This is another name for a skeletal muscle cell
muscle fiber
Each myofibril contains two types of myofilaments. What are these two myofilaments called?
actin and myosin
One neuron and the skeletal muscle it stimulates is called a what?
motor unit
This is a single, brief jerky contraction of the skeletal muscle fiber. It is represented by a single stimulus with one muscle contraction and then relaxation. This is a graded response.
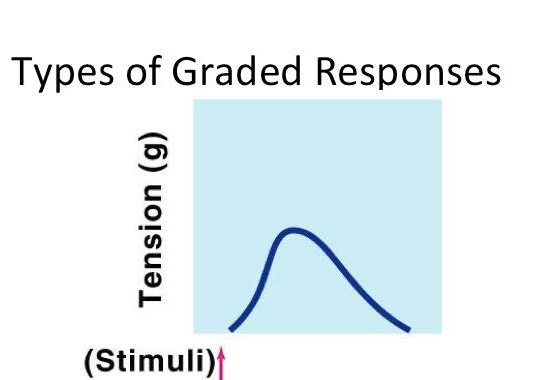
twitch
Resistance exercises that build muscle are also known as what kind of exercises.
isometric
This muscle type is striated and voluntary
skeletal muscle
The plasma membrane of the muscle cell is called the what?
sarcolemma
The long threadlike extensions of a neuron. It is represented by the blue section below.
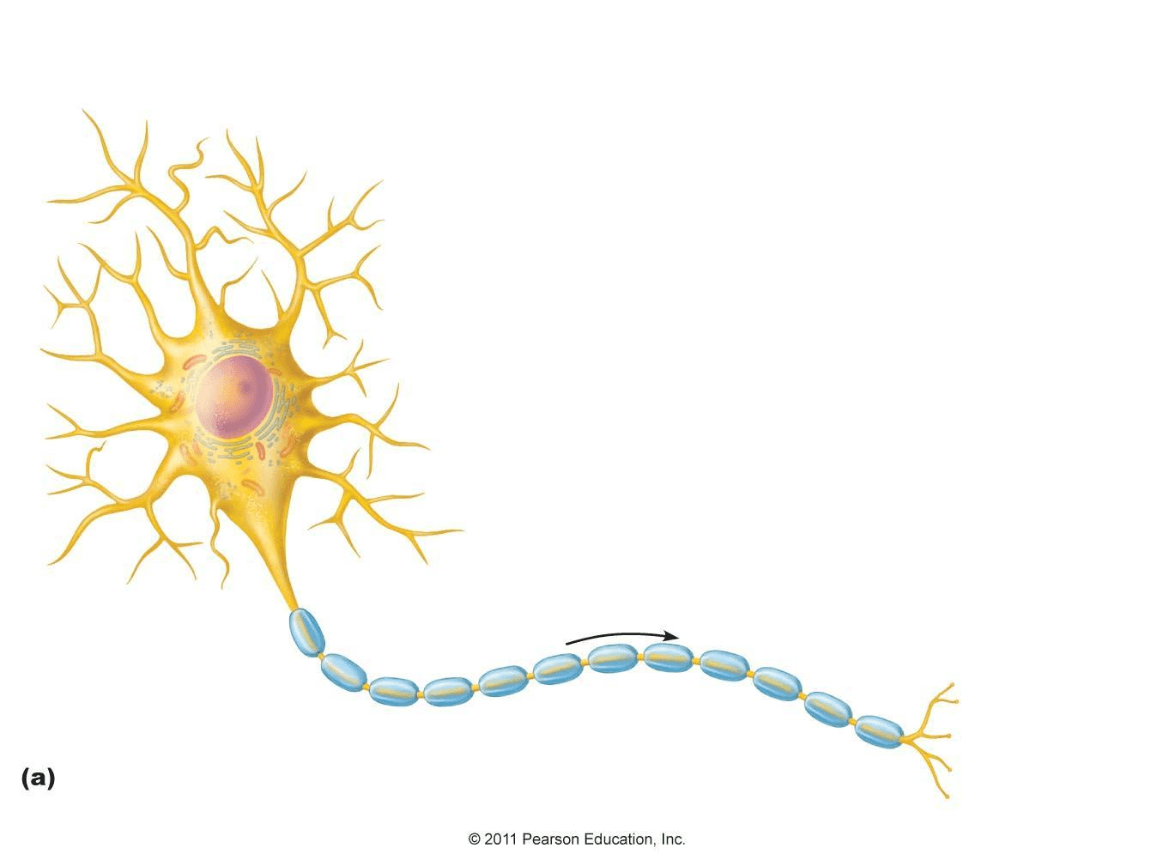
axon
This is a graded response that is involves a smooth contraction without any evidence of relaxation. Results from a very rapid rate of stimulation.
