This is is characterized by chronic inflammation of the airways and hyperresponsiveness of the bronchial smooth muscles (bronchospasm).
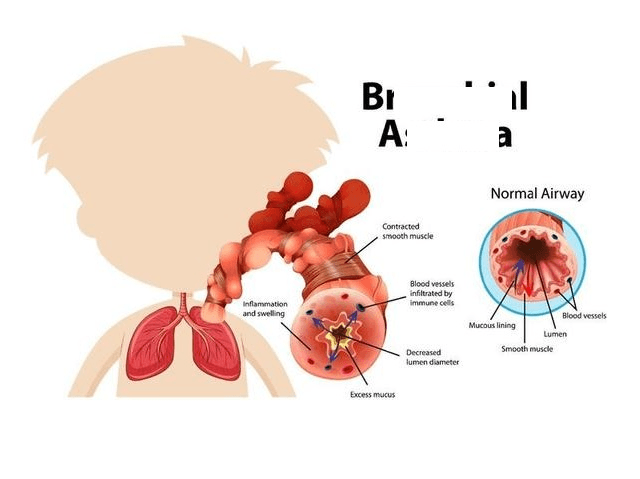
What is asthma?
This is the most common type of arthritis, affecting more than 30 million people in the United States. It is otherwise referred to a degeneratyive joint disease?

What is osteoarthritis?
This is a chronic, progressive, systemic inflammatory disease that destroys synovial joints and other connective tissues, including major organs.

What is Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
These ABG values represent this acib-base imbalance.

What is respiratory acidosis?
This procedure is done by performing a linear excision through the eschar to the superficial fat that allows for expansion of the skin and return of blood flow or chest expansion.
What is an escharotomy?
This technique reduces the risk for infection when performing pin care.

What is aseptic technique.
This assessment is done to detect abnormalities like decreased or absent pulses, cool skin temperature, and dusky color show circulation problems. Numbness and tingling, decreased sensation, and mobility show neurologic changes.

What is Neurovascular checks, or neurovascular status assessment?
 This procedure involves the insertion of a needle into the pleural space and is commonly done to aspirate fluid trapped in the pleural space.
This procedure involves the insertion of a needle into the pleural space and is commonly done to aspirate fluid trapped in the pleural space.
What is thoracentesis?
This is a condition where lungs collapse partially or completely. Mild cases show no signs and symptoms, but might develop breathing difficulty when it spreads.
What is atelectasis?
It is an opacity in the lens of the eye that may cause a loss of visual acuity.

What is a cataract?
When an “attack” of gout occurs, the patient has severe pain and inflammation due to the accumulation of this material in one or more small joints, usually the great toe.

What are uric acid crystals?
Elevating the head of bed to 30 degrees or more when a tube feeding is infusing will prevent this complication.

What is aspiration pneumonia?
This is a disorder of the inner ear that can lead to dizzy spells (vertigo) and hearing loss.
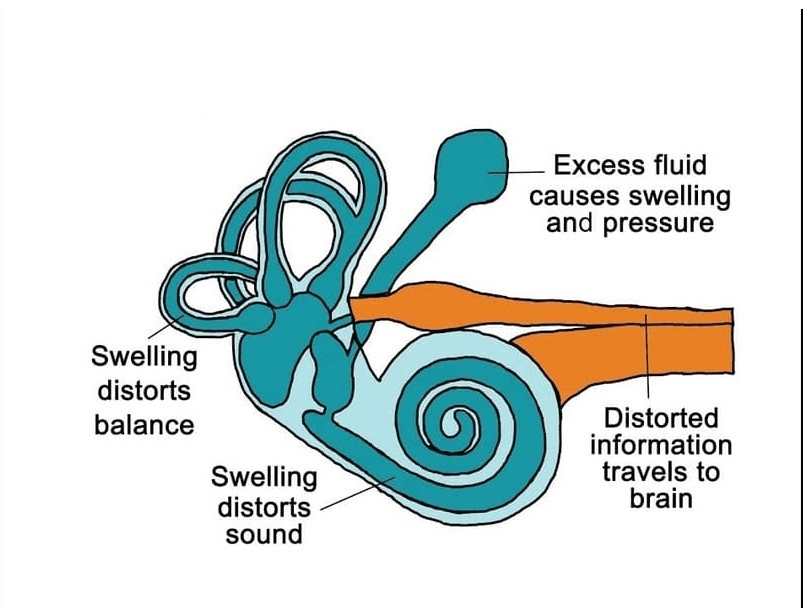
What is Meniere's disease?
This is the greatest threat to life in a patient with a major burn injury because it causes edema in the respiratory passages.

