This muscle group covers the humerus bone
What is: The Biceps
What structure connects muscle to bones?
What is: Tendons?
Muscle groups work in _________ pairs in order to get the body to move. (fill-in-the-blank)
What is: antagonistic
What is the longest muscle in the human body?
This muscle group covers the front of the femur
What is: The Quadriceps?
Muscle groups attach to at least 2 points. What do we call the point that does not move for stability?
What is: The Origin?
What do we call the muscle group that initiates a movement?
What is: Agonist
What do you call a bundle of muscle fibers?
What is: A fascicle?
Which muscle group is highlighted below?

What is: The Trapezius
What is the thick protein filament in muscle fibers?
What is: Myosin?
What do we call the space where neurons connect with muscle fibers to initiate movement?
What is: The Neuromuscular Junction?
What do we call it when myosin pulls on actin towards the center of the sarcomere?
What is: Power Stroke?
Which muscle group is highlighted in the image below? (It is part of the forearm)
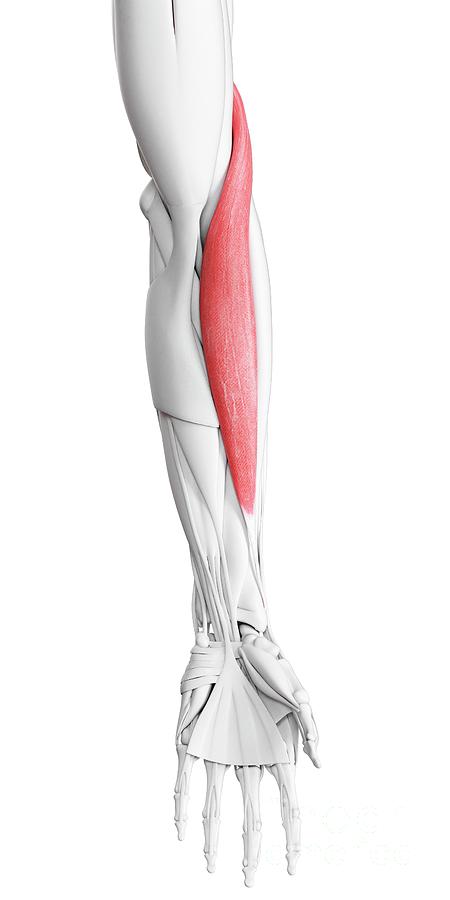
What is: The Brachioradialis
What is the following image a diagram of?

What is: Sarcomere?
Name 2 things muscle fibers need in order to contract
Acceptable Answers:
Neurotransmitter, Acetylcholine, Calcium, Power Stroke, Sodium, Potassium, ATP, Energy
What is the technical term for muscle growth and what do you call muscle growth that adds sarcomeres to our muscle fibers?
What is: Hypertrophy and Myofibrillar Hypertrophy?
Which tendon is highlighted in the image below
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13642/Achilles_tendon.png)
What is: The Achilles Tendon?
What do we call the connective tissue that covers fascicles?
What is: Perimysium?
What is the Sliding Filament Theory?
Once muscle fibers receive input from neurons, myosin filaments latch on to actin filaments and pull on them, causing the sliding motion that generates muscle contraction. (any similar response works)
When the biceps contract, the triceps ______ (finish the sentence)
What is: relax?