This is the process where organisms that are better adapted (suited) to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring.
What is Natural Selection?
All of these are examples of evidence for natural selection except this one:
a. The fossil record
b. Embryos
c. Homologous Structures
d. Acquired (not inherited) traits
What are Acquired Traits?
Modern horses evolved from Eohippus. This is what happened to the size of horses as they evolved over time. 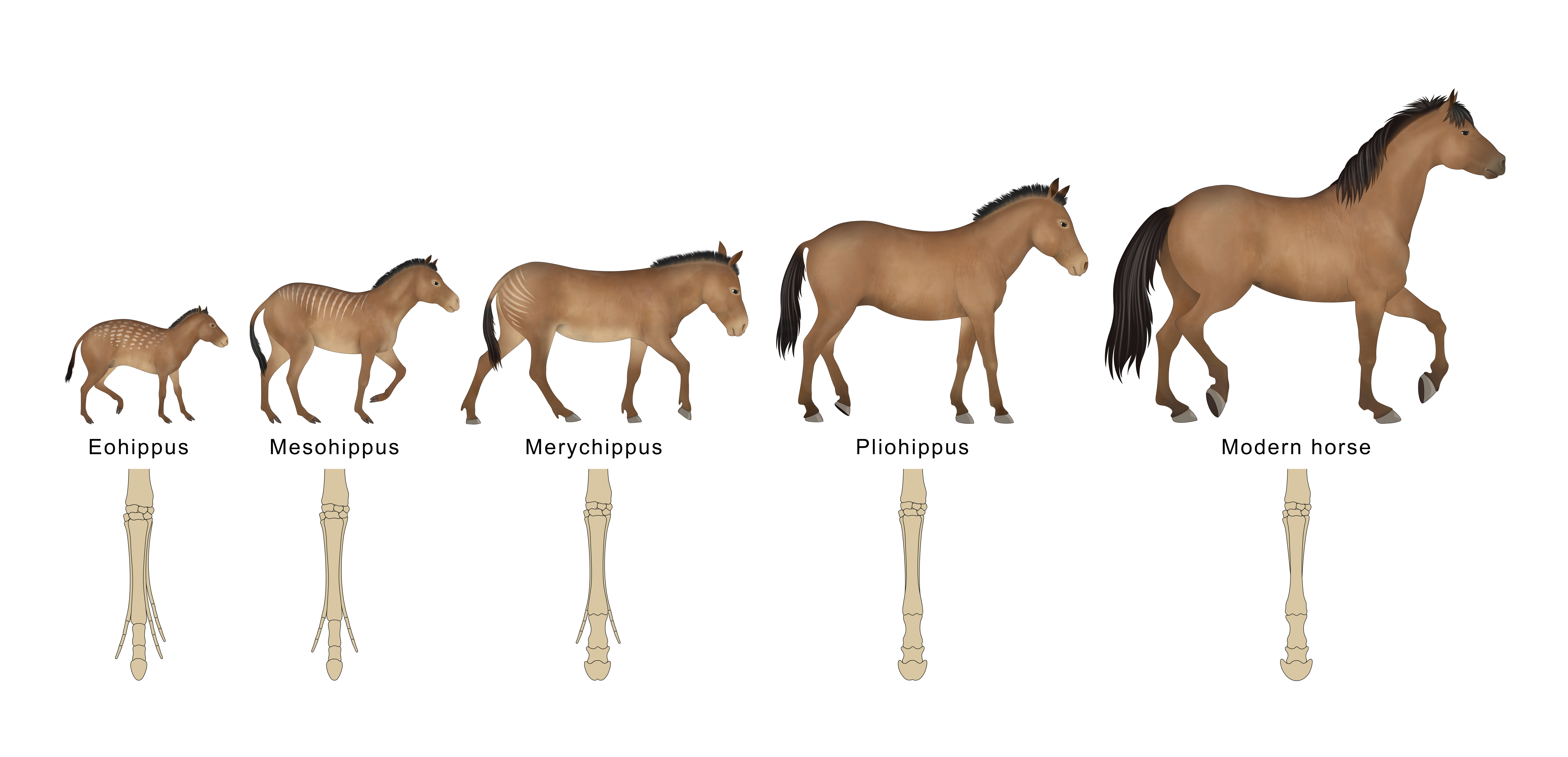
They got bigger (they grew)
This word is used to describes organisms who have a similar bodily structure even though it might serve different functions in each species. (like flying for chickens and running for cats)
What is a homologous structure?
