Scientific name for nearsightedness
What is myopia?
Part of the brain primarily responsible for visual processing.
What is the occipital lobe?
When too warm, blood vessels will __________.
What is dilate?
The area highlighted in blue.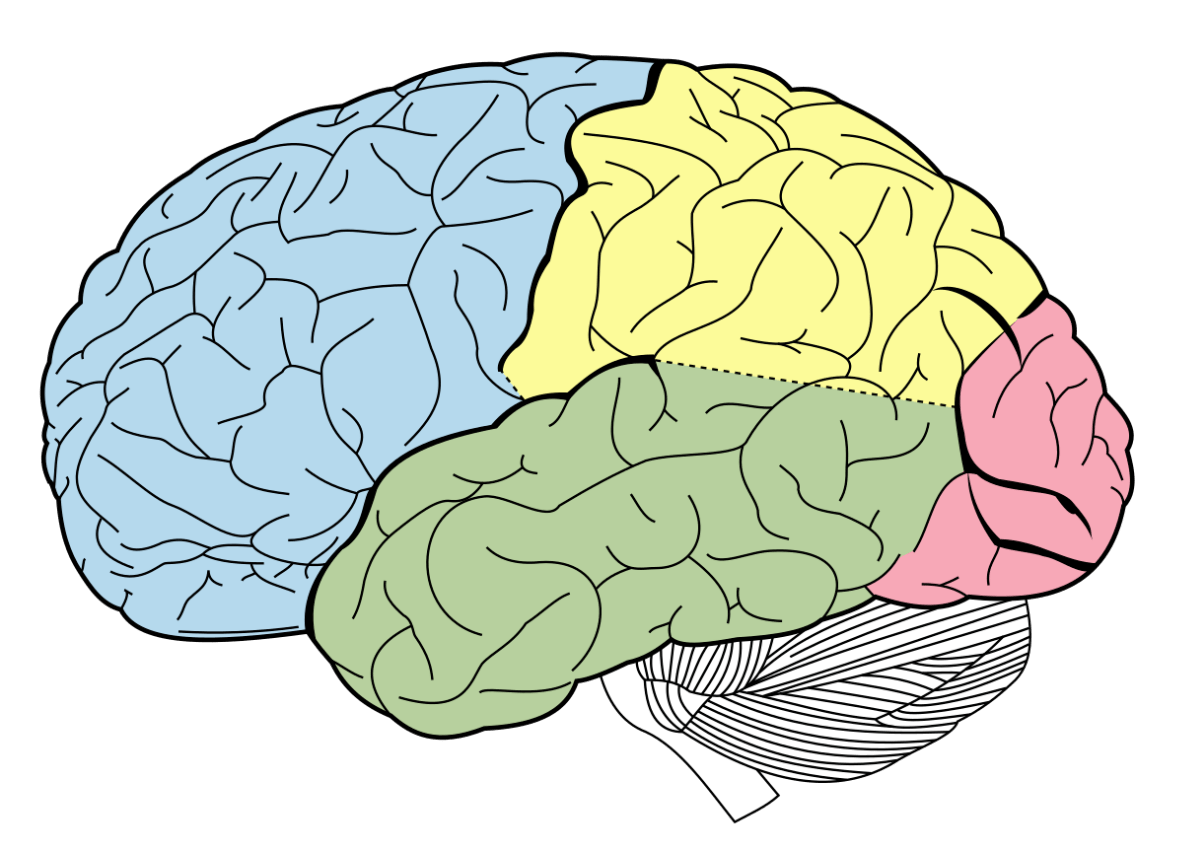
What is the frontal lobe?