What is is smoke or heat inhalation?
It is a group of diseases that damage the optic nerve.
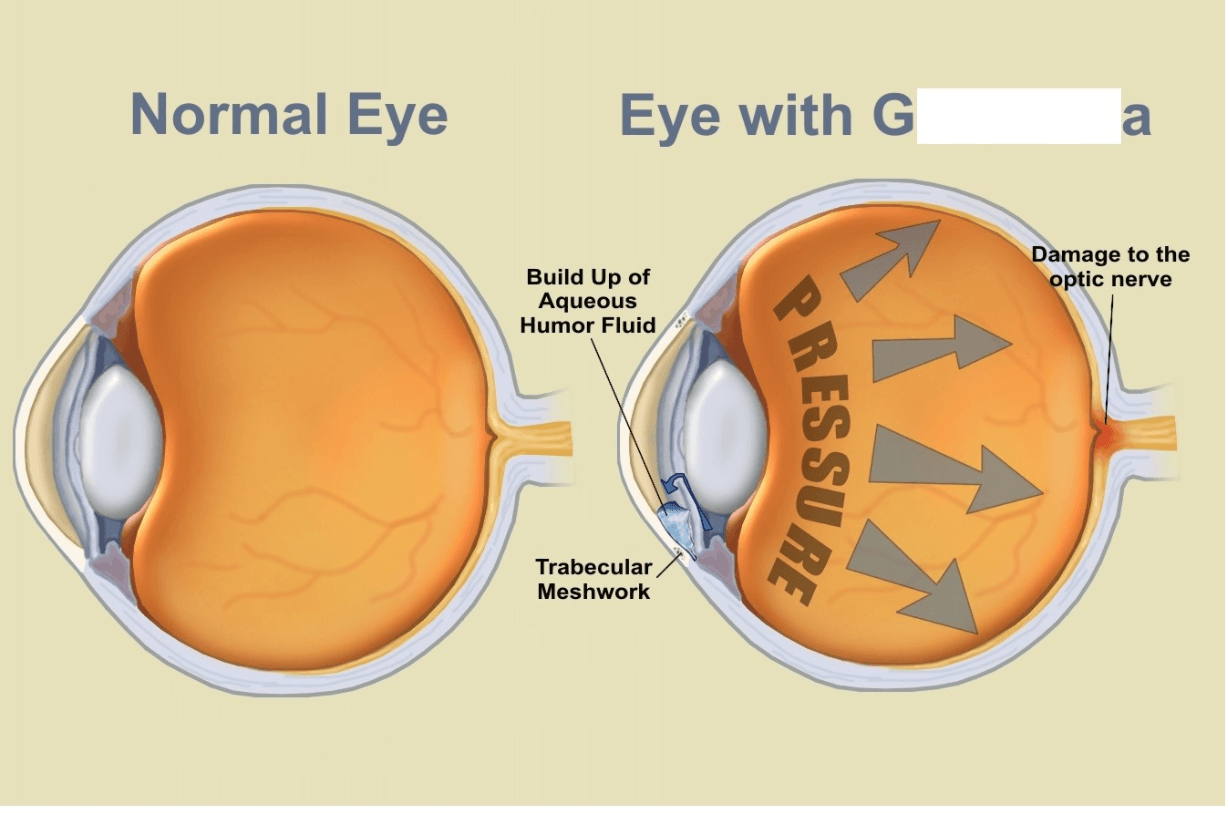
What is glaucoma?
This surgical procedure is done by direct visualization through a surgical incision. The fractured bone ends are reduced (aligned) and held in place by internal fixation devices such as metal plates and screws or by a prosthesis with a femoral component similar to that used for total joint replacement.

