response to nervous stimuli
excitability
responds to changes in body's need for oxygen - found in walls of heart. cannot be controlled
cardiac
allows for free and painless flexion and extension of joints
ROM
Bacterial infection resulting in spasms and then paralysis of muscles
tetanus
Which muscle would MOST likely be used to administer a flu vaccination (0.5 mL) to a 22 years old man?
deltoid
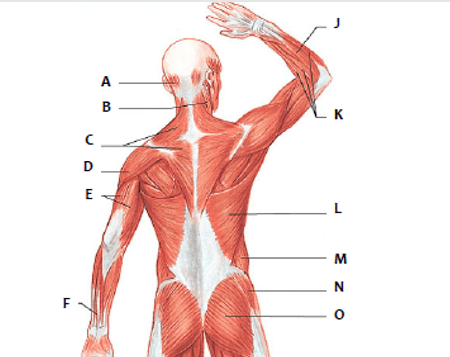
Which muscle is represented by "R"?
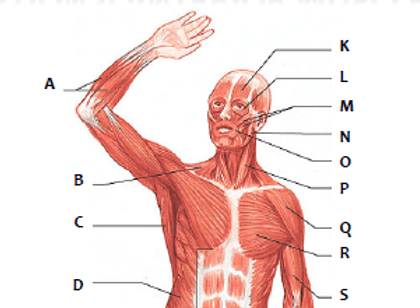
pectoralis
Which muscle is represented by "A"?
occipitalis
shortening and thickening that results in movement
contractability
involuntary responds to the autonomic nervous system; non-striated. cannot be controlled
visceral or smooth
circular movement turning a body part on its axis
circumduction
results from excessive stretching of a muscle
Which muscle would MOST likely be used to administer a flu vaccination to a 9 months old infant?
vastus lateralis or rectus femoris
Which muscle is represented by "P"?
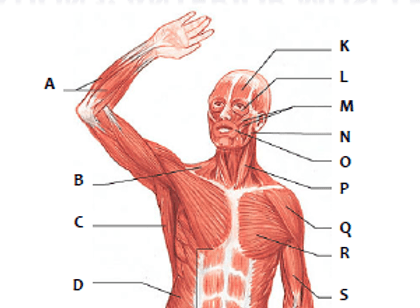
sternocleidomastoid
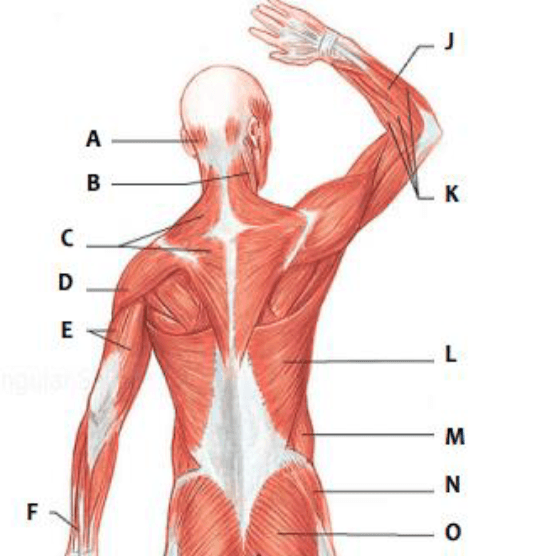
Which muscle is represented by "E"?
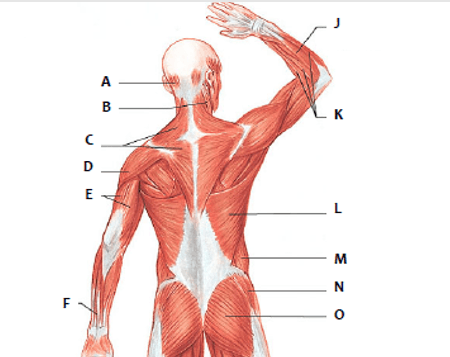
triceps
allows muscle to return to original shape after movement
elasticity
striated; contracts quickly and tires easily. can be controlled
skeletal or voluntary
results in a decrease in the angle between body parts
flexion (bending)
results in muscular weakness and eventual paralysis, is genetic and occurs more frequently in young boys
muscular dystrophy (Duchenne's type)
paralysis of these muscles, between the ribs, may result in death
intercostal muscles
Which muscle is represented by "L"?
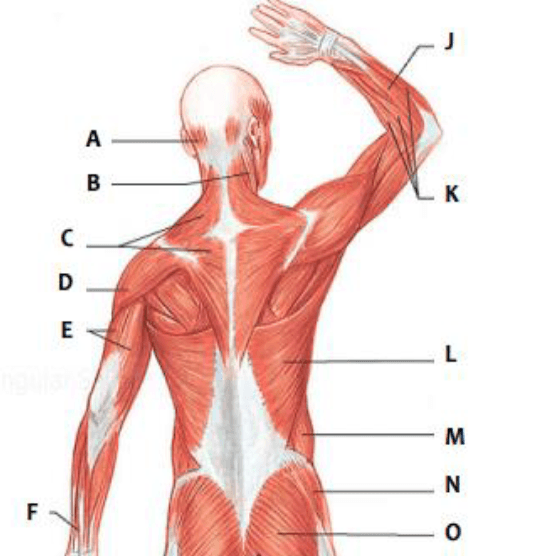
latissimus dorsi
Which muscle is represented by "C"?
trapezius
muscle stretching
extensibility
ability to produce heat and energy
skeletal muscles
results in straightening of a body part
extension
occurs when muscles shorten and thicken permanently due to lack of use
contractures
when a muscle attaches to a bone, the end that does not move is known as the ____
origin
Which muscle is represented by "F"?
sartorius
Which muscle is represented by "Q"
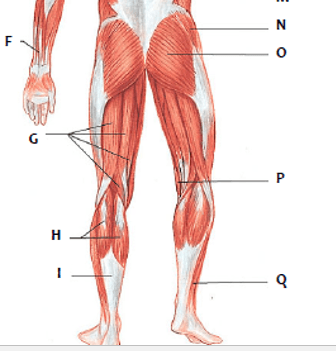
peroneus longus
type of muscle that contracts in unison or at the same time
cardiac
TWO methods of muscle attachment to bone and stabilization
tendons and fascia
body part is moved towards the midline or midsagittal plane
adduction
disorder that affects the sternocleidomastoid muscle
torticollis
osteoporosis
Which muscle is represented by "V"?
gastronemius
Which muscle is represented by "P"
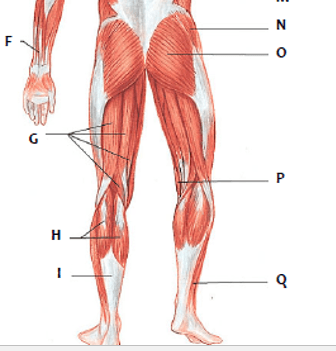
sartorius