Mechanism of Action for Metformin
First line treatment for DM type II. This medications lowers blood glucose without causing hypoglycemia. It is described as an insulin sensitizer.
This medication reduces hepatic production of glucose (gluconeogensis), decreases intestinal absorption of glucose, and enhances insulin sensitivity. In the intestines it increases the anaerobic glucose metabolism in the intestinal cells, leading to reduced net glucose uptake and increased delivery of lactate to the liver.
It is excreted in the kidney. Renal clearance of metformin is 3.5 times higher than cr clearance, which shows that renal tubular secretion os the major route of metformin elimination. WATCH those Kidneys!!
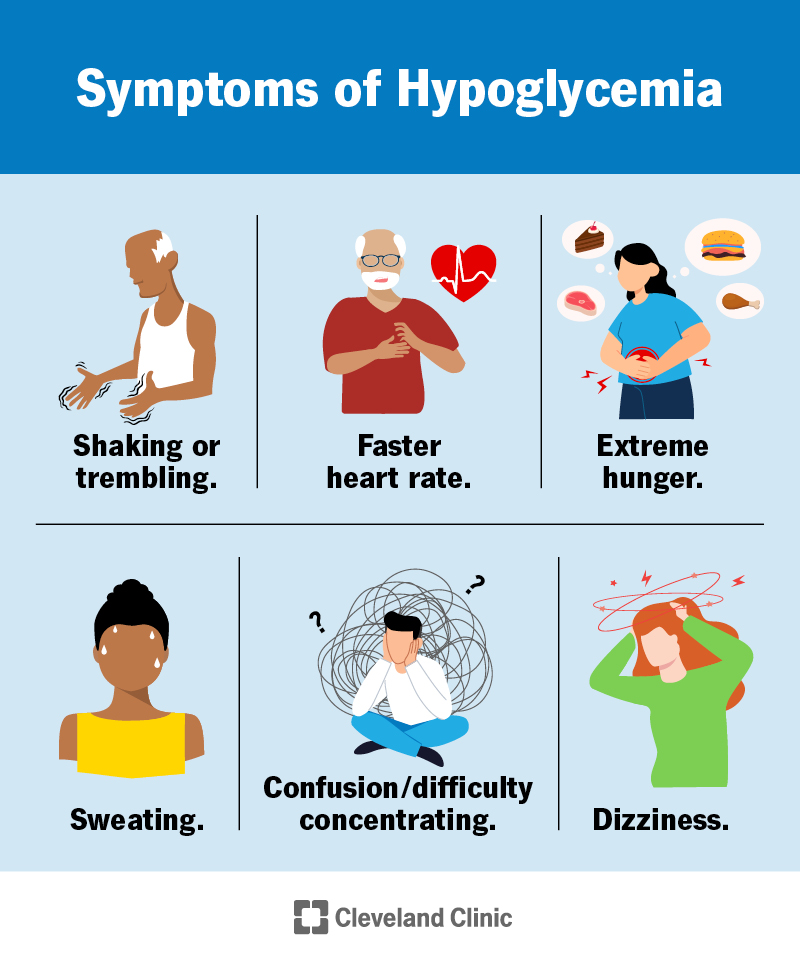
Assessment of Hypoglycemia
<70 mg/DL
Rule of 15 (explain this)
Assessment - Shaking/trembling, diaphoresis, tachycardia, confusion, hungry, fatigue, lack of concentration, and anxiety

Nursing Interventions for back problems
Prevention is KEY
ergonomics - how to sit at a desk, lift objects
Eat right
exercise
BMI stable



Discuss how cognition is affected in this unit
Concepts: Metabolism, Mobility, Health Systems
Exemplars: Diabetes, Thyroid Disease, Osteoporosis, Back Problems, Hip Fractures, Fractures, Parkinson Disease, Access to Care
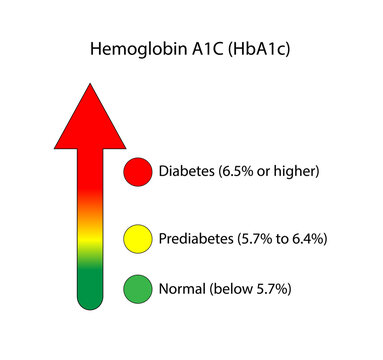
Hemoglobin A1C
it is a blood test that shows the average blood sugar (glucose) level over the past 2-3 months.