What is open reduction with internal fixation?
A shrinker sock or bandage is commonly used on the residual limb in order to promote this.
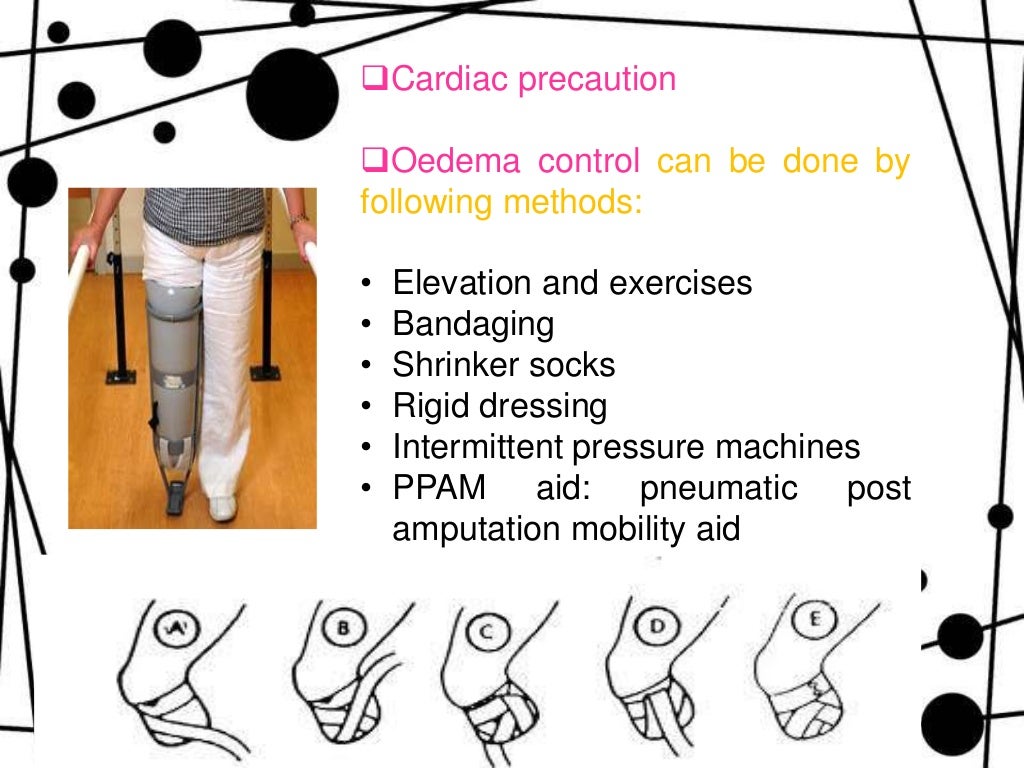
What is decrease swelling and prepare the residual limb for the prosthesis?
Mechanisms of this disorder incude: Inflammation and fibrosis of bronchial wall; hypertrophied mucus glands leading to excess mucus leading to obstructed airflow; loss of alveolar tissue leading to decreased surface area for gas exchange; loss of elastic lung fibers leading to airway collapse.

What is COPD?
This tansmission-based precaution is used for infections related to Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB), rubeola virus (measles), varicella-zoster virus (chickenpox), and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) for aerosol generating procedures.

What is airborne precautions?
It is the most common type of skin cancer. This tumor is mainly seen on sun-exposed areas of the body, appearing as a small pearly or translucent papule with a rolled and waxy edge, depressed center, telangiectasia (lesion formed by dilation of vessels), crusting, and ulceration

What is basal cell carcinoma?
This orthopedic complication is dangerous and is often characterized by these symptoms:
- Pain (severe, unrelenting, and increased with passive stretching)
- Paresthesia (painful tingling or burning)
- Pallor (but there may be warmth or redness over the area)
- Paralysis (late symptom)
- Pulselessness (late and ominous sign)
- Poikilothermia (temperature matches environment; i.e., the extremity is cool to touch).

