A 39-year-old woman is evaluated during a follow-up visit for recently diagnosed stage 2 hypertension confirmed with home blood pressure monitoring measurements taken over the past month. She also has a 12-year history of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Medications are metformin and empagliflozin.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 144/88 mm Hg, pulse rate is 88/min, and respiration rate is 18/min. BMI is 28. The remainder of the examination unremarkable.
Laboratory studies show a serum creatinine level of 0.9 mg/dL (79.6 µmol/L), normal electrolyte levels, and a urine albumin-creatinine ratio of 330 mg/g.
The patient is instructed in lifestyle modifications to control hypertension.
Lisinopril
Felodipine
HCTZ
HCTZ-Amlodipine
A 54-year-old man is evaluated during a new patient visit. He has a 30-year history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and 10-year history of hypertension. Medical history is also significant for obesity and hypercholesterolemia. Medications are amlodipine, atorvastatin, canagliflozin, metformin, and lisinopril-hydrochlorothiazide. At his last visit to his previous physician, serum creatinine level was 1.4 mg/dL (123.8 µmol/L), and estimated glomerular filtration rate was 58 mL/min/1.73 m2.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 158/82 mm Hg, and pulse rate is 62/min; other vital signs are normal. BMI is 38. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Laboratory studies:
Albumin: 3.5 g/dL (35 g/L)
Creatinine: 1.6 mg/dL (141.4 µmol/L)
Electrolyte: Normal
Estimated glomerular filtration rate: 50 mL/min/1.73 m2
Urinalysis
No blood; 2+ protein
Results of kidney ultrasonography and referral to an ophthalmologist for a dilated retinal examination are pending.
Which of the following is the most appropriate test to assess the prognosis of this patient's chronic kidney disease?
Spot urine albumin-creatinine ratio
A1c
Kid biopsy
PTH
A 38-year-old man is evaluated during a follow-up visit for proteinuric chronic kidney disease. Family history is significant for end-stage kidney disease in two uncles and a female cousin. He has no other medical problems, and his only medication is lisinopril. The patient is of African descent.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. There are features of generalized anasarca, with marked edema of the lower extremities. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
Laboratory studies:
Albumin : 2.2 g/dL (22 g/L)
Total cholesterol: 264 mg/dL (6.8 mmol/L)
Creatinine : 1.8 mg/dL (159.1 µmol/L)
Urinalysis: No blood; 4+ protein
Urine protein-creatinine ratio : 7850 mg/g
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Membranous
Minimal change
Lupus nephritis
A 62-year-old man is evaluated in the emergency department for abrupt onset of sharp chest pain radiating to his upper back that started 90 minutes ago. Medical history includes difficult-to-control hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Medications are metformin, empagliflozin, rosuvastatin, amlodipine, hydrochlorothiazide, and lisinopril.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 210/120 mm Hg in the right arm and 180/100 mm Hg in the left arm, pulse rate is 118/min, respiration rate is 20/min, and oxygen saturation is 97% with the patient breathing ambient air. The patient is diaphoretic and in distress. Cardiac examination reveals tachycardia with a 3/6 diastolic murmur heard along the upper left sternal border. Lungs are clear to auscultation. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
Emergency CT imaging confirms the diagnosis of ascending aortic dissection.
Referral for emergency surgical consultation is obtained.
Which of the following is the most appropriate initial intravenous treatment?
Esmolol
Hydralazine
Nitroprusside
Nicardipine
A 28-year-old man is evaluated for hematuria that he noted on awakening and a 3-day history of fever, runny nose, and cough. One year ago, he had an episode of gross hematuria after running a half marathon. Evaluation at that time resulted in a biopsy diagnosis of IgA nephropathy. He has no other medical problems and takes no medications.
On physical examination, temperature is 37.9 °C (100.2 °F), and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg; other vital signs are normal. The nasal mucosa is edematous, with serous discharge. Examination of the oropharynx reveals erythema without exudate. There is no lymphadenopathy. Lungs are clear to auscultation. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
Laboratory studies show a serum creatinine level of 0.9 mg/dL (79.6 µmol/L); urinalysis shows 3+ blood, trace protein, too numerous to count erythrocytes, and no casts. Streptococcal rapid antigen test is negative.
Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
Prednisone
Amoxil
CT abd/pelvis
A 43-year-old man is evaluated for one episode of gross hematuria 3 days ago. He reports no flank pain and no associated trauma on exertion. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable. He does not smoke cigarettes and takes no medications.
Physical examination findings, including vital signs, are normal.