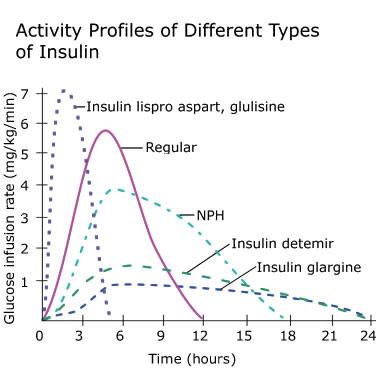
Discuss the difference between Bolus and Basal Insulins - Onset, Peaks, and Duration
Concentration in US is 100 units per mL (U100)
Rapid - Bolus, O: 5-15 mins, P: 1-2H, D: 4-6H
Regular- Bolus; O: 30m-1hr, P: 2-4h, D: 6-8H
NPH-Basal; O: 1-2H, P: 4-6H, D: 12H
Long - Basal; O: 1.5-2H, P:plateaus and flat action, D: 12-24H
Assessment of hypothyroidism
Brain fog, mental health issues, thinning hair, eyebrow thinning, peripheral neuropathy, jaundice, goiter, HTN, heart attack risk, slow metabolism (obese), gallstones, stomach bloating, heartburn, constipation, dry skin, menstrual changes, weakness, cold intolerance, decrease sweating, irritable, brittle nails
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Hypothyroidism-hyperthyroidism-5180646_final-82b76c2edd074f59aa005f72ba2a3994.jpg)

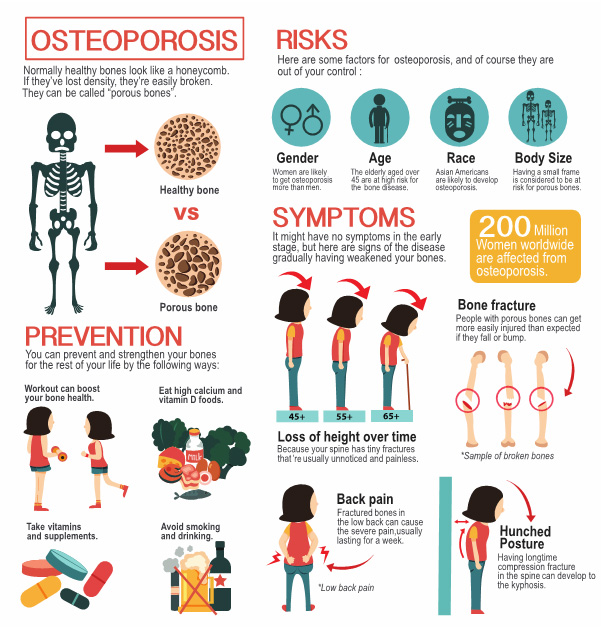
Nursing Interventions for Osteoporosis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK568781/
Causes
Osteoporosis involves the process of osteoblast and osteoclast function. In primary osteoporosis, osteoblast activity slows while osteoclast activity.[1] Normally, these two functions are balanced but become imbalanced with aging due to changes in hormones. Secondary osteoporosis can occur due to prescribed glucocorticoids.
Assess - age, menopausal, female, ethnicity, smoking, medication Rx., alcohol consumption, ht loss, and kyphosis, small frame.
wt bearing exercises -
Medication Rx - bisphosphanates (alendronate) increase bone density, Hormone related tx (calcitonin)
assist with DME and teach on each one
assist with self care
OT/PT
diet high in calcium and vit D
Limit smoking and alcohol


discuss how oxygenation can be affected in this unit
Concepts: Metabolism, Mobility, Health Systems
Exemplars: Diabetes, Thyroid Disease, Osteoporosis, Back Problems, Hip Fractures, Fractures, Parkinson Disease, Access to Care
Bone Density studies (Discuss def and nursing priorities)
DISCUSS CONTRAST and how this can affect the CT result and what a nurse should be concerned with?
A bone density test determines if you have osteoporosis — a disorder characterized by bones that are more fragile and more likely to break.
The test uses X-rays to measure how many grams of calcium and other bone minerals are packed into a segment of bone. The bones that are most commonly tested are in the spine, hip and sometimes the forearm.
DISCUSS CONTRAST and how this can affect the CT result and what a nurse should be concerned with?
What are the medications listed for the Incretin Enhancers? What are the differences between these medications?
- Incretin Enhancers- peptide hormones produced by special cell types of the intestines, which are secreted following the ingestion of foods, by then decreasing postprandial blood glucose levels that participate in regulation of glucose homeostasis.
- GLP-1 (albiglutide, ecenatide, dulaglutide, liraglutide)--> incretin hormones GLP-1 , increase the insulin synthesis and release from the pancreatic beta cells. GLP-1 lowers glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells leading to reduced hepatic glucose production.
- Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP-4)- (alogliptin, linagliptin, stgaliptin)--> Prolongs the action of incretins. Increases insulin secretion and reduces glucagon secretion by preventing the inactivation of glucagon like peptide (GLP-1).
Assessment of Hyperthyroidism
weight loss, short or light menstrual periods, puffy or bulging eyes, heat intolerance, tachycardia, diarrhea, fatigue, hair loss, insomnia,
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Hypothyroidism-hyperthyroidism-5180646_final-82b76c2edd074f59aa005f72ba2a3994.jpg)
Nursing Interventions for Hip Fractures
Assess Hip and type of surgery
Assess falls
Assess needs for DME
Interventions
- Walker
-PT
-OT
-prevention of DVT
-Implement Abductor pillow
-reposition for skin-surgery interventions (breathing, infection, and ...)
-offer pain management



