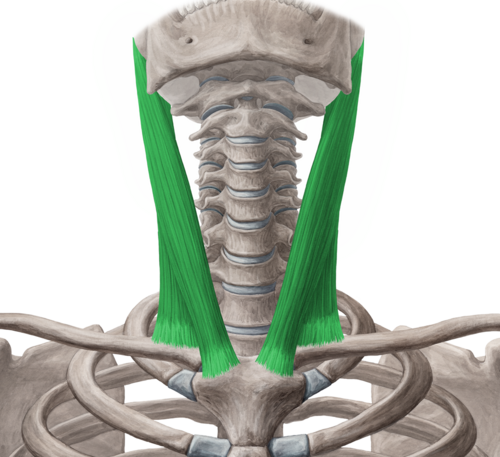
Sternocleidomastiod