Laboratory studies:
Blood urea nitrogen : Normal
Creatinine : Normal
Urinalysis : No protein; 1+ heme pigment; 10-15 erythrocytes/hpf; 0-2 leukocytes/hpf; no nitrites; no leukocyte esterase
Random urine protein-creatinine ratio : 20 mg/g
Contrast-enhanced CT urogram of the kidneys shows no stones, masses, or cysts.
Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic test to perform next?
Cystoscopy
Repeat UA
Kidney biopsy
24h urine protein measurement
An 87-year-old man is evaluated in the emergency department for a 36-hour history of lower abdominal discomfort, urinary frequency, and nocturia. He has no other symptoms. Medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis. Medications are metformin, hydrochlorothiazide, and rituximab. He began taking over-the-counter chlorpheniramine last week for symptoms related to seasonal allergies.
On physical examination, he is afebrile. Blood pressure is 158/64 mm Hg, and pulse rate is 78/min. There is tenderness to palpation of the lower abdomen. The prostate is diffusely enlarged.
Laboratory studies show a blood urea nitrogen level of 50 mg/dL (17.9 mmol/L) and a serum creatinine level of 2.4 mg/dL (212.2 µmol/L). Urinalysis shows a specific gravity of 1.012, 1+ blood, 1+ protein, 1+ leukocytes, 3 nondysmorphic erythrocytes/hpf, 1-3 leukocytes/hpf, and no casts.
Which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management?
Bladder US
Kidney US
non-con CT abd/pelv
MRI abd/pelv
A 46-year-old man is evaluated for confirmed primary hypertension. The patient is asymptomatic and takes no medications. He is a current smoker with a 20-pack-year history. Family history is significant for hypertension in his mother and father; his father had a stroke at age 55 years.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 154/96 mm Hg in both arms, pulse rate is 74/min, and respiration rate is 18/min. BMI is 30. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Laboratory studies:
Fasting lipid profile:
Total cholesterol
220 mg/dL (5.7 mmol/L)
LDL cholesterol
160 mg/dL (4.1 mmol/L)
HDL cholesterol
48 mg/dL (1.2 mmol/L)
Creatinine
1.0 mg/dL (88.4 µmol/L)
Electrolytes
Normal
Glucose, fasting
80 mg/dL (4.4 mmol/L)
Urinalysis
No protein, erythrocytes, or leukocytes
A 12-lead ECG is normal.
The patient is instructed in lifestyle modifications, including smoking cessation, exercise, and a low sodium diet. Moderate-intensity atorvastatin is initiated.
Which of the following is the most appropriate additional therapy?
Amlodipine-valsartan
Amlodipine
Valsartan
Chlorthalidone
A 45-year-old man is evaluated during a routine visit in September. He has advanced chronic kidney disease due to IgA nephropathy. Medical history is also significant for chickenpox but with no history of shingles. Medications are carvedilol, diltiazem, lisinopril, and sevelamer. His vaccination history includes completion of only required childhood vaccinations and recent COVID-19 immunization.
Laboratory studies:
Hepatitis A virus IgM antibody : Negative
Hepatitis B surface antigen : Negative
Hepatitis B surface antibody : Positive
Hepatitis C virus antibody : Negative
Inactivated influenza vaccine is administered.
Which of the following is the most appropriate additional vaccine to administer at this visit?