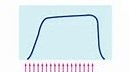
fused or complete tetanus
This aspect of skeletal muscle activity cannot be consciously controlled, but even at relaxation, some muscle fibers are contracting.
Muscle Tone
This type of muscle is mostly in the walls of hollow visceral organs
smooth
Myofibrils are made up of chains of tiny contractile units called what?
sarcomeres
This is the change in electrical potential associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a muscle or nerve cell.
action potential
This way of providing energy for muscle contraction is the only one that provides hours in energy duration. 95% of ATP used for muscle activity comes from this type.
Aerobic respiration
This is the place of muscle attachment where the muscle is attached to the immoveable or less moveable bone
origin
Number 5 points to what? (It is several muscle fibers surrounded by a connective tissue covering, the endomysium)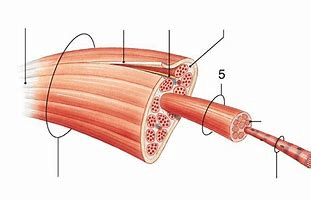
fascicle
This is what we call the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of the muscle fiber
sarcoplasmic reticulum
The neurotransmitter released by the nervous system that stimulates skeletal muscle
acetylcholine
Direct Phosphorylation of ADP uses what high energy molecule to obtain its third phosphate group?
Creatine phosphate (CP)
What body movement is this?
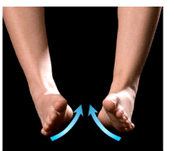
inversion
What connective tissue layer is the arrow pointing to?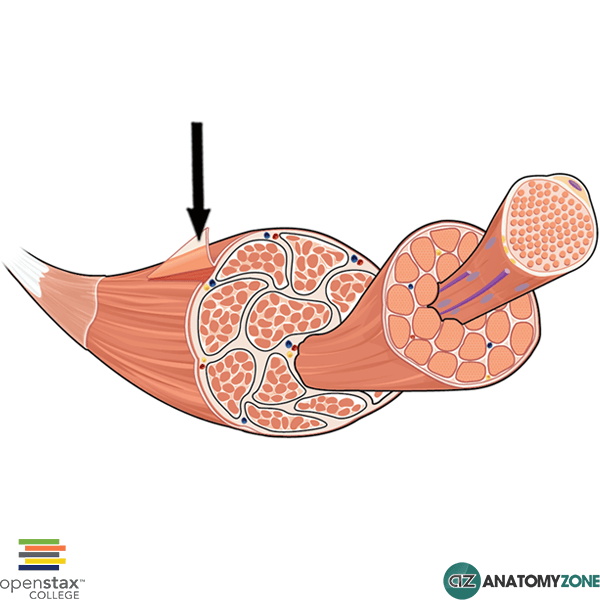
epimysium
What are the dark lines representing in the picture below?

Z line or the Z disc
This is the regulatory protein that actually blocks myosin heads from binding to actin filaments. This is the part that actually blocks the binding site, it is not the part that takes up the calcium ions.
tropomyosin
Under anaerobic glycolysis, the pyruvic acid generated during glycolysis is converted to what in the absence of oxygen?
lactic acid
What body movement is this?
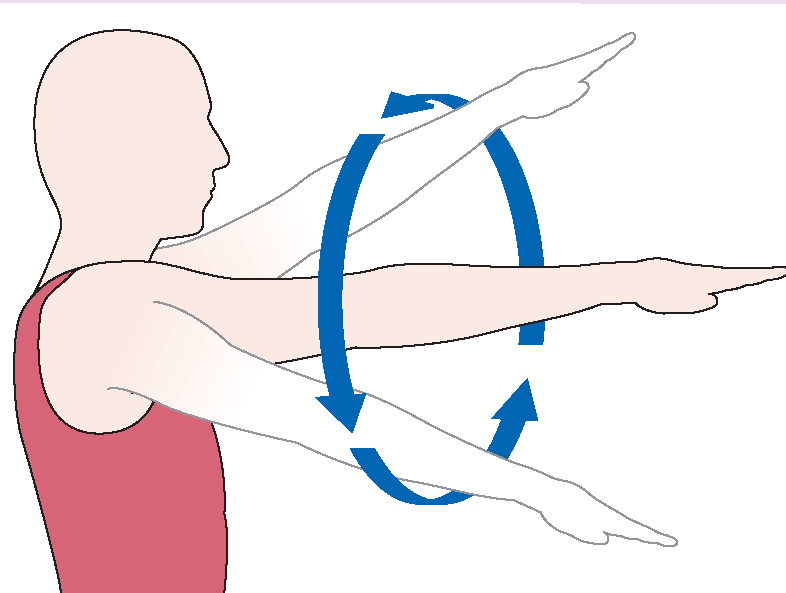
Circumduction