discuss nutrition throughout this unit
Concepts: Metabolism, Mobility, Health Systems
Exemplars: Diabetes, Thyroid Disease, Osteoporosis, Back Problems, Hip Fractures, Fractures, Parkinson Disease, Access to Care
Thyroid panel (def and nursing priorities)
TSH, T3, and T4
To evaluate thyroid gland function related to the primary cause of hypothyroidism and assess for congenital disorders, tumor, and inflammation. To monitor the effectiveness of thyroid replacement or suppressant therapy.
Interfering Factors
Factors that may alter the results of the study
- Drugs and other substances that may increase TSH levels include amiodarone, antithyroid medications, iodide-containing medications and radiographic medium, lithium, lovastatin, methimazole,metoclopramide, morphine, propranolol, and TRH.
- Drugs and other substances that may decrease TSH levels include acetylsalicylic acid, amiodarone, anabolic steroids, carbamazepine, corticosteroids, glucocorticoids, heparin, and thyroid hormones.
Levothroxine is used for what? What labs do you monitor? Any nursing assessment priorities for this medication?
Treat hypothyroidism - TSH (increase) T3 and T4 (decrease). It is synthetic T4
Watch for s/sx og Hyperthyroidism (Thyroid storm)
take on an empty stomach 30m-1H before breakfast
Avoid Soybean, papaya, and grapefruit
Dietary fiber reduces T4 bioavialibility
Assessment of Hyperglycemia
Polyuria, polyphagia, polydipsia, weakness, fatigue, dry skin, blurred vision, sleep after eating, nausea, sores not healing, HOT

Nursing Interventions for Hypoglycemia
Rule of 15
Discuss how infection can occur or can increase complications through this unit
Concepts: Metabolism, Mobility, Health Systems
Exemplars: Diabetes, Thyroid Disease, Osteoporosis, Back Problems, Hip Fractures, Fractures, Parkinson Disease, Access to Care
swallow studies (def and nsg care)

