Functions
Miscellaneous
the 4 main sections of the brain
what is the cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem and cerebellum?
main function of white matter in cerebrum
what is a pathway for communication
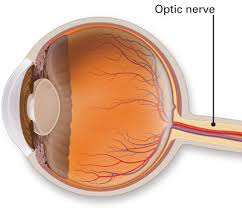
The number of this cranial nerve.
II or 2.
nerve that controls eye movement and innervates medial, superior, and inferior rectus and inferior oblique
what is the oculomotor nerve
cranial nerves that are both sensory and motor
what is the trigeminal, facial, glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves
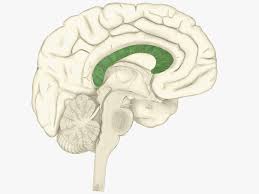
The name of structure highlighted green.
Corpus callosum
serves as the autonomic control center and controls that pituitary gland
what is the hypothalamus

olfactory nerve
abducens nerve
what is the nerve that controls lateral eye movement and innervates the lateral rectus muscle
the ridge/folds of cerebrum
what is the gyrus
the groove that separates the cerebral hemispheres
what is the longitudinal fissure?
what region of brain stem serves as the respiratory and cardiovascular center
what is the medulla oblongata
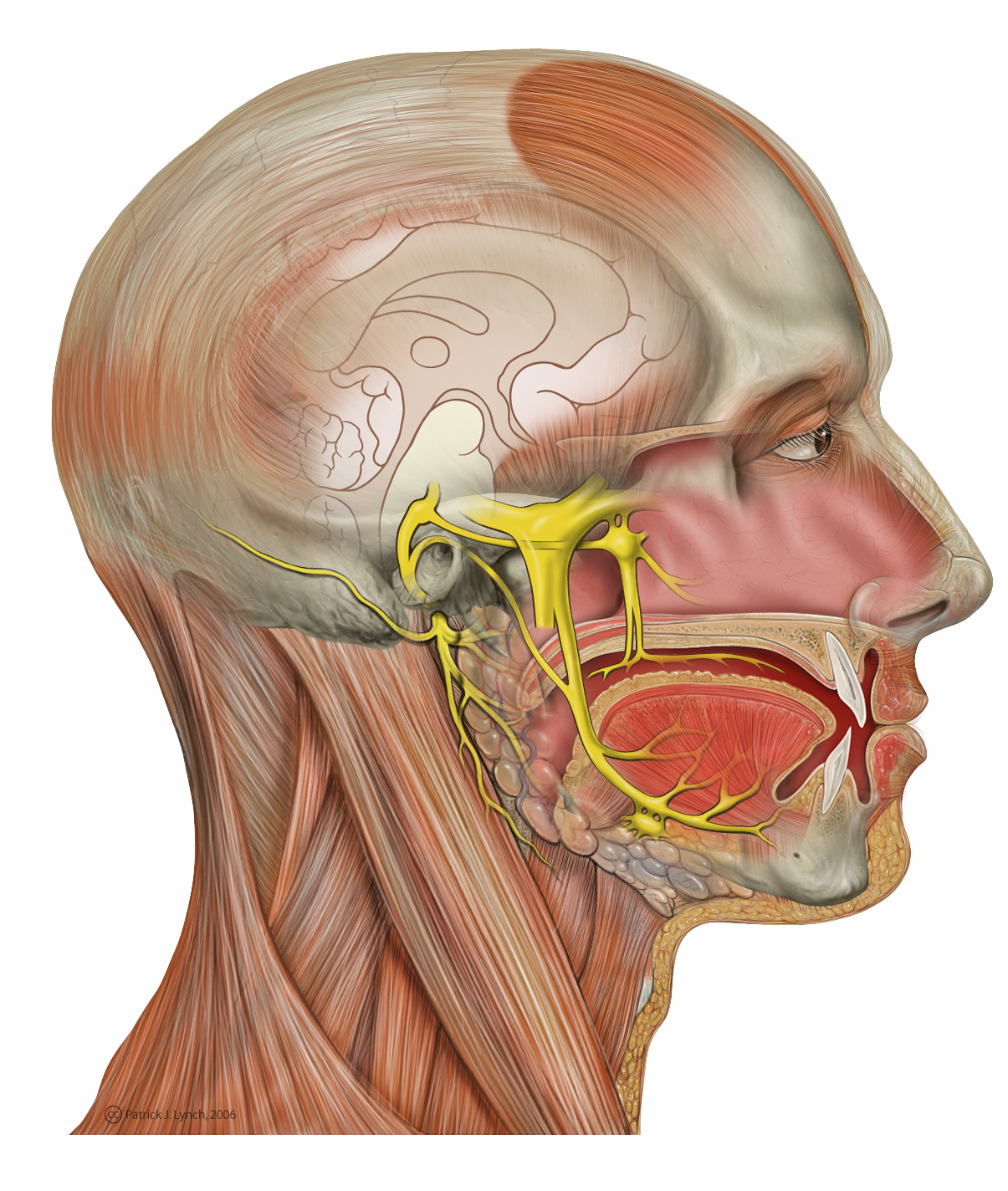
trigeminal nerve
facial nerve
what is the nerve that innervates most facial muscles, and controls salivary glands
Does the arbor vitae of the cerebellum comprise white matter or gray matter?
White matter.
the region where the optic nerves cross each other
what is the optic chiasma
some functions of CSF
what is waste removal, protection and providing buoyancy
cranial nerve 8
vestibulocochlear nerve
The muscle controlled by the trochlear nerve.
Superior oblique muscle.
what is the sulcus
the main organs of the CNS
what is the brain and spinal cord?
The two centers that the medulla oblongata controls.
Respiratory and Cardiovascular
innervates the genioglossus
what is the hypoglossal nerve
nerve that innervates the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid/moves head and shoulders
what is the accessory nerve
hormone that affects circadian rythem
what is melatonin