What is the first step of the scientific method?
Ask a question or state a problem
The variable that is being tested in the experiment. Also known as the "test variable".
Independent Variable
What is a variable?
A variable is something that changes
Ryan states that "The only way for a scientist to obtain information and knowledge is by doing experiments."
Is Ryan's statement correct? Explain.
Ryan's statement is not correct since not all scientists do experiments. Many scientists rely on direct observation and discovery to obtain their data such as astronomers, paleontologists, and marine biologists
Must be supported by data and evidence
Both Laws and Theories
"If I replace the battery in my car, then my car will get better gas mileage" This statement is an example of what step of the scientific method?
A Hypothesis (If, Then Statement)
The variable being measured in the experiment. Also referred to as the "outcome variable"
Dependent Variable
John wants to test which size of soccer (football) ball is easiest to juggle with his feet. He tests a size 3, size 4 and a size 5 ball. He then counts the seconds the ball stays in the air for each of the trials.
What is the dependent variable?
The number of seconds the ball stays in the air
What are two ways that the results of an experiment can be made more reliable?
Repetition of the experiment
Replication of the experiment and comparing results
Adding more test subjects
Accurately writing and following the experimental procedure
Explains why something happens
Theory
"According to my experiments, the Energizer maintained its voltage for approximately 3% longer period of time than the Duracell battery. My hypothesis was that Energizer would last the longest in all of the devices tested. My results do support my hypothesis."
The statement above is an example of what step in the scientific method?
Conclusion
What is a controlled variable in an experiment?
A controlled variable is a factor that the researcher keeps the same in the experiment so that results of the experiment are not effected.
John wants to test which size of soccer (football) ball is easiest to juggle with his feet. He tests a size 3, size 4 and a size 5 ball. He then counts the seconds the ball stays in the air for each of the trials.
What is the independent variable?
Size of the soccer balls
Class question:
Brian predicts that plants grown with True Green fertilizer would be at least twice as tall as plants grown with Evergreen fertilizer after 6 weeks. Based on the table below, what should Brian's conclusion be about his prediction?
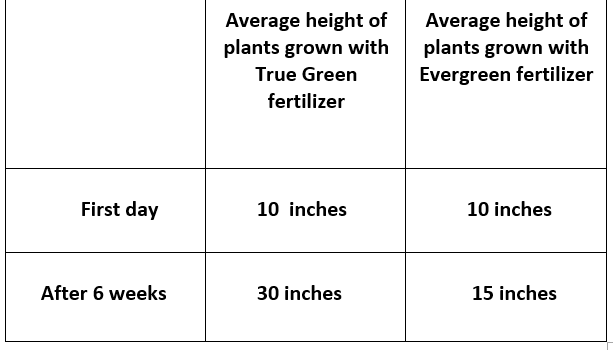
The data supports Brian's hypothesis since the plants grown with True Green had an average of 30 feet and the plants grown with Evergreen had an average of 15 feet after 6 weeks. 30 feet is exactly twice as much as 15 feet. (15 x 2 = 30).
States what will happen. Describes a repeating pattern that we can observe in nature. For example, "The force of an object is equal to its mass times acceleration F = MA"
Law
Kristin makes the hypothesis
"Our universe is surrounded by another, larger universe that we can have absolutely no contact with."
What is the problem with Kristin's hypothesis?
it is not testable. There are no observations that a scientist can make to tell whether or not the hypothesis is correct
Explain the difference between repetition and replication of an experiment.
Repetition- When someone does an experiment more than once.
Replication- When another person copies an experiment that has already been done.
John wants to test which size of soccer (football) ball is easiest to juggle with his feet. He tests a size 3, size 4 and a size 5 ball. He then counts the seconds the ball stays in the air for each of the trials.
What would be a controlled variable in this experiment?
The brand of soccer ball
The same person juggling the ball
The technique used to juggle the ball
Mark wants to see how salt will affect the height of sunflower plants. He gives one group of plants salt water and another group of plants plain water. After a two week period, the height is measured.
What is the experimental and control group in this experiment?
Experimental group- plants that receive salt water
Control group- plants that receive plain water
Can be modified (changed) if new evidence no longer supports it
Both laws and theories
What are the seven steps of the scientific method? (in the correct order)
Ask a question or state a problem, Research, Hypothesis, Experiment, Collect and analyze results, Conclusion, Communicate results
What is the difference between the experimental group and control group in an experiment?
Experimental group- receives what is being tested
Control group- does not receive what is being tested
Describe two differences between the independent and dependent variable.
The independent variable describes what is being tested and the dependent variable describes what is being measured
Class question:
Chris predicts that a paper airplane without any added weight would travel farther than a paper airplane with two paper clips. The following table shows Chris's results from the experiment. What should his conclusion be based on his prediction?

The data does not support Chris's hypothesis since both the airplane without the added weight and the airplane with 2 paper clips went an average of 10 feet. Chris predicted that the plane without any added weight would have traveled a further distance.
What are three things that laws and theories have in common?
Both are supported by evidence
Both are accepted by the majority of scientists
Both can be changed if new evidence no longer supports it
Both are based on tested hypotheses