Functions
Miscellaneous
Groove between the folds of cerebral cortex
What is a sulcus
Function of the cerebellum
What is Fine Motor Movement
The number of this cranial nerve.
II or 2.
Cranial nerve that controls Hearing; equilibrium (balance)
What is the Vestibulocochlear
Two primary functions of cerebrospinal fluid
1) Protection from impact 2) Provides buoyant environment 3) waste removal and nourishment
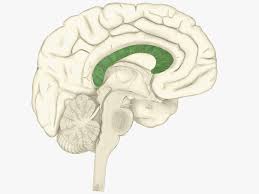
The name of structure highlighted green.
Corpus callosum
Functions the Vision and Alertness
What is the Midbrain
Smell (Olfactory)
1 or I
Cranial nerves that control smell
The cerebrospinal fluid flows through the cranial cvity using the following five structures
1) Central canal 2) Cerebral aqueduct 3) Fourth ventricle 4) Lateral ventricles 5) Third ventricle
Ridge that makes up the folded material in cerebral cortex
What is a gyrus
Functions the bladder control, taste, equilibrium
What is the Pons
Eye movement (Trochlear)
4 or IV
Movement of tongue during speech and swallowing
What is the Hypoglossal
Does the arbor vitae of the cerebellum comprise white matter or gray matter?
White matter.
The groove that separates the cerebral hemispheres
What is the Longitudinal Fissure
Functions various autonomic functions
What is the Medulla oblongata
Facial (Facial expression; taste)
7 or VII
The muscle controlled by the trochlear nerve.
Superior oblique muscle.
Is the cerebellar cortex deep or superficial to the arborvitae
Superficial
The lobes separated by the 1) central sulcus and the 2) lateral sulcus
What are the Frontal lobe and the Temporal lobe
The two centers that the medulla oblongata controls.
Respiratory and Cardiovascular
Glossopharyngeal (taste; movement of pharynx when swallowing)
9 or IX
Taste; movement of pharynx when swallowing
What is the Glossopharyngeal
The medulla oblongata contains the respiratory and cardiovascular centers. What do these centers regulate?
Respiratory - Rate (how fast/slow we are breathing - uses this to see if we need more oxygen. Cardio - (2) - heart beat and size of blood vessels (cardiac and vasomotor)