The term used for inflammation of *just* the cortical bone.
What is osteitis.
A possible cause for a growth retardation lattice in a calf.
What is bovine viral diarrhea virus.
*Growth retardation lattices are just in the metaphysis. If this calf had the entire medullary cavity affected, that would be osteopetrosis - this can be congenital (i.e. genetic) or acquired (i.e. viral). Both are due to osteoclast dysfunction.
What is synovial hyperplasia.
Or: capsular fibrosis, osteophytosis, pannus formation
The type of muscle necrosis expected with ischemic muscle injury (of any category).
What is non-selective necrosis.
The causative agent of wooden tongue.
The width growth of bone is achieved by this type of ossification.
What is intramembranous ossification.
The underlying cause for Ricket's.
What is hypovitaminosis D.
What is the most likely route of infection in this bone from a foal?
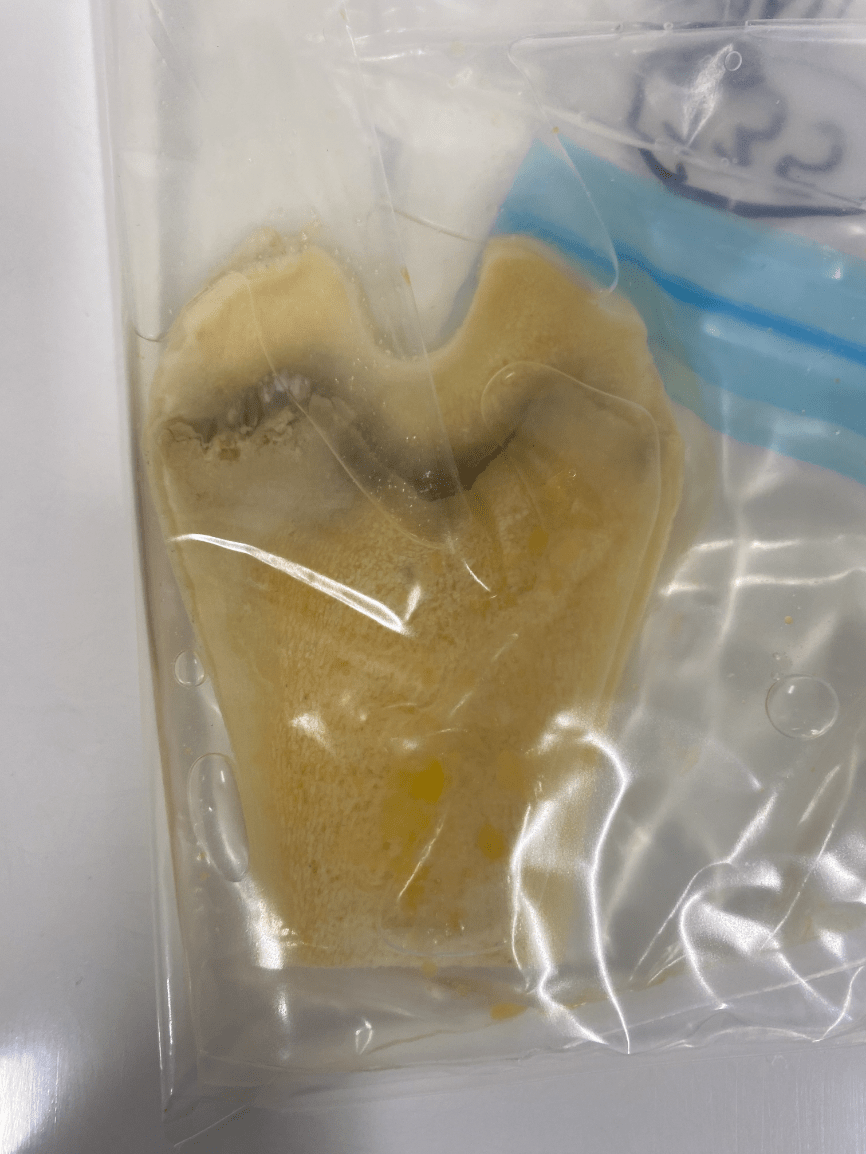
What is hematogenous.
*This is suppurative physitis and so hematogenous is the #1 route for physeal infections.
What is fibrosis.
Vitamin E deficiency in pigs can cause changes in skeletal muscle and which other organ?
What is the heart (mulberry heart disease).
The typical route of infection in a horse with "pigeon fever".
What is direct muscle injury (due to penetrating foreign body or injection).
What type of fracture is present here?

What is articular.
*Note the lack of physis* If this were in a skeletally immature animal, this would be a Salter-Harris type III because it involves the epiphysis.
The expected serum chemistry change in renal secondary hyperparathyroidism.
What is hyperphosphatemia (or hypocalcemia).
The causative agent of diskospondylitis in dogs.
What is Brucella canis.
In this form of myasthenia gravis, the patient will have reduced numbers of acetylcholine receptors.
What is congenital myasthenia gravis.
Which species is highly susceptible to ionophore toxicity?
What is the horse.
Biopsy from the semimembranous muscle of an adult Fresian (draft breed) horse with extertional myopathy finds PAS positive, digestion resistant inclusions in skeletal muscle. The gene mutated in this disease.
What is GLYS1 (equine polysaccharide storage myopathy).
What is the first phase of secondary bone healing?
What is a hematoma.
The mutated gene in "spider lamb" syndrome.
What is FGF3R.
The most likely disease in an 8 month old German shepherd puppy that presents with lameness and multiple enostoses within the diaphysis of the humerus (similar to that shown below).
What is panosteitis.
Cachexia related to cancer will typically result in this type of muscle atrophy.
What is symmetric muscle atrophy.
A recently captured antelope voids dark red urine prior to death. Which "muscle" is not affected?
What is the heart.
Capture myopathy can develop myoglobinuria which can damage renal tubules --> ATI due to pigment nephropathy
The disease in a dog with bilateral temporalis and masseter muscle atrophy and plasmacytic myositis on biopsy.
What is masticatory myositis.
*This disease is antibody driven and so has plasma cells > lymphocytes on biopsy
What is the term used to describe nodular bone proliferation that extends outward from the cortical surface?
What is exostosis.
The underlying cause of epiphysiolysis in pigs.
What is osteochondrosis.
The underlying pathogenesis of immune-mediated polyarthritis.
What is deposition of immune complexes within the synovium.
*the causes of Ag-Ig complexes falls into 1 of 4 categories: 1) Breed related, 2) SLE-related, 3) reactive to systemic disease/adverse drug reactions and 4) idiopathic.
Healing after selective necrosis occurs because this cell type is not affected.
What are satellite cells.
What is hypoglycin A.
DAILY DOUBLE:
The vector that carries this protozoa which forms onion-cysts in a skeletal muscle in dogs.
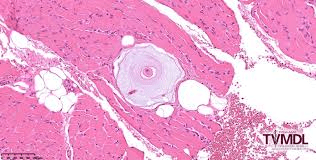
What is the tick Amblyomma maculatum.