Name one risk factor for NEC
Low Birth Weight , prematurity, microbial dysbiosis, systemic inflammation
Name 3 clinical Gi findings, suspicious for NEC
1. abdominal distention
2. bloody stools
3. emesis
A baby is noted to have increased apnea/bradycardic episodes overnight. The nurse also tells you that he had a stool that looked bloody. On your exam you feel like the baby's abdomen is more distended but still soft. Baby's ABG is shows pH 7.3, CO2 55. Does this baby have NEC?
No, Stage 1 (Bell Staging)
suspected NEC
NPO (Stop feeds)
Reduces the incidence of NEC
What is breastmilk
This risk factor's awareness month is celebrated in February
CHD (congenital heart disease)
In a baby with NEC, a blood ABG might show this
respiratory or metabolic acidosis
Baby is noted to have increased A/B overnight with no increased WOB. Abdominal exam is unremarkable. Should you get a KUB?
Not necessarily, not concerning for NEC
A baby has stage 2 NEC, what is the management of this
NPO
Empiric antibiotics
Serial abdominal exams
what antibiotics are used in NEC
Ampicillin
Gentamicin
Metronidazole
Overuse of this medication can be a risk factor for NEC
Antibiotics
These findings on an XR make you concerned for NEC
pneumatosis
A baby is having more A/B overnight, the nurse tells you the baby's abdomen is tender, pH 7.24, CO2 33, XR shows pneumatosis. What else might you find on a CBC and BMP(platelets and Na)?
thrombocytopenia , hyponatremia
Bell Stage 2 NEC
This is an absolute indication for surgery
penumoperitoneum
Duration of antibiotic therapy
2 weeks
90% of cases of NEC occur in this population
What is VLBW infants born < 32 weeks
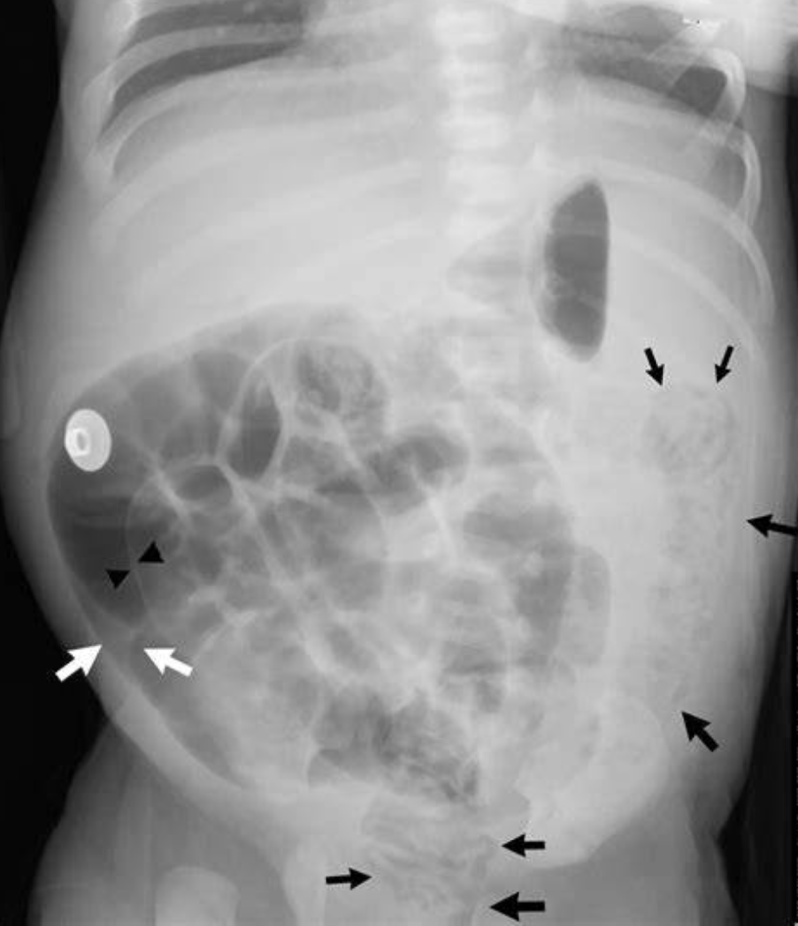
What is pneumatosis intestinalis
A baby w/ A/B episodes, metabolic and respiratory acidosis, pneumatosis intestinalis suddenly develops hypotension. What new finding might you see on KUB? that would suggest stage 3 NEC
pneumoperitoneum
How should a baby with NEC receive nutrition?
TPN via a central line
what does a football sign mean on XR?
Seen with massive pneumoperitoneum
In supine position air collects anterior to abdominal viscera
True or False: Hyperosmolar feedings increase the risk of NEC
True
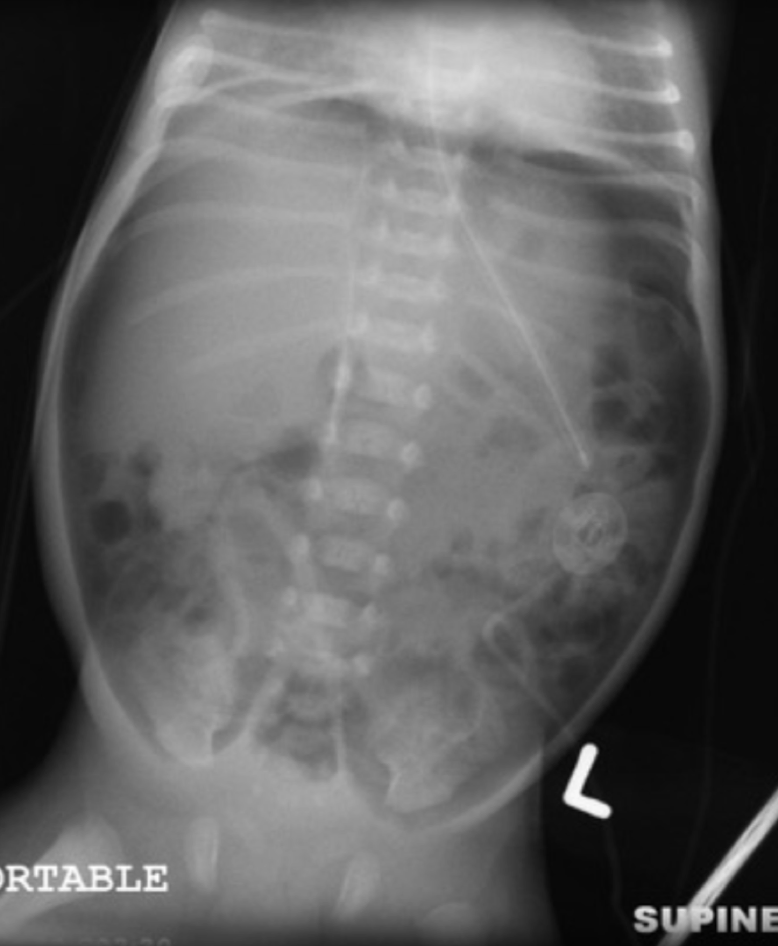
pneumoperitoneum
How is Stage 2 NEC managed
Medically
You see pneumatosis intestinalis on KUB. What should you do next?
manage medically: NPO, antibiotics, serial abdominal exams
most common portion of GI tract affected by NEC
Terminal ileum and colon