Definition
Barium swallow, also known as esophagography, is the radiographic or fluoroscopic examination of the pharynx and the fluoroscopic examination of the esophagus after ingestion of thick and thin mixtures of barium sulfate.
This test, is commonly performed as part of the upper GI series, is indicated for patients with history of dysphagia and regurgitation. Further testing is usually required for a definitive diagnosis.
After the barium is swallowed, it pours over the base of the tongue into the pharynx. A peristaltic wave propels it through the entire length of the esophagus in about 2 seconds. When the peristaltic wave reaches the base of the esophagus, the cardiac sphincter opens, allowing the barium to enter the stomach. After passage of the barium, the cardiac sphincter closes. Normally, it evenly fills and distends the lumen of the pharynx and esophagus, and the mucosa appears smooth and regular.
Fast after MN
usually takes 30 mins
will drink mictures through the exam
they will be tilted various ways on a tab;e
withhold H2 blockers and PPIs
remove jewerly
make sure to encourage LARGE amounts of fluid after to expel barium
stools will be milky, chalky, or light colored for 24-72 hrs
contraindicated if abd distention and/or absent stools (barium impaction)
Mechanism of Action for Calcium Salts? What are a THREE top assessments for a nurse to complete?
Calcium Carbonate, Calcium Chloride, Calcium gluconate, calcium phosphate
