Functions
Miscellaneous
Divides both the frontal lobe and parietal lobe above from the temporal lobe
Lateral sulcus
A group of subcortical structures (as the hypothalamus, the hippocampus, and the amygdala) of the brain are concerned especially with emotion and motivation.
Limbic system
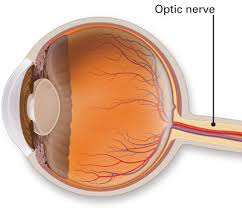
The number of this cranial nerve.
II or 2.
Olfactory
sensory; a sense of smell.
what is the movement of a limb/extremity so that the distal end makes a circle, while the proximal end remains fixed
Example:
Circumduction
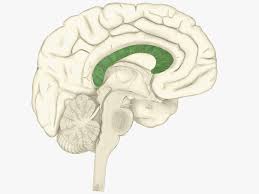
The name of structure highlighted green.
Corpus callosum
The outer layer of the brain, thinking, organizing, and creative center.
Cerebral cortex
Sense of smell
Olfactory receptors in the nasal cavity to olfactory nerve tracts to the olfactory area in the temporal lobe of the brain
sensory
optic
sense of sight
what is the posterior movement of the joint
Example:
retraction
separates cerebral hemispheres
Longitudinal Fissure
Connects the spinal cord to the remainder of the brain and contains many ascending and descending nerve tracts. Consists of the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain.
brainstem
what does motor control
Moves eyes
Accommodation of lens for near vision
Constriction of the iris in response to light
Sensory proprioceptive information from the eyes
oculomotor
motor eyemovment
Does the arbor vitae of the cerebellum comprise white matter or gray matter?
White matter.
separates cerebral hemispheres from cerebellum
Transverse Fissure
Located in the upper back half of the brain. Receives and processes sensory information from the body and skin senses as well as other sensory areas in the brain. Association areas are involved with spatial reasoning and sensing the position of the body in space.
parietal lobe
Motor Nerve
Lateral (side to side) eye movement
eyeball muscle
Trochlear
The muscle controlled by the trochlear nerve.
Superior oblique muscle.
what is the anterior movement at the joint
protrusion
The outermost layer of the cranial and spinal meninges. Protects the brain and spinal cord. And carries blood from the brain toward the heart.
Dura mater
The two centers that the medulla oblongata controls.
Respiratory and Cardiovascular
sensory of touch, pain, and temperature for the eye, upper and lower jaw.
The great sensory nerve of the face.
trigeminal
abducens
eye movemet
movement of the thumb back to anatomical position
Reposition