What is the long tail that comes off the neuron? (E)
The axon
What is lobe #6? What is it responsible for?
Frontal Lobe: Executive functions, personality, Reasoning
What are the bundles of fibers found in your PNS that sense the world around you?
Chemical messenger that carries signals between neurons
What do CNS and PNS stand for?
CNS - central nervous system
PNS - peripheral nervous system
What is letter A pointing to?
The dendrites
What is #2? What is it responsible for?
Occipital Lobe: Visual processing (sight)
What do the thermoreceptors in your hands sense?
Temperature
What is the synapse?
The space between two neurons where the signal passes onto the next
What structures are included in the CNS?
Brain and spinal cord
What is the function of the dendrites?
Receive signals from neighboring neurons
What is #5? What is it responsible for?
Temporal lobe: Processes auditory information and language
What are the two sensory functions of the inner ear? 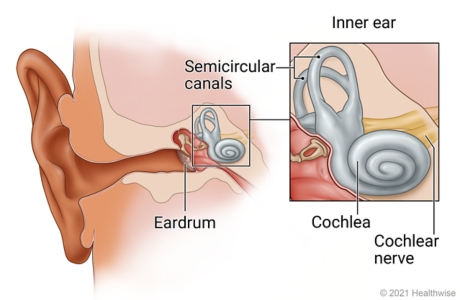
Hearing and balance
Affects mood and overall wellbeing (happiness neurotransmitter)
What structures are included in the PNS?
Nerves
What is the function of the axon/synaptic end bulbs?
What is #1? What is it responsible for?
Parietal lobe: Processing sensory info, Proprioception
What structures in your eyes allow you to see color?
Cones
What affect does glutamate have on the body?
Allows you to learn and remember things
What are the two types of cells in nervous tissue?
Neurons and Glial cells (neuroglia)
What is the function of the myelin sheath?
Insulates the axon so signals travel faster
What is #3? What is it responsible for?
Cerebellum: balance, coordination, speech
Papillae (tastebuds) and the olfactory epithelium
Explain what causes some drugs to become addictive (include the neurotransmitter that is involved)
Some drugs stimulate the release of dopamine (or mimic dopamine) to cause a feeling of pleasure. People become addicted to that pleasure and will repeat the behavior to replicate the "good" feeling
Explain the functions of both neurons and glial cells in the body
Neurons -- transmit signals across body
Glial cells -- support and protect neurons