Pneumococcal
Hep A
Hep B
Zoster
A 52-year-old woman is evaluated during a follow-up visit for hypertension management. She has a 10-year history of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetic retinopathy was diagnosed 1 year ago. She also has obesity and hyperlipidemia. Medications are hydrochlorothiazide, metformin, empagliflozin, and atorvastatin.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 138/86 mm Hg; other vital signs are normal. BMI is 32. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
Laboratory studies:
Creatinine
0.9 mg/dL (79.6 µmol/L)
Electrolytes
Normal
Urine albumin-creatinine ratio
550 mg/g
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
>60 mL/min/1.73 m2
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
ARB/ACE
Amlodipine
Atenolol
Doxazosin
A 66-year-old man is evaluated in the hospital for acute kidney injury following percutaneous coronary angiography and stent placement 48 hours ago. His medical history is also significant for hypertension, hyperlipidemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and diabetic kidney disease. Medications are lisinopril, hydrochlorothiazide, basal and prandial insulin, atorvastatin, metoprolol, clopidogrel, and aspirin.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 132/88 mm Hg, and pulse rate is 58/min without postural changes. Skin is warm and dry. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Laboratory studies:
Hematocrit : 36%
Platelet count : 127,000/µL (127 × 109/L)
Blood urea nitrogen : 54 mg/dL (19.3 mmol/L)
Creatinine : 3.6 mg/dL (318.2 µmol/L); on admission, 3.3 mg/dL (291.7 µmol/L)
Urinalysis : Specific gravity 1.010; pH 5.5; trace protein; trace leukocytes; 1-3 erythrocytes/hpf; 1-3 leukocytes/hpf; 3-5 granular casts/hpf
Kidney ultrasound shows a 10.5-cm right kidney, 11.3-cm left kidney, and normal cortical echogenicity; there is no hydronephrosis.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
ATN
Pre-renal AKI
HUS
Atheroembolic-induced
A 62-year-old woman comes to the office for kidney transplantation evaluation. She has end-stage kidney disease. A peritoneal dialysis catheter was placed 2 weeks ago. She also has hypertension. Medications are amlodipine, benazepril, furosemide, metoprolol, and sodium bicarbonate.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. A peritoneal dialysis catheter is present. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Laboratory studies:
Hepatitis B core antibody
Positive
Hepatitis B surface antibody
Positive
Hepatitis B surface antigen
Negative
Hepatitis C antibody
Positive
Hepatitis C viral load
2.8 million IU/mL
Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
Discuss HPC treatment and timing
Avoid transplant
Entecavir
Ribavirin
A 19-year-old woman is evaluated for a 2-week history of fatigue, poor appetite, arthralgia of the hands and knees, and a rash, all of which appeared 1 day after a trip to the beach. She has no other medical problems and takes no medications.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. A malar rash characterized by pink-violet papules and plaques with sparing of the nasolabial folds is noted. The remainder of the examination, including joint examination, is normal.
Laboratory studies:
Albumin : 3.1 g/dL (31 g/L)
C3 : 50 mg/dL (500 mg/L)
C4 : 9 mg/dL (90 mg/L)
Creatinine : 1.1 mg/dL (97.2 µmol/L)
Antinuclear antibodies : Titer, 1:160
Urinalysis : 3+ blood; 3+ protein; many erythrocytes; occasional dysmorphic erythrocytes; rare erythrocyte casts
Kidney ultrasound shows kidneys of normal size and echogenicity.
Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic test to perform next?
Kid bx
Skin bx
ESR
Extractable nuclear antigen profile
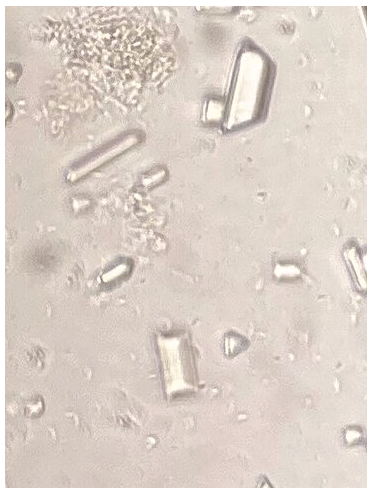
Infection with which bacteria?
Proteus
E. coli
Staph saprophyticus
GBS
A 65-year-old man is evaluated for fatigue and weakness progressing over the last 3 months. His medical history is otherwise unremarkable, and he takes no medications.
Findings on physical examination, including vital signs, are normal.
Laboratory studies:
Hemoglobin
9 g/dL (90 g/L)
Albumin
3.0 g/dL (30 g/L)
Creatinine
0.9 mg/dL (79.6 µmol/L)
Electrolytes :
Sodium
138 mEq/L (138 mmol/L)
Potassium
3.4 mEq/L (3.4 mmol/L)
Chloride
118 mEq/L (118 mmol/L)
Bicarbonate
14 mEq/L (14 mmol/L)
Glucose
74 mg/dL (4.1 mmol/L)
Phosphorus
2.1 mg/dL (0.7 mmol/L)
Total protein
8.0 g/dL (80 g/L)
Urinalysis
pH 5.0; no blood; no protein; no erythrocytes; 1+ leukocytes; trace glucose
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's laboratory findings?
RTA 2
RTA 1
RTA 4
Bartter
Liddle
A 38-year-old woman seeks treatment for polyuria and nocturia that began 6 weeks ago after starting lithium for bipolar disorder. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable. Her only other medication is olanzapine.
Physical examination findings, including vital signs, are normal.
Laboratory studies show a serum sodium level of 145 mEq/L (145 mmol/L) and a urine osmolality of 200 mOsm/kg H2O.
Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
Amiloride
Decrease H20
Increase protein
Add furosemide