The primary cell that builds all the structures of the nervous system
Neuron
What division of the NS is responsible for increased digestion?
parasympathetic nervous system
What is the purpose of neurotransmitters?
Send a signal from one neuron to the next neuron across the synapse
Name FOUR Functional parts of a neuron
1- cell body (soma) 2- dendrite 3- axon 4- myelin sheath 5- axon terminals 6- receptors
What does PNS stand for?
peripheral nervous system
The division of your peripheral nervous system that is made up of the nerves that control involuntary body responses and functions.
Autonomic nervous sysytem
Name the two types of neurotransmitters giving an example of each
Excitatory (Glutamate)
Inhibitory (GABA)
Name the tiny empty space between axon terminals of one neuron and dendrites of the connecting neuron
Synaptic gap
Two subdivisions of the Autonomic Nervous System involved in controlling the visceral muscles, organs, and glands
Sympathetic nervous system - "Fight or Flight"
Parasympathetic nervous system - "Rest and Digest"
Identify all the types of responses to sensory stimuli
Conscious Responses
Unconscious Responses - physiological (sympathetic and parasympathetic) and Spinal Reflex
Describe what Neuromodulators are, and give two examples:
• Neuromodulators are chemical molecules that have an effect on multiple postsynaptic neurons
• Dopamine and Serotonin
What does a dendrite do?
Receives neurotransmitters from another neuron's axon terminal buttons
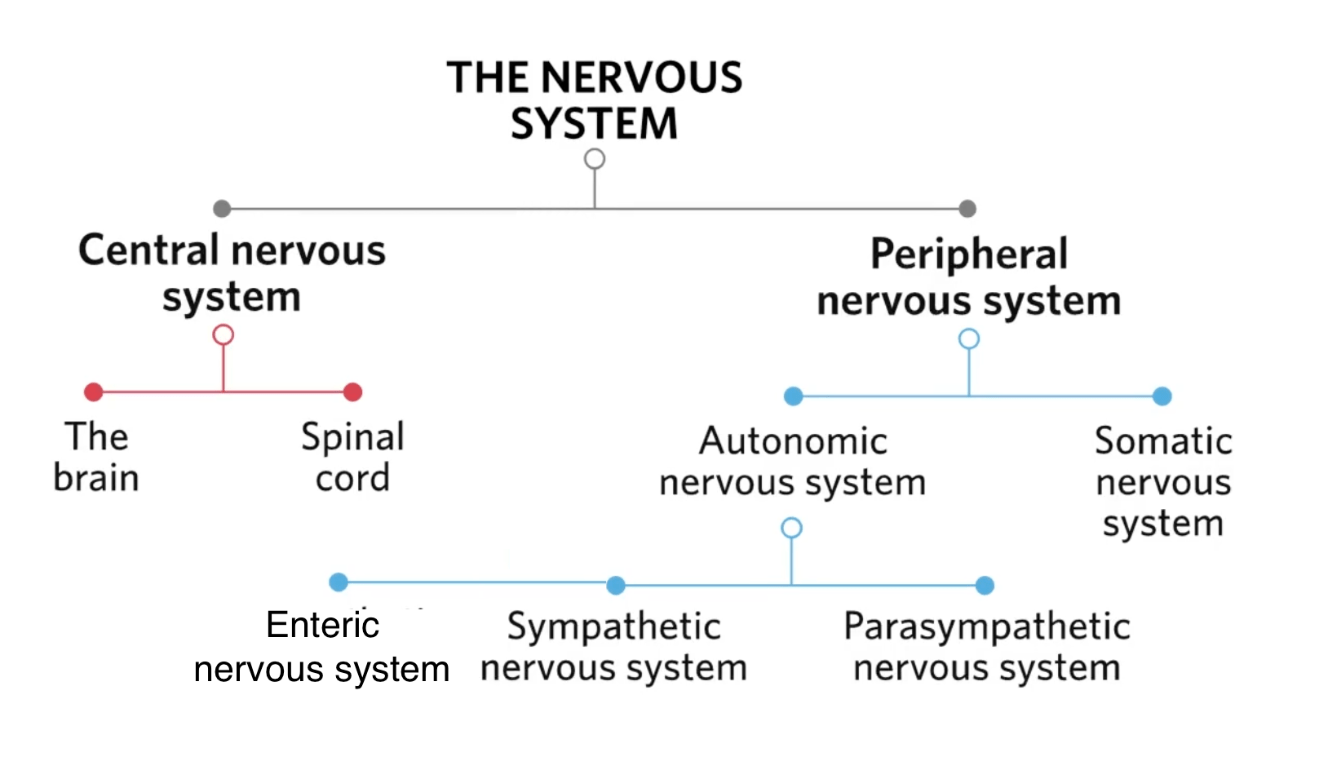
List all divisions and subdivisions of the Human Nervous System
Describe the processes in a spinal reflex:
Stimulus is recieved by the sensory neuron, signal travels to spine and immediately activates the motor neuron (via an interneuron).
(extra info) After, a sensory signal continues to the brain for interpretation.
Describe the role of dopamine:
Dopamine is a neuromodulator, meaning that it effects the activity of multiple neurons at the same time. It has important roles in voluntary movements, the experience of pleasure and reward-based learning and memory. It can be excitatory and inhibitory.
What determines if a neuron fires or not?
The balance of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters on its dendrites
Explain the responses of the human nervous system when Oleg Markov's heart rate increases and his pupils dilate before a big game of footy:
Need to include:
• The type of response (unconscious response)
• The division(s) of the NS responsible (Autonomic; Sympathetic)
Explain the responses of the human nervous system, when Grace calls out "Ben" and Ben turns his head to see who called his name
Need to include:
• The type of response (conscious response)
• The division(s) of the NS responsible (Somatic, Sensory and Motor Neurons)
• The sequence of neural activation: Stimulus → Sensory Neurons → CNS (brain) → Motor Neurons → to skeletal muscles in neck to turn head
Describe the role of serotonin:
Serotonin is a neuromodulator, meaning that has an effect on multiple postsynaptic neurons. It is primarily responsible for mood regulation and the sleep-wake cycle. It has an inhibitory effect on the post-synaptic neruons.
Describe the effect on neural firing if a drug acts like glutamate?
It binds to glutamate receptors and increases the likelihood of a neuron firing