A client's serum osmolarity is >300. Blood would be considered:
What is hemoconcentrated?
The greatest determinant of serum osmolality
What is serum sodium NA+ ?
3 Methods in which enteral feedings can be administered
What are Continuous feedings,Cyclic feedings and Intermittent feedings?
These methods are most reliable for verification of N/G tube placement
What is:Initial x-ray (only once)Gastric pHGastric residualVerification before each tube feedingLocation where tube is inserted
The 2 elctrolytes that need to be monitored when a client is diagnosed with hypoparathyroidism
What is hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia?
The type of urine output expected when a client's serum sodium is 156mEq/L.
What is decreased urine output?
This type of IV fluid solution has the same osmolality as blood(serum)
What is isotonic solution?
Clients with swallowing disorders, a functional GI system,high risk for aspiration or has a disease that prevents or limits food absorption may require:
What is enteral nutrition?
The following are normal levels for:
135-145 mEq/LL
3.5-5 mEq/L
8.5-10.6 mg/dL
1.6-2.6 mEq/L
2.5-4.5 mEq/L
What is:
Na+
K+
Ca2+
Mg2+
PO4-
This electrolyte disorder is the most common
What is Hyponatremia serum Na+ less than 135 mEq/L
Sometimes fluid in the human body moves to an area that makes it physiologically unavailable
What is Third Spacing?
The most common IV fluid administered for most hydration needs
What is 0.9% Sodium Chloride (0.9%NSS)?
There are several vital assessments a nurse would perform prior to insertion of a nasogastric tube
What are:Verify the order(suction or no suction)Assess nares for patentcy(ask client to hold each nares one at a time and breathe)Select the nostril with good air flowAssess LOC and gag reflex
These baseline lab studies should be assessed before starting enteral tube feedings with clients
What are serum glucose BUN and electrolytes?
Tachycardia,flat neck veins,tacypnea and poor skin turgor are clinical manifestations related to:
What is fluid voume deficit?
Substances that carry an electrical charge (positive or negative) and are measured in mEq/L
What are electrolytes?
Urine,Diarrhea,Ostomy/gastric drainage have something in common
What are Sensible fluid losses?
The best position for a client prior to insertion of a nasogastric tube
What is high Fowlers position?
A client's HOB will be elevated to a certain degree for tube feedings during and post-feeding.
What is 30-45o unless contraindicated?
The nurse anticipates a client with a serum Phosphorous of 7.1 mEq/L to have a symptom related to their calcium level
What is Tetany?
This category of IV fluids are solutes that readily dissolve,for instance 0.9% Sodium Chloride
What are crystalloids?
When there is a low fluid volume in the vascular system, increased amounts of this hormone is released to compensate
What is ADH-Anti Diuretic Hormone?
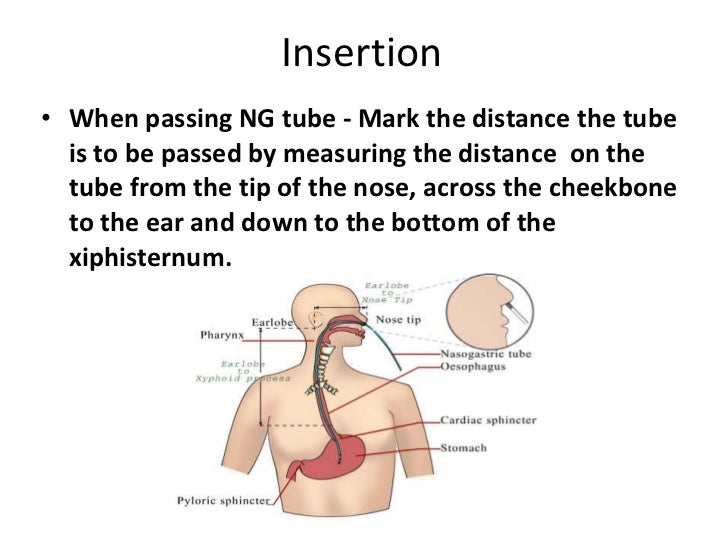
This type of measurement needs to be conducted prior to nasogastric tube placement
This step needs to be taken prior to administering oral tablets to a client with a gastric tube.
What is:Verify if tablets can be crushed If tablets can be crushed use 15-30mL of water for each tabletGive each tablet separatelyFlush tube before giving med with 30mL sterile water,flush tube after each med with 30mL sterile water
The precautions that would be taken for a client with a serum sodium of 117 mEq/L, or 168 mEq/L
What are seizure precautions