It’s not my spidey-sense that’s tingling, but rather this part of the neuron that receives stimuli.
What are dendrites?
Coming from a definition to split or divide, this is the area that vesicles must cross to continue sending a message between neurons.
What is the synaptic cleft?
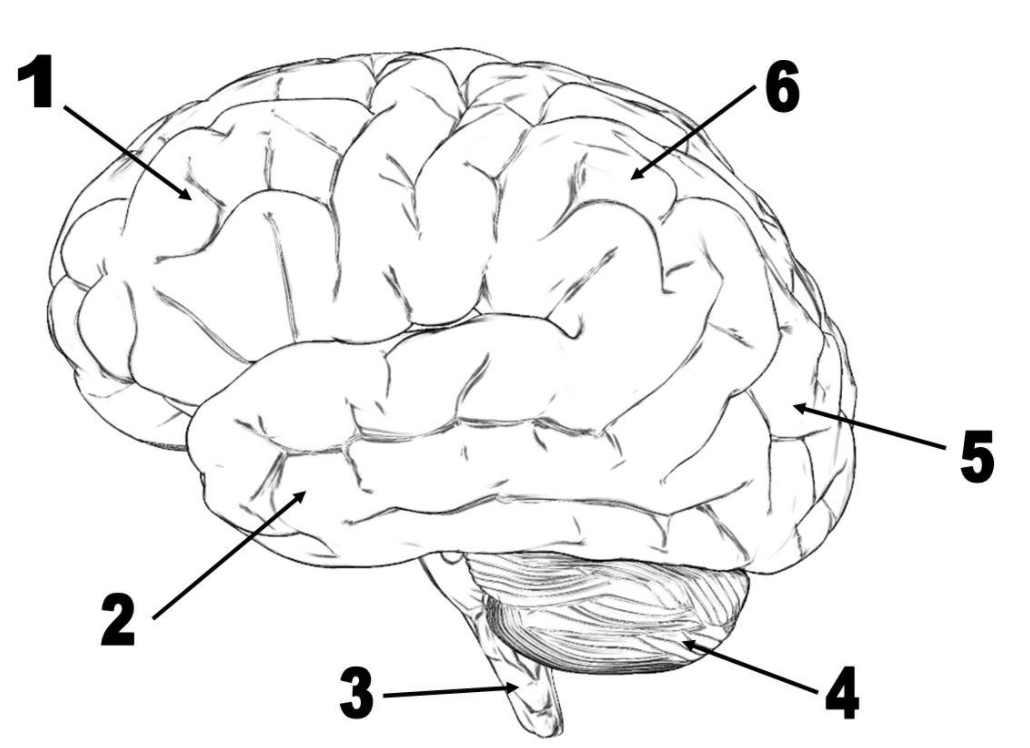
Lobe number 1
Structure A
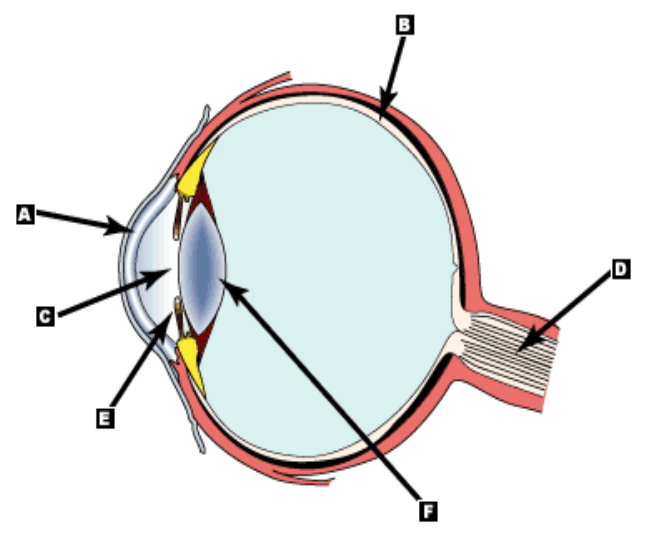
What is the cornea?
The medical term for nearsightedness.
What is myopia?
Originating from the Latin word terminus ad quem, this part of the neuron is located towards the end of the cell.
What is axon terminal?
This chemical messenger begins inside a vesicle and gets released into the synaptic cleft.
What is a neurotransmitter?
Lobe number 5
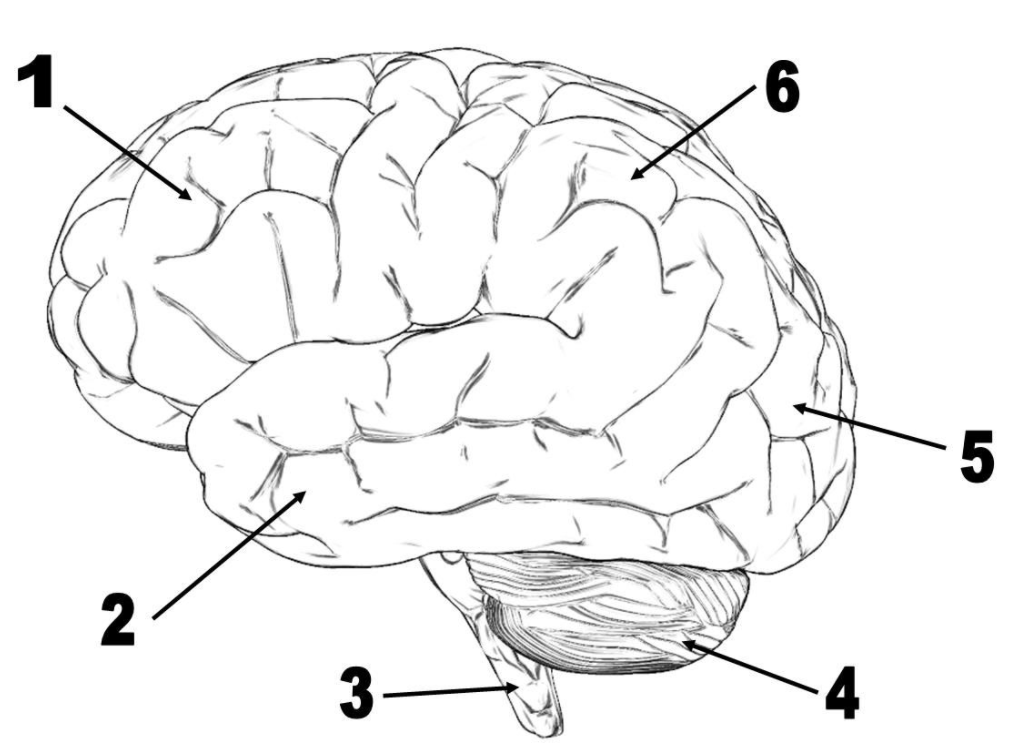
What is the occipital lobe?
Structure D
