How should you counsel patients regarding the risk of nausea and vomiting to their pregnancy?
No increased risk of harm or miscarriage. (Actually has been shown to be associated with an increased live birth rate.)
If nausea and vomiting persists after first-line therapy, what pharmacologic therapy is next recommended?
Doxylamine (Unisom) and pyridoxine (vitamin B6)
Please name three physiologic or anatomic changes that lead to an increased risk of VTE in pregnancy.
Hypercoagulability, increased venous stasis, decreased venous outflow, compression of the inferior vena cava, decreased mobility.
When is the risk of VTE highest during the course of pregnancy and postpartum?
First week after delivery.
What agent can be used to reverse heparin? Does it work for LMWH?
Protamine sulfate
Less predictable for LMWH
Please name three risk factors for developing hyperemesis gravidarum.
Increased placental mass (e.g. molar pregnancy, multiple gestation)
History of motion sickness
Migraine headaches
Family history of hyperemesis gravidarum
History of hyperemesis gravidarum in a previous pregnancy
What precaution(s) must you take before treating a patient with ondansetron (Zofran)? For what are you screening?
EKG to screen for QTc prolongation
Which inherited thrombophilias are considered low risk for VTE during pregnancy? Which ones are considered high risk?
Low risk: Factor V Leiden heterozygote, prothrombin G20210A heterozygote, protein C deficiency, protein S deficiency
High risk: Factor V Leiden homozygote, prothrombin G20210A homozygote, compound factor V Leiden and prothrombin G20210A heterozygote, antithrombin deficiency.
What is the most common site where DVTs are diagnosed during pregnancy?
Ileofemoral (64%).
Vitamin K, fresh frozen plasma, prothrombin complex concentrate.
Please name three commonly used criteria to diagnose hyperemesis gravidarum.
- Persistent vomiting not related to other causes
- Weight loss exceeding 5% of prepregnancy body weight
- A measure of acute starvation (e.g. ketonuria, ketonemia)
- Electrolyte, thyroid, and/or liver abnormalities
If nausea and vomiting persists after second-line therapy, what pharmacologic therapy is next recommended?
Dimenhydrinate (Dramamine) or diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or prochlorperazine (Compazine) or or promethazine (Phenergan)
A patients presents to your office for her first prenatal visit. Upon reviewing her history you discover her sister was diagnosed with protein S deficiency after a lower extremity DVT. The patient underwent testing and was also found to had protein S deficiency. How should you manager her VTE risk during pregnancy? What about postpartum?

Please name the diagnostic criteria for antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. How should you manage their risk of VTE during pregnancy?
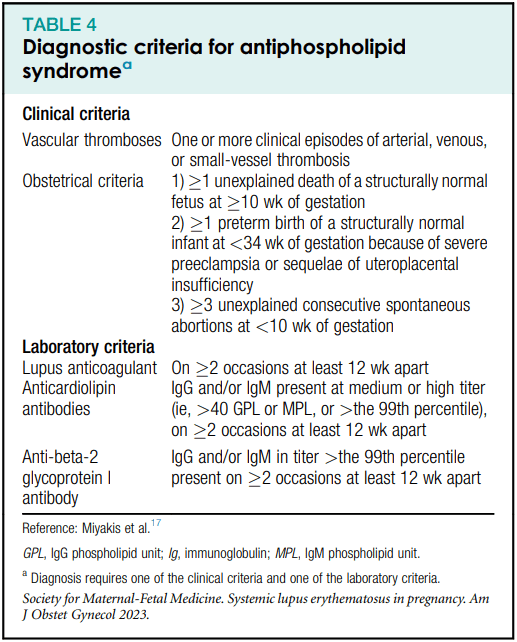
Obstetric APLS: Aspirin + prophylactic heparin/LMWH
Thrombotic APLS: Aspirin + therapeutic heparin/LMWH
When should patients continue vitamin K antagonist therapy during pregnancy?
In the setting of mechanical heart valves.
What precaution should you take before treating a dehydrated patient with nausea/vomiting with fluids containing dextrose? What are you trying to prevent?
Pre-treat with thiamine (vitamin B1)
Wernicke encephalopathy
What is first-line therapy for nausea and vomiting in pregnancy?
1. Convert prenatal vitamin to folic acid supplement only
2. Ginger capsules 250 mg qid
3. Consider P6 accupressure with wrist bands
If patients cannot safely take heparin products, what is the preferred anticoagulant? What is its mechanism of action?
Fondaparinux, synthetic pentasaccharide that binds to and activates antithrombin, accelerating the inhibition of factor Xa.
