The two main organs in this system
Brain and Spinal Cord
Responsible for our "fight or flight" response
Sympathetic Nervous System
Somatosensory cortex is located here.
Cerebral hemispheres
Progressive atrophy of the brain leading to dementia.
Alzeimer’s
A disorder that results in the destruction of myelination that prevents nerves from carrying an impulse resulting in increased muscle weakness over time
multiple sclerosis
Impulses are carried toward the CNS by this type of neuron.
Sensory or Afferent
Functions during "resting and digesting" or normal activities
Parasympathetic nervous system
Allows communication between the cerebral hemispheres.
Corpus Collosum
Swelling that increases pressure.
Edema
This diagram shows damage to brain tissue in a localized area due to bleeding. This is known as a what?
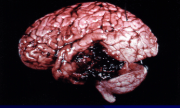
Contusion
Type of substance that the blood/brain barrier lets through.
fat soluble/ lipids
These type of neurons contain sensory and motor fibers.
Inter-neurons / mixed
Control skeletal muscle activity, balance, and equilibrium.
Cerebellum
Disorder treated by providing dopamine or similar drugs. Often characterized by muscle rigidity and tremors
Parkinson’s Disease
In terms of the action potential and synapse, explain how Novocaine prevents sensation.
It prevents the stimulus from opening sodium channels, thus preventing depolarization which creates the necessary action potential to carry the impulse.
Extension of the brain
Spinal Cord
Name three things that only the sympathetic nervous system controls.
Blood vessels, skin, some glands, adrenal medulla
Inflammation of the protective layers of the CNS (the meninges)
Meningitis
Caused by blockage to blood vessels in the brain (scientific name).
Cerebrovascular Accident
List and describe the four things necessary for a reflex arc.
Sensory receptor: reacts to stimulus
Effector organ: organ stimulated
Afferent neuron: Sensory (signal sent TOWARD the CNS)
Efferent neuron: Motor (signal sent away from CNS)
The central nervous system first appears in embryos as this structure
the neural tube
The peripheral nervous system has 12 pairs of ______________ that control much of the motor and sensory functions of the head and neck.
cranial nerves
What are the four main regions of the brain?
Cerebral hemispheres
Diencephalon
Brain stem
Cerebellum
Reason one must check if the direction a baby is head down before a natural birth.
The umbilical cord is likely to be wrapped around the neck cutting off oxygen to the brain during birth and resulting in cerebral palsy.
FINAL JEOPARDY QUESTION:
You are an ER physician and a patient is rushed to the hospital with severe pain to the right side of his body, blurred vision, and slurred speech. Answer the following questions:
a. What is your diagnosis and what is the cause?
b. Which side of the brain is damaged?
c. What are the symptoms the patient expressed?
d. What are risk factors for this diagnosis?
e. What would be a method of treatment?
f. What would a positive Babinski sign show.
a. CVA: Stroke- temporary loss of blood flow to the brain
b. Left side of the brain (crossed somatosensory cortex)
c. Severe pain to the right side of his body, blurred vision, and slurred speech
d. Hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and a positive family history.
e. Blood thinners such as aspirin, anti-hypertension drugs, etc.
f. Damage to the CNS.