What do we use a pedigree for?
To track traits within a family
What do we call any change in the nucleotide sequence?
A (genetic) mutation
What is an adaptation?
A trait that turned out to be beneficial, allowing organisms to reproduce and pass that trait on to their offspring.
Which type of substitution mutation causes sickle cell anemia?
A missense mutation (changes a glutamate to a valine)
What is a dominant allele?
A "loud" allele that hides recessive alleles.
How many females are shown in the following pedigree?
8
What category of mutations substitute one or more nucleotides with the same number of nucleotides?
Substitution mutations
Babies who have a small birthweight may die from losing heat too fast, while babies who are too large can die from becoming stuck in the birth canal. Therefore, the ideal birthweight (and the birthweight that will be selected for) is somewhere in the middle. What type of selection is this?
Stabilizing Selection
The mutation that leads to sickle cell anemia involves only one amino acid being changed in the protein. How many codons on mRNA are affected by this mutation?
ONE
What is a recessive allele?
A "quiet" allele, you only see it if there are NO loud dominant alleles.
What is the genotype for individual II-5 in the following AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT pedigree?
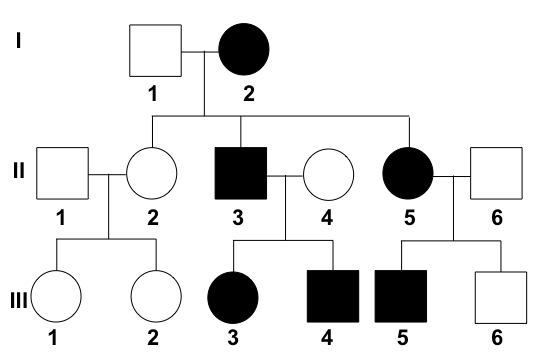
Heterozygous
Which type of substitution mutation changes a codon from one amino acid to another amino acid?
A missense mutation
In giraffes, having a short neck makes it more difficult to reach food, while giraffes with longer necks are able to reach higher branches. Therefore, giraffes with longer necks survive longer and reproduce more, and longer necks become more common. Which type of selection is this an example of?
Directional Selection
Sam has the genotype HbAHbS
Molly has the genotype HbAHbA
Al has the genotype HbSHbS
Who has sickle cell anemia?
Al has sickle cell anemia because is homozygous recessive (has both of the mutated, recessive alleles that cause sickle cell.)

What does it mean for an organism to be heterozygous?
This pedigree shows what type of inheritance pattern?
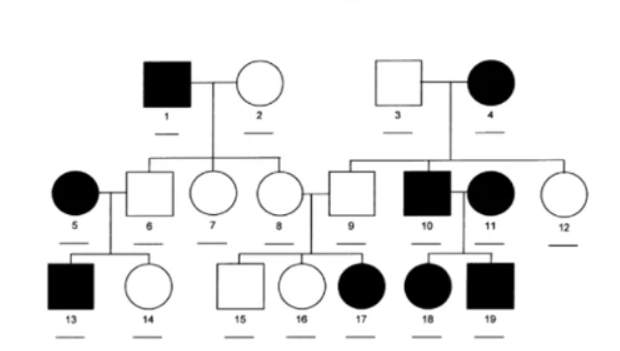
Autosomal recessive

Which type of substitution mutation changes an amino acid to a stop codon?
The image below illustrates which type of natural selection?
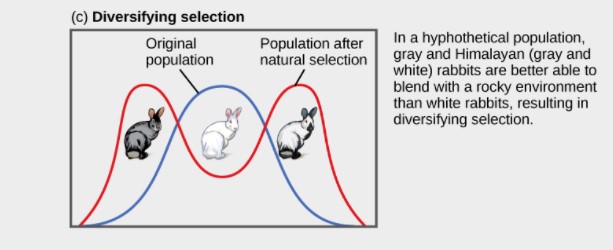
Disruptive Selection
In areas where malaria is endemic (regularly occurring), which genotype would be MOST favorable for individuals to have?
Heterozygous (a dominant and a recessive allele)
If two heterozygous organisms reproduce, what is the likelihood of their offspring showing the dominant trait?
75%
What is the relationship between individuals III-4 and II-2?
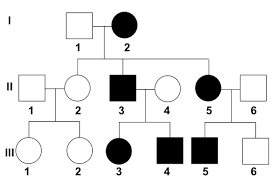
II-2 is III-4's Aunt
III4 is II-2s Nephew
An insertion or a deletion of a nucleotide both cause which type of mutation?
A frameshift mutation.
In an environment where there are light colored birch trees and both light and dark colored moths exist, which trait would be favored and what kind of selection would we expect to see?
The environment would favor the light colored moths, resulting in directional selection.
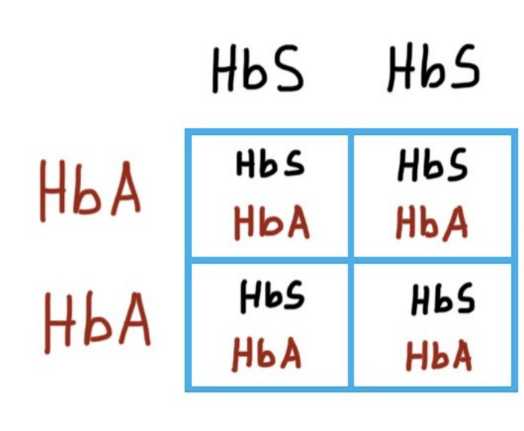
To not have sickle cell, the offspring cannot be HbSHbS and to not be suceptible to malaria, they cannot be HbAHbA. Therefore, we are looking for heterozygous offspring. To have all heterozygous offspring, the parents must be
HbAHbA and HbSHbS
If a homozygous dominant individual reproduces with a heterozygous individual, what is the likelihood one of their offspring would show the recessive trait?
0%. It's impossible because the homozygous dominant individual can only pass down dominant alleles, and the dominant alleles will cover the recessive ones.