Terms used for the hand and finger deformites below. It is often seen with rheumatoid arthritis.
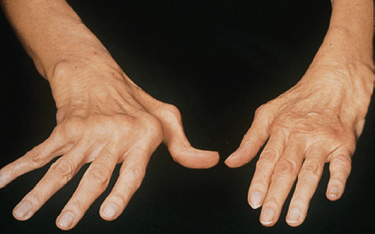
What is ulnar deviation and swan neck deformity.
This is the term for the abnormal shortening of a muscle, joint, or both.
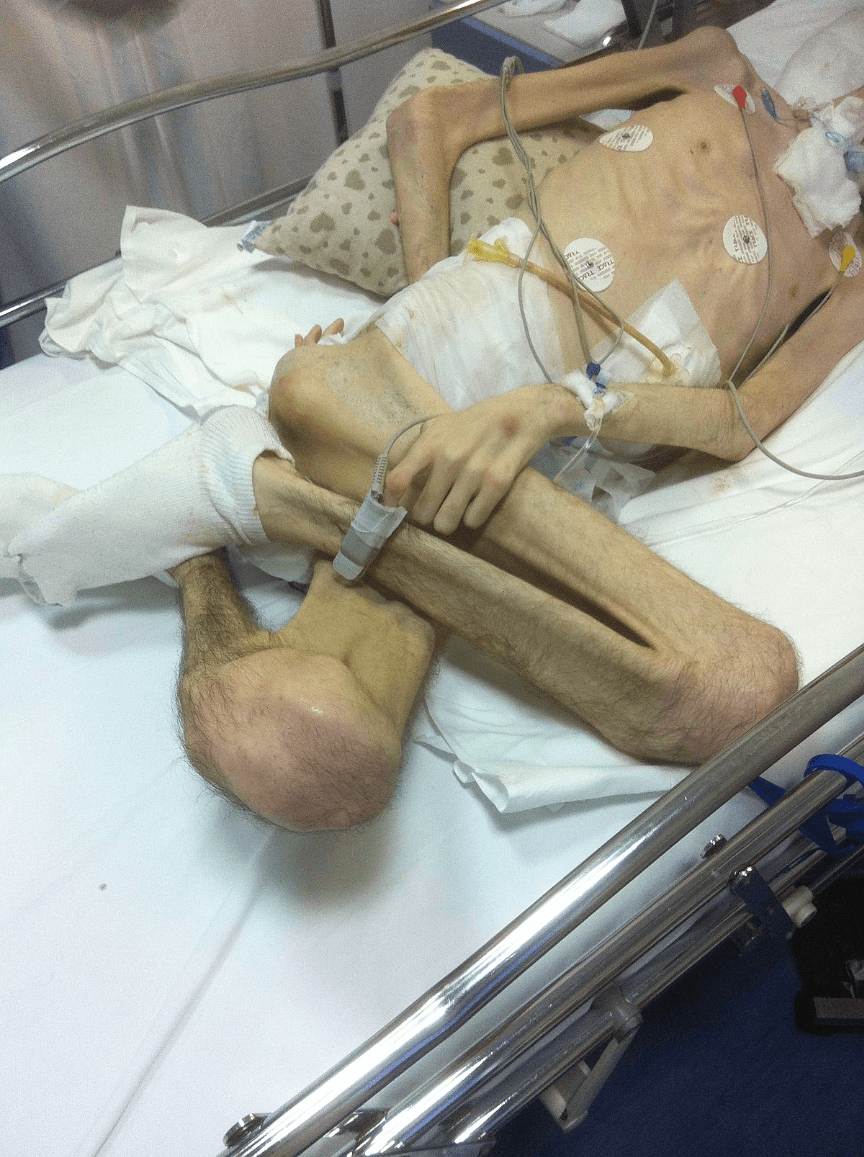
What is a contracture?
This is dense fibrous connective tissue whose purpose is to connect muscles to bone.
What is a tendon?
This is the medical term used for numbness and tingling, often described as "pins and needles."
What is paraesthesia?
These are short band of tough, flexible, fibrous connective tissue which connects bone to bone. They provide stability while allowing controlled movement at joints.
What are ligaments?
These hip movements should be avoided after the patient has had a surgical replacement of the joint (3 out of 4).
What are adduction, internal or external rotation, flexion greater than 90 degrees?
One of three major muscle types. It is a form of striated muscle tissue, which is under the voluntary control of the somatic nervous system. It accounts for half of the human's body weight.
What is skeletal muscle?
Dietary sources of this vitamin, which plays a major role in calcium absorption and bone health, include fortified milk and cereals, egg yolks, saltwater fish, and liver.
What is Vitamin D?
People who are unable to engage in regular weight-bearing activities, such as those on prolonged bed rest or those with some physical disabilities, have increased bone resorption from calcium loss, and their bones become _______ (reduced in terms of mass) and weak.
What is osteopenic?
This type of joint is freely movable. Examples are the ball and socket joints and hinge joints.
What are synovial (diarthrosis) joints?
The movement which allows the arm to move away from the midline.
What is abduction?
This procedure allows direct visualization of a joint through the use of a fiberoptic endoscope. Biopsy and treatment of tears, defects, and disease processes may be performed The procedure takes place in the operating room under sterile conditions with either injection of a local anesthetic agent into the joint or general anesthesia.
What is arthroscopy?
These bone cells function in bone formation by secreting bone matrix.
What are osteoblasts?
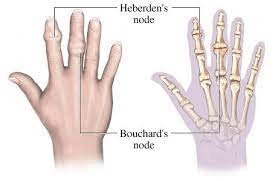 Heberden's nodes are small bony growths that appear at the finger joint closest to the tip of the finger. Bouchard's nodes, a similar symptom, appear at the finger's middle joint.
Heberden's nodes are small bony growths that appear at the finger joint closest to the tip of the finger. Bouchard's nodes, a similar symptom, appear at the finger's middle joint.
These nodes are symptoms of of the hands.
What is osteoarthritis?
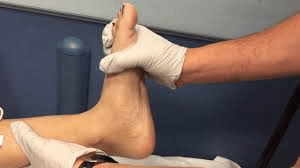 This is the term for the rhythmic contraction of the ankle. It can be elicited by forceful sustained dorsiflexion of the foot by the examiner.
This is the term for the rhythmic contraction of the ankle. It can be elicited by forceful sustained dorsiflexion of the foot by the examiner.
What is clonus?
This is a lateral S-shaped curvature of the thoracic and lumbar spine.
What is scoliosis?
Long bones are comprised of two ends, called the __________ and the shaft, called the ________________.
What are the epiphyses and the diaphysis?
These are small sacs of synovial fluid. They are found at bony prominences or joints to relieve pressure and decrease friction between moving parts.
What are bursae?
Electromyography (EMG) provides information about the electrical potential of the ______ and the nerves leading to them.
What are muscles?
The dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA or DEXA)
is used to evaluate this.
What is a bone mineral density (BMD)?