Calcium is essential in cardiac function, muscle contratction, coagulation of bloodm and maintaining structural integrity of cell membrances. It also is important for bone and teeth.
Might not be used in hypothyroidism
assess for renal and cardiac function
assess for s/sx of hypercalcemia - frequent urination, thirst, fatigue, bone pain, HAs, N/V, constipation, decrease appetite, forgetfulness, depression and irritability.
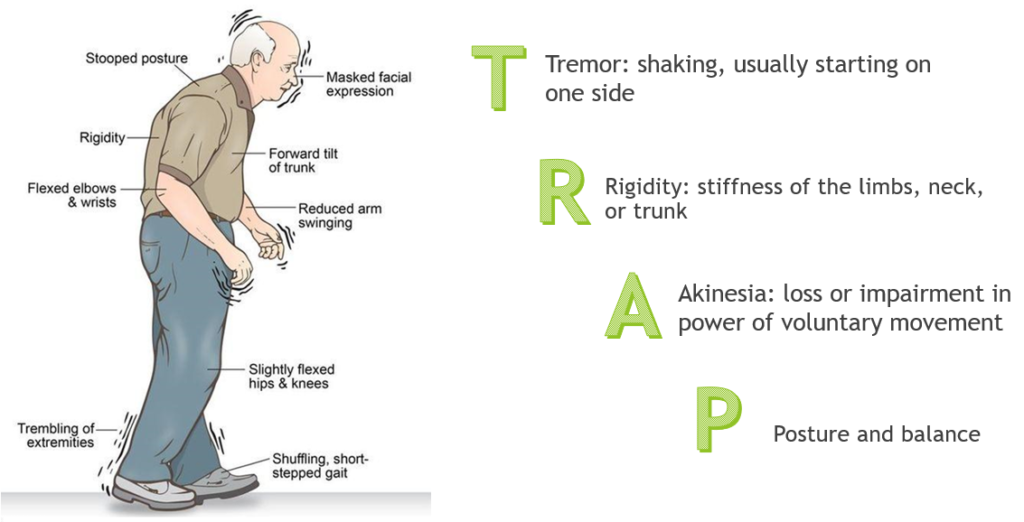
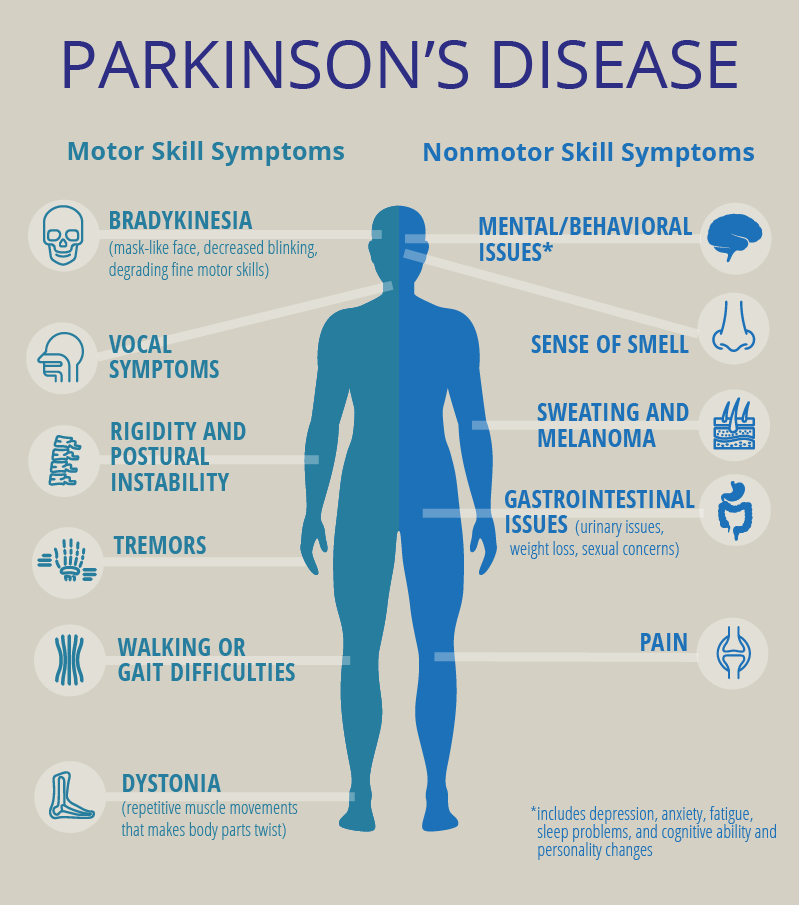
Assessment of parkinsons
bradykinesia, vocal symptoms, swallowing issues, rigid posture, tremors, walking or gait issues, dystonia (repetitive movements), mental or behavioral, sweating, GI changes, wt loss, urinary inc.,
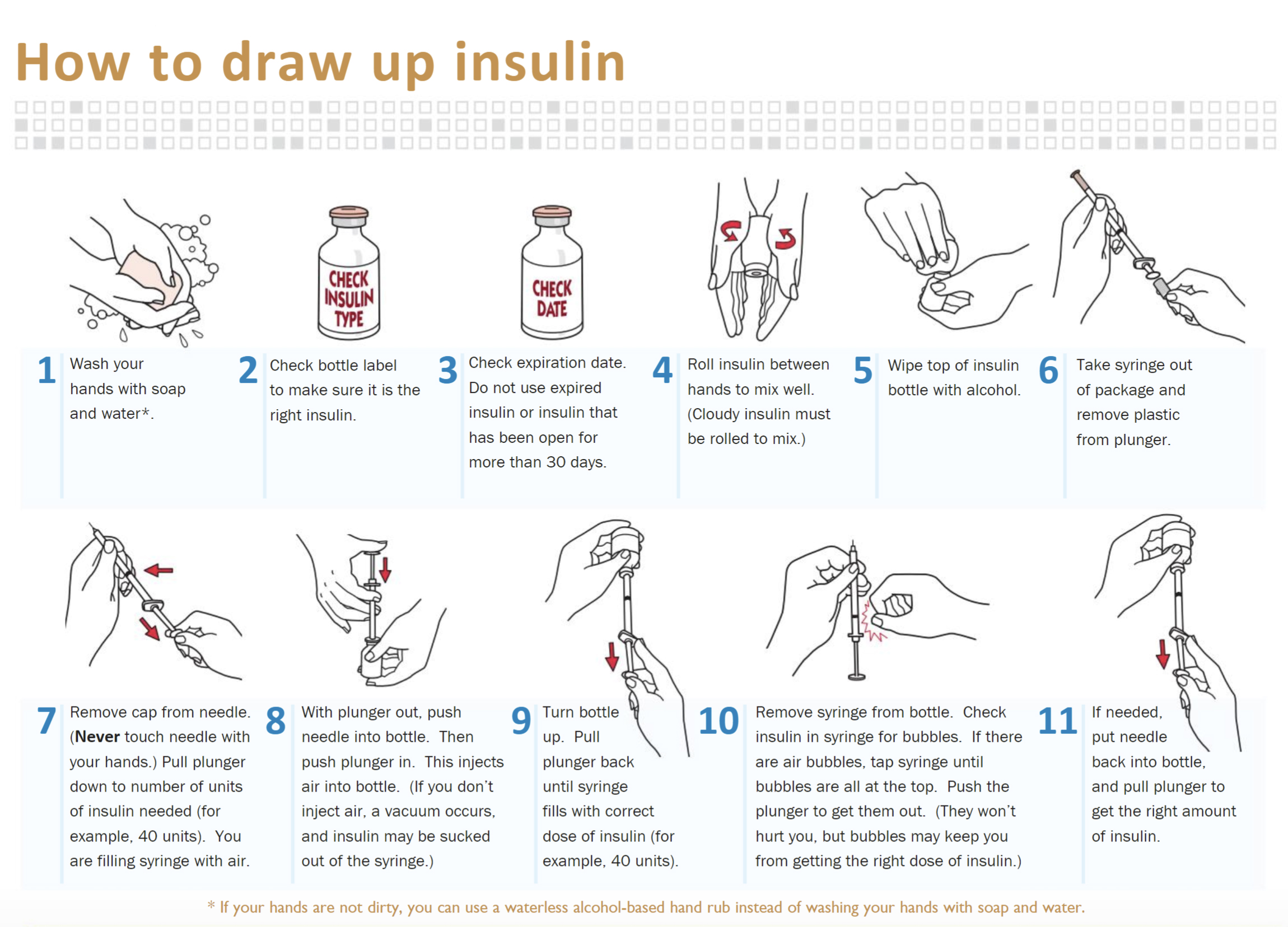
Nursing Interventions for Insulin management
EDUCATE each insulin and O, P, D
EDUCATE when to offer a snack
EDUCATE which foods to eat and avoid
EDUCATE on rotating sites
EDUCATE on hyper and hypoglycemia
EDUCATE on rolling the insulin (no shacking vial)
EDUCATE on expiration
EDUCATE on refrigerating when not using
EDUCATE on absorption rate of insulin according to location administered in
educate on how to draw up insulin
educate on clear to cloudy


Discuss leadership/delegation that can occur through this unit
Concepts: Metabolism, Mobility, Health Systems
Exemplars: Diabetes, Thyroid Disease, Osteoporosis, Back Problems, Hip Fractures, Fractures, Parkinson Disease, Access to Care
BUN and Creatinine (discuss why these labs are monitored in THIS unit)
and why the Kidneys
and ....