This CT layer covers each individual muscle fiber.
Endomysium
This is the name for the cytoplasm of a muscle fiber.
Sarcoplasm
The sarcomere is the repeating functional unit of skeletal muscle contraction. It is composed of thick and thin filaments made of these 2 proteins.
Thin filament = actin
Thick filament = myosin
The energy currency of the cell
ATP
I have multiple nuclei, striations, and a long cylindrical shape. I function to produce voluntary movement, produce heat, and protect organs.
Skeletal Muscle
This is the fluid filled gap between the axon terminal of a motor neuron, and the muscle fiber it innervates. Neurotransmitters are released in this space.
NMJ
Build up of this waste product from anaerobic respiration is the primary cause of muscle fatigue.
Lactic acid
This prefix refers to flesh.
sarco
This CT layer covers each individual muscle
Epimysium
This fiber-like organelle is made up of repeating subunits of myosin and actin.
Myofibril
This portion of the sarcomere is where thick and thin filaments overlap, and is also called the "dark band" 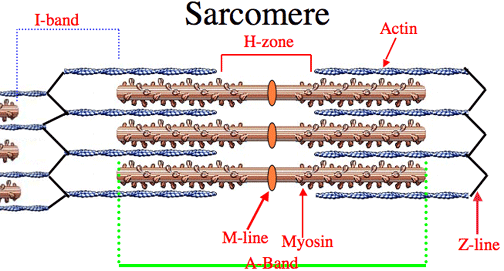
A Band
Sally is running a 10 mile race.This is the most likely pathway her muscles are using for ATP regeneration.
Aerobic respiration
I am uninucleate, have striations, and intercalated discs. I function to pump blood through blood vessels.
Cardiac Muscle
This is the neurotransmitter that stimulates muscle contraction.
Acetylcholine
This term describes the amount of oxygen needed to restore ATP levels back to normal, eliminate lactic acid waste, and restore tissue level oxygen back to normal after intense anaerobic exercise.
Oxygen Recovery uptake
These are arranged so as to give skeletal muscle its striations.
Myofilaments
This is a broad tendon-like sheet of CT that attaches skeletal muscle to muscle, bone, or other tissue like skin.
Aponeurosis
This organelle stores and releases the calcium ions involved in muscle contraction.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
One sarcomere extends from ________________ to ________________, or the points where actin filaments anchor.
Z disc
Where does aerobic respiration take place in the muscle cell?
Mitochondria
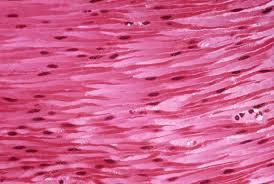
I am the muscle tissue shown here
Smooth Muscle
_______ is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum floods the muscle fiber and binds to troponin in order to expose the active sites on actin filaments.
Calcium
The contraction of some muscle fibers in a relaxed muscle.
Muscle tone
The contractile unit of a muscle cell.
Sarcomere
This CT layer covers each fascicle.
Perimysium
This specialized structure controls what enters and exists the muscle fiber. It is similar to a plasma membrane.
Sarcolemma
Which number represents the I band?
7 - The light band where there are only thin actin filaments.
This molecule that is abundant in muscle tissue can donate a high energy phosphate to ADP in order to generate ATP during brief, but powerful activities.
Creatine phosphate
Muscle that is found in hollow organs, blood vessels.
Smooth
This temporary structure is formed between myosin heads and actin. It is the formation of this structure, and the power stroke of myosin, that causes sarcomere shortening (AKA contraction).
Sliding filament theory
This occurs when a body stiffens and becomes unmoveable after death. It can last up to 72 hours.
Rigor Mortis
Skeletal muscles must connect to at least 2 points. These bones are called the ___ and ____.
Origin and Insertion
This connects muscles to bone.
Tendon
What is the level of organization of muscle from largest to smallest.
Muscle - Fascicles - Muscle fibers or cells - Myofibrils - Myofilaments
When a muscle fiber contracts the sarcomere does this as thin filaments are pulled over thick filaments within the structure.
Shortens
This type of respiration produces lactic acid as a byproduct.
Anaerobic respiration
I am the muscle tissue seen here.
Cardiac muscle
This travels down the motor neuron until the synaptic cleft is reached.
Action potential
Delayed relaxation of skeletal muscles following a voluntary contraction
Myotonia
The state of having one contraction follow another contraction without returning to a fully relaxed state.
Tetanus