What is compartment syndrome?
This musculoskeletal injury complication occurs when small fat droplets are released from yellow bone marrow into the bloodstream. The droplets then travel to the lung fields, causing respiratory insufficiency.
What is fat embolism?
This type of fracture is one in which the broken ends of the bone are shattered into many pieces.
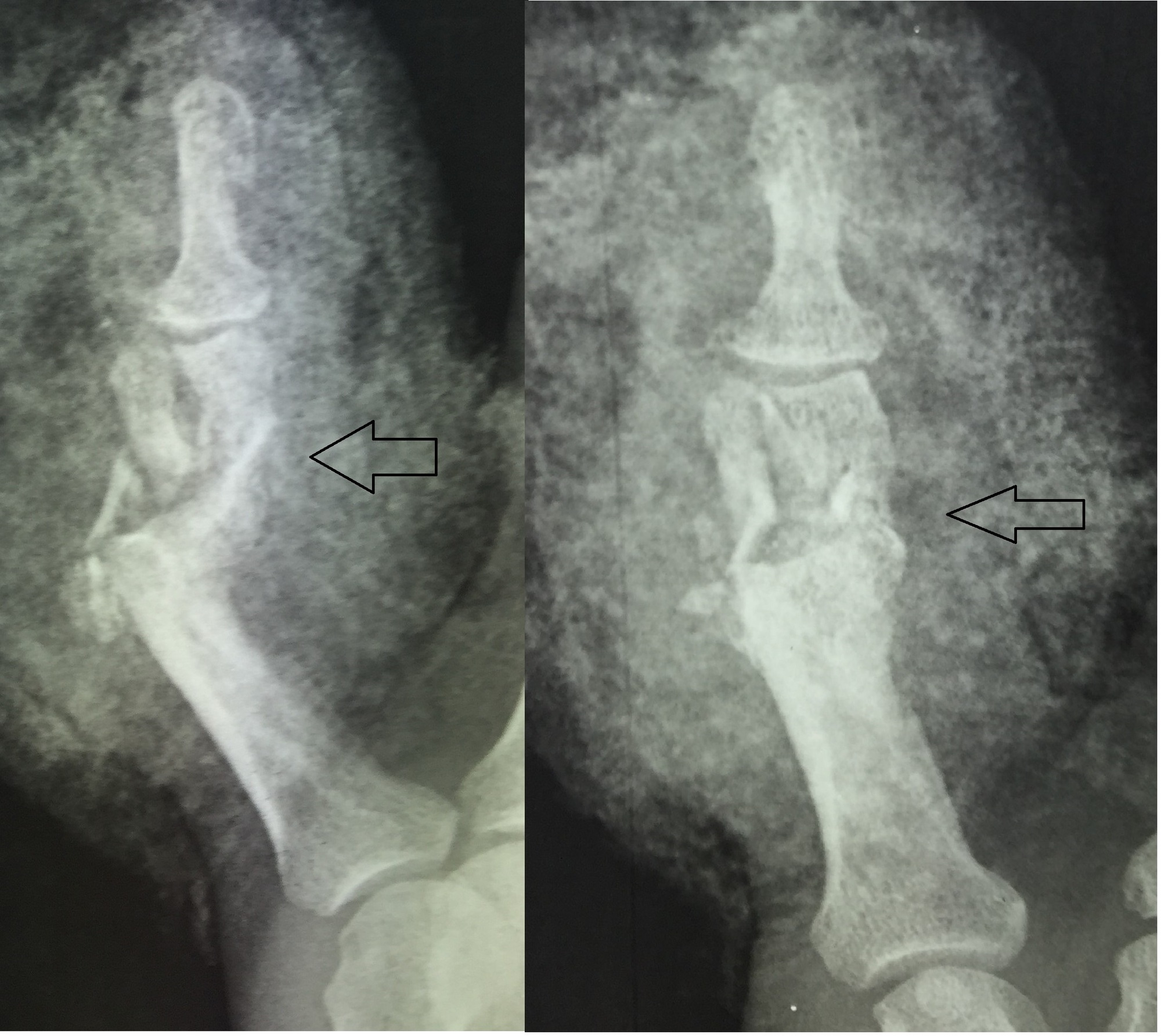
What is a comminuted fracture?
This transmission-based precaution is used against Adenovirus, coronavirus (COVID-19), diphtheria (pharyngeal), Haemophilus influenzae (epiglottitis, meningitis, pneumonia), influenza, mumps, mycoplasma pneumonia, Neisseria meningitidis (meningitis, pneumonia, pertussis, pneumonic plague, rubella, group A streptococcus)
What is droplet precautions?
This form of skin cancer arises from the epidermis. It can occur on sun-exposed areas of the skin and mucous membranes, mainly seen on the lower lip, neck, tongue, head, and dorsal surfaces of the hands. The lesion appears as a single, crusted, scaled, eroded papule, nodule, or plaque.

What is squamous cell carcinoma?