Part of eye labelled as C.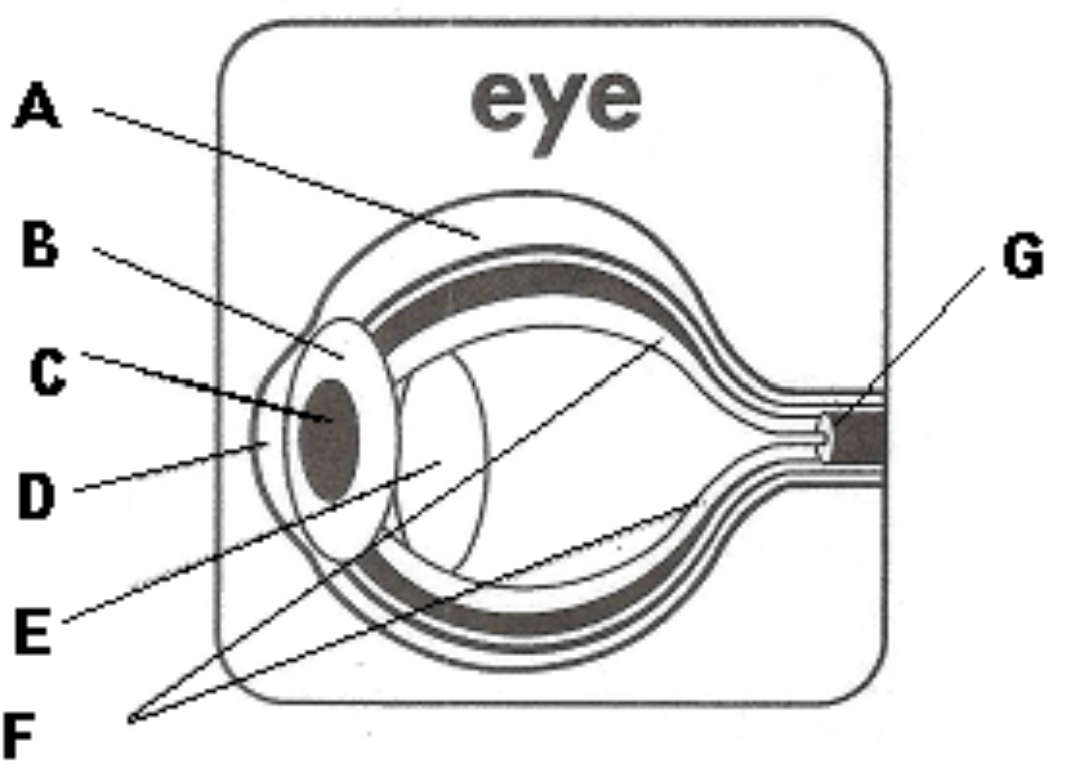
What is the pupil?
In order for a clear image to be produced, light must be focused on this part of the eye.
What is the retina?
Part of the brain responsible for coordination and balance.
What is the cerebellum?