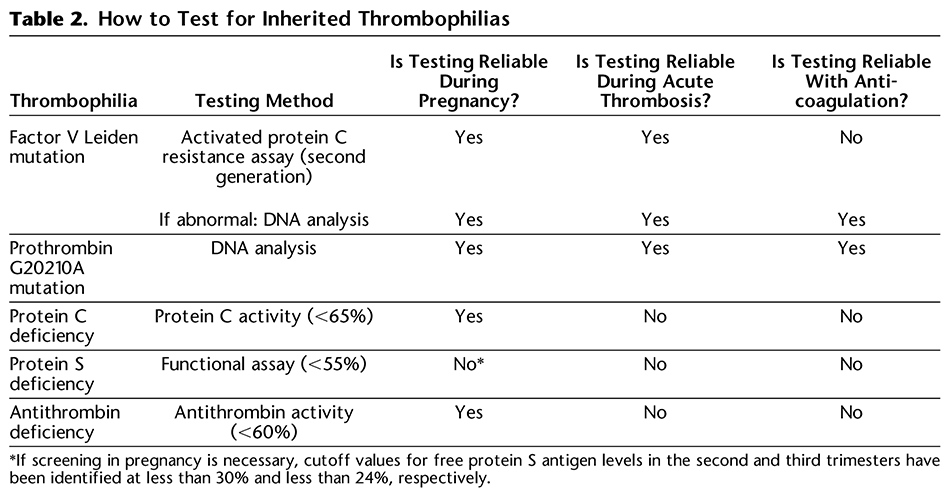
For which inherited thrombophilias is testing during pregnancy reliable? For which is it reliable while on anticoagulation?
According to Lactmed, how should patients who were dabigatran be counseled regarding breastfeeding? Rivaroxaban? Apixaban?
Dabigatran and rivaroxaban are poorly secreted into breastmilk and continuation is reasonable.
Apixaban is secreted at high levels into breastmilk so patients should avoid it while breastfeeding.
What recently discovered hormone been linked to maternal hyperemesis gravidarum?
Growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15)

If you have a patient with dehydration whose nausea and vomiting is refractory to IV antiemetics and you want to try corticosteroid therapy, what corticosteroid should you try? How much and how frequently? If it works, over how long should you taper?
Methylprednisolone 16 mg q8h, orally or IV, for 3 days. Taper over 2 weeks to lowest effective dose, limit therapy to 6 weeks total.
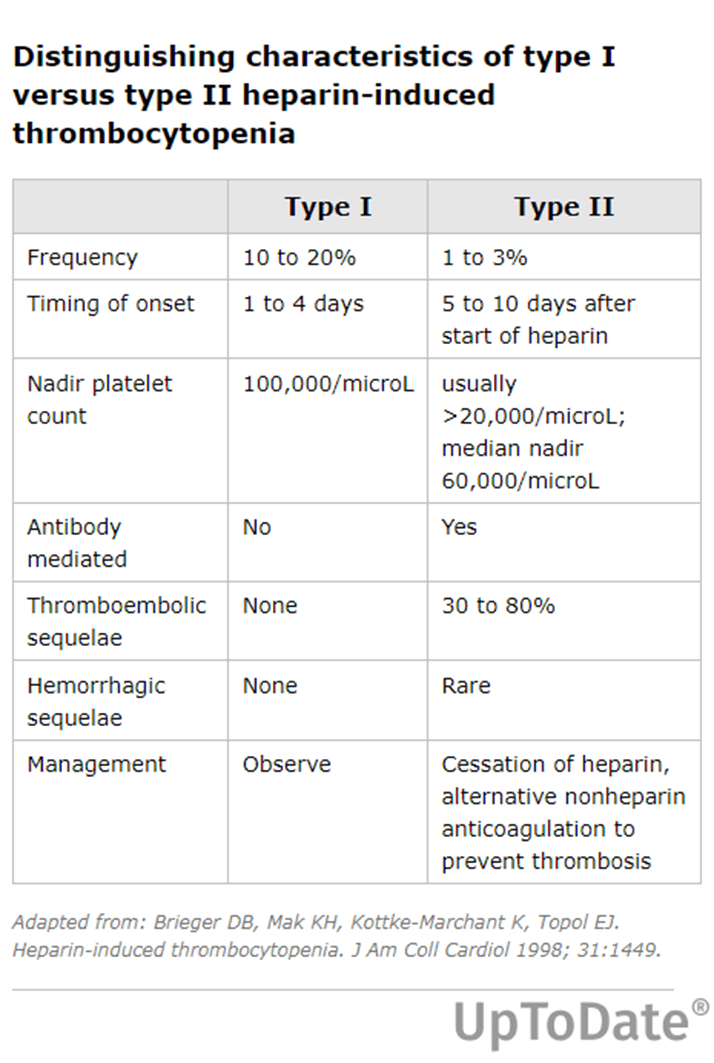
What are the differences between HIT types 1 and 2?
HIT type I (HIT I) is a mild, transient drop in platelet count that typically occurs within the first two days of heparin exposure.
HIT type II (HIT II) is a clinically significant syndrome due to antibodies to platelet factor 4 (PF4) complexed to heparin, referred to as "HIT antibodies" or "PF4/heparin antibodies"
Does helical CT or ventilation perfusion scanning convey lower radiation exposure to the fetus?
Which provides lower radiation exposure to the maternal breasts?
Helical CT has lower fetal exposure (0.0033-0.02 mGy vs 0.32-0.64).
Ventilation perfusion scanning has lower breast radiation exposure.
What agent can you use to reverse rivaroxaban? Apixaban? Dabigatran?
Apixaban and rivaroxaban: Recombinant coagulation factor Xa andexanet alpha (AndexXa).
Dabigatran: Idarucizumab (Praxbind).