This is a physical or behavioral characteristic (a trait) of an organism that enhances its ability to survive and reproduce in its environment.
What is an Adaptation?
This is the process where humans choose and enhance specific traits in plants and animals, also known as selective breeding.
What is Artificial Selection?
This term refers to the study of how embryos develop from a single fertilized egg.
What is embryology?
Based on the image below: The trilobite is located at layer B. This layer or layers is/are older than layer B. (Which layer or layers is/are older than layer B?)
What is layer A?
This word is used to describes organisms who have a different bodily structure even though it might serve similar functions in each species. (like swimming in penguins and fish)
What is an analogous structure?
This is a word that describes organisms within a species that are not identical; some organisms have mutations.
What is variation?
This is a term equivalent to the term "Survival of the Fittest".
What is Natural Selection?
All organisms and species are made of the same DNA bases (Adenine A, Thymine T, Cytosine C, and Guanine G)
True or False
What is TRUE?
Fossils always show that species stayed the same over time. (true or false)
What is False?
Based on the diagram below, these two organisms have the most recent common ancestor.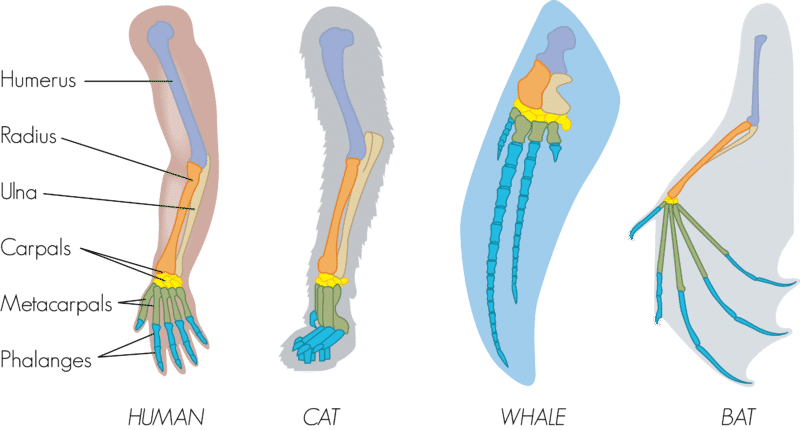
Who are the cat and the human?
This word means an adaptation where an organism uses coloration, pattern, or shape to blend into its environment, making it difficult for other animals to detect or recognize it.
What is camouflage?
This is a word that describes where individuals in a population strive for limited resources like food, water, mates, or territory.
This is a term that means that different species evolved from a single, earlier life form at some point in evolutionary history.
What is a common ancestor?
These two organisms are the LEAST related to each other based on the cladogram below.
What are cats and amphibians?
All of these organisms have a common ancestor with each other. (true or false)
What is True?
This is used to describe a population where more offspring are produced than can survive (similar to overpopulation)
What is overproduction?
The individuals with the most advantageous traits are more likely to do this.
A branching tree diagram (cladogram) represents this.
What are Common ancestors?
What are related Organisms/species?
These traits are the traits that Marsupials and Dogs have in common, based on the cladogram below. 
What is fur, amniotic egg, and four limbs?
The front limbs of a human, a bat, and a whale are an example of this type of structure.
A homologous structure
What is the name of the process where random changes in the DNA of an organism can lead to new traits that may benefit the species in survival?
What is a mutation?