These allow your body to detect external body temp.
What is receptors in the skin?
The area highlighted in green.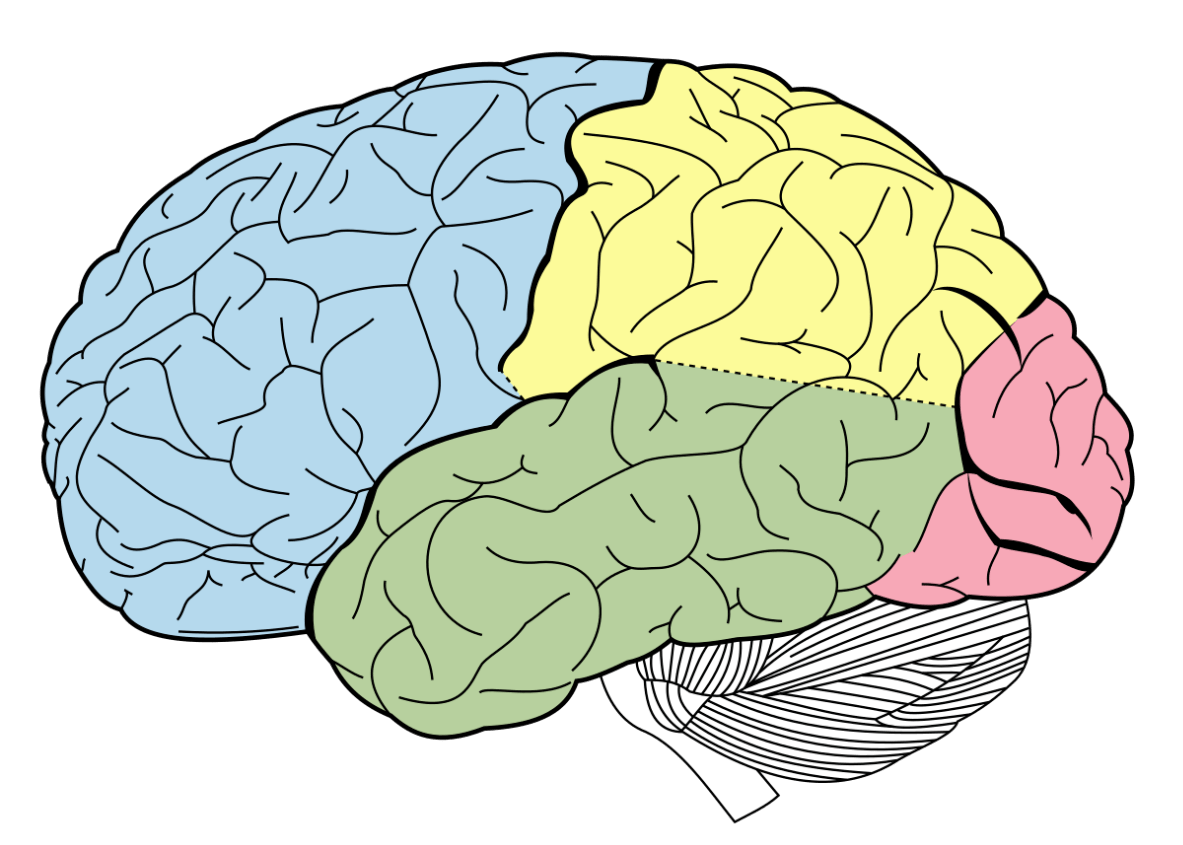
What is the temporal lobe?
Part of the eye labelled as G.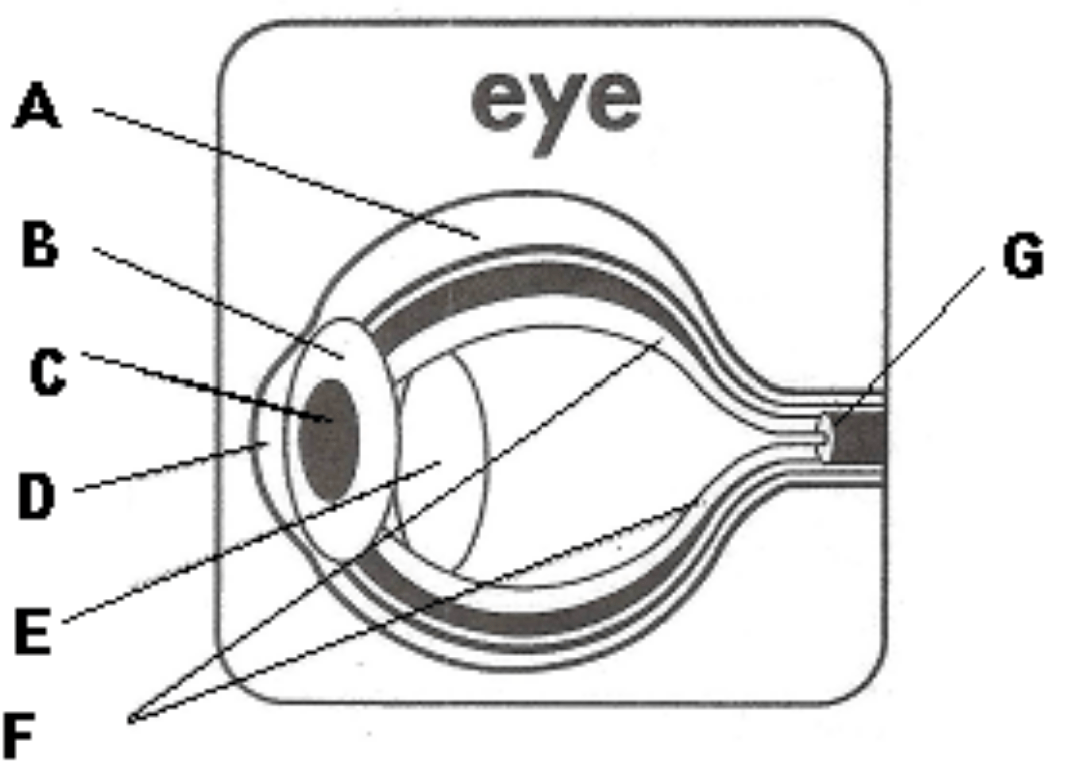
What is the optic nerve?
When accommodating (near vision), the lens changes shape to be...
What is rounder/thicker?
Controls unconscious activities such as breathing and heartrate.
What is the medulla?
Above normal body temperature, enzymes start...
What is denaturing?
Area in red on the brain diagram.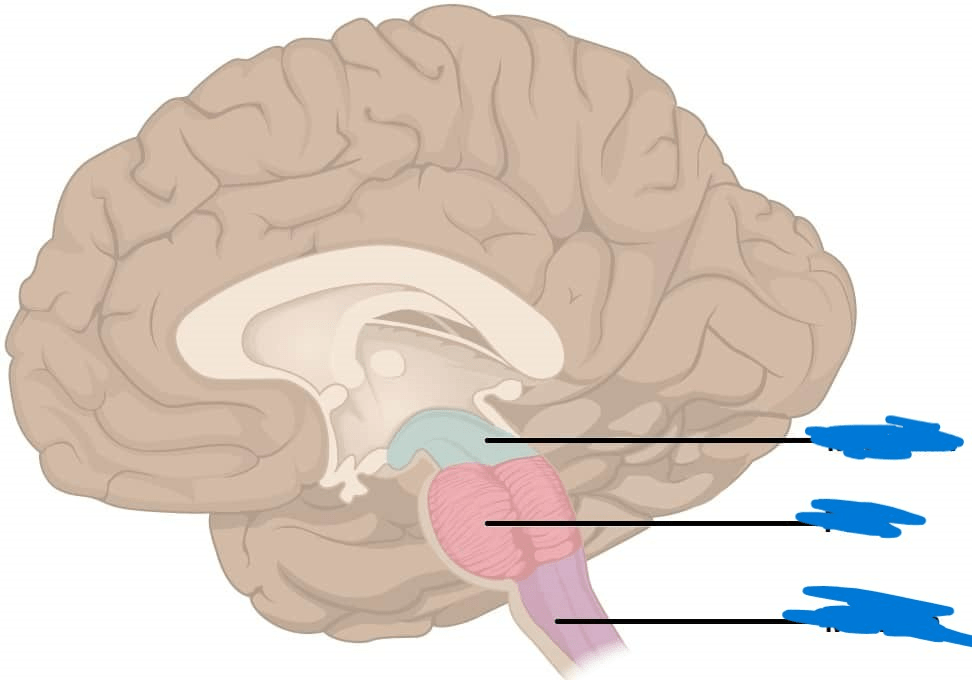
What is the pons?
Part of the eye labelled as A.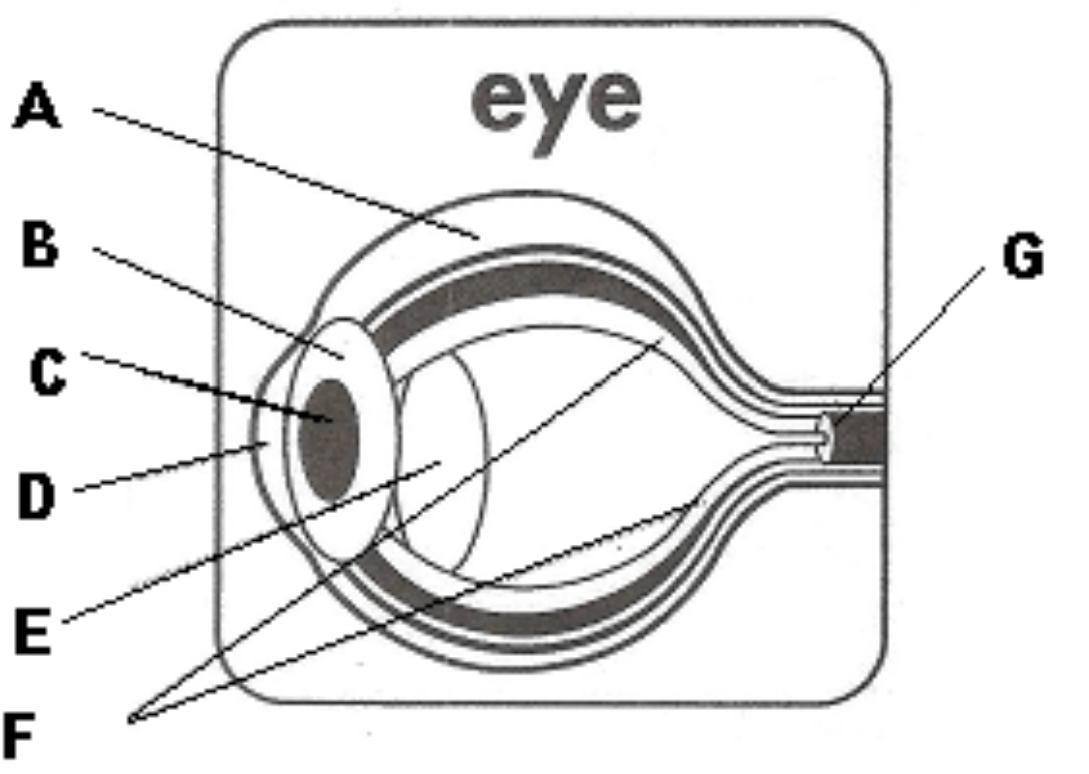
What is the sclera?
_________ muscles in the iris contract when the eye is exposed to bright light.
What is circular muscles?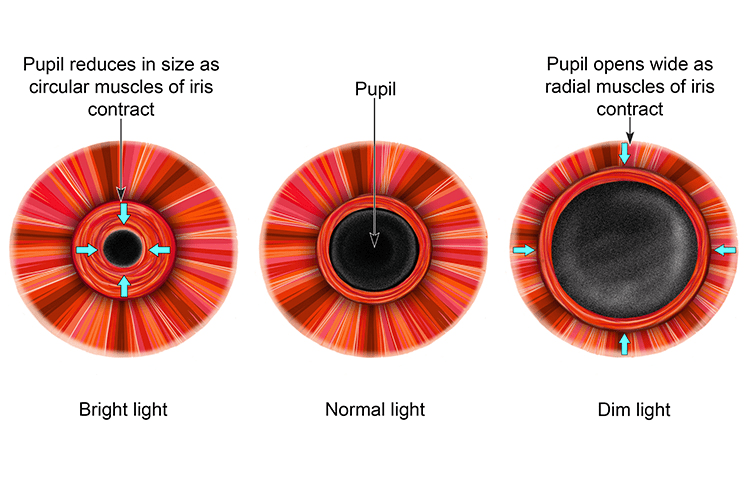
Part of the cortex primarily responsible for sensation (sense of touch).
What is the parietal lobe? OR sensory cortex.
Condition wherein body temperature is below normal temperature.
What is hypothermia?
Part of the brain highlighted in purple.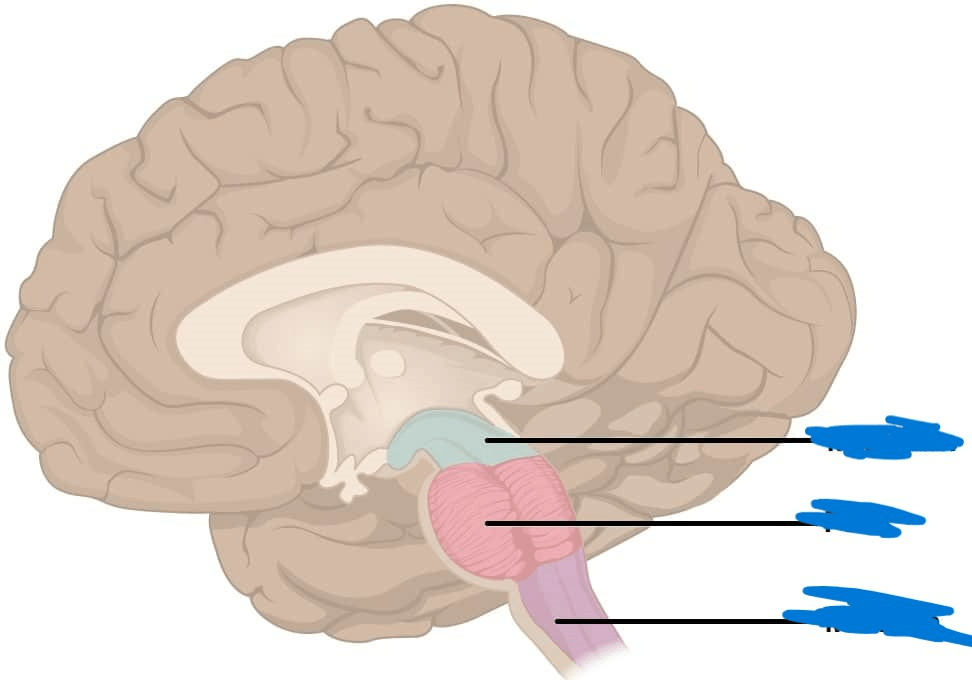
What is the medulla?
Photosensitive layer of cells/tissue in the eye.
What is the retina? (photosensitive = detects light)
__________ lenses are needed to correct for hyperopia.
What is convex lenses?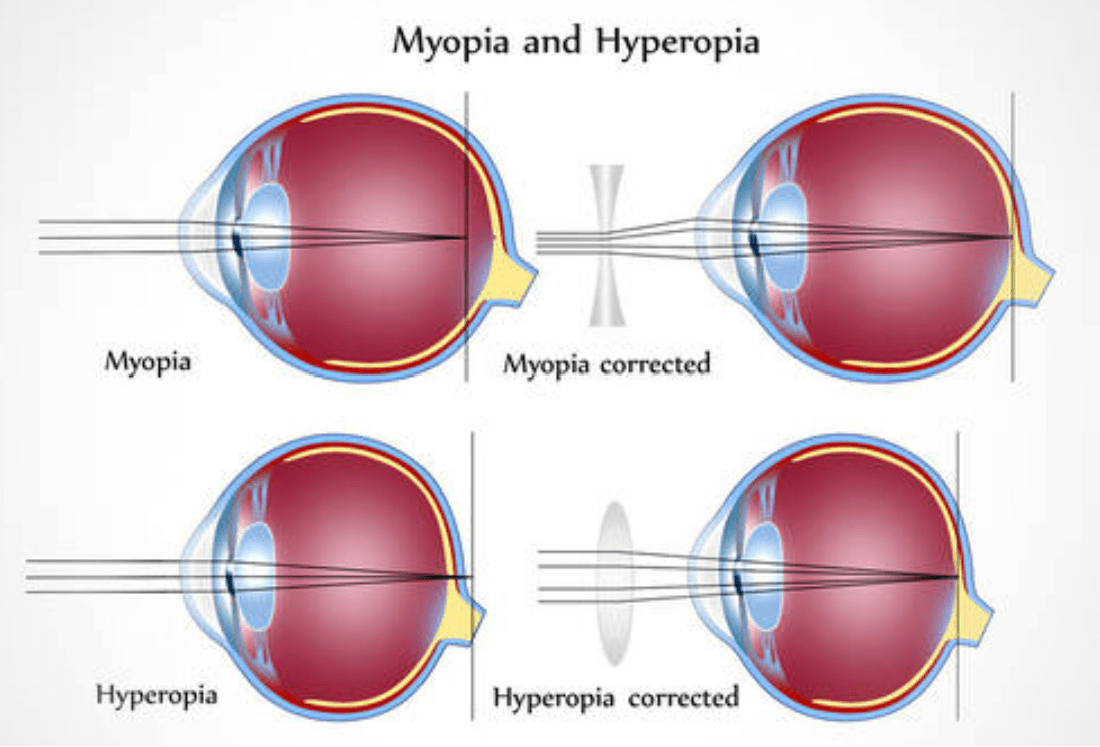
Thermoregulatory centre of the brain. Also controls thirst, hunger, and sleep.
What is the hypothalamus?
Chemical reaction the body uses to produce heat.
What is respiration?
Area of the brain highlighted in green.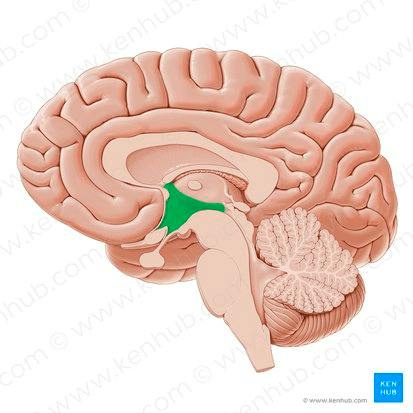
What is the hypothalamus?
Outer layer of the eye that helps to refract light onto retina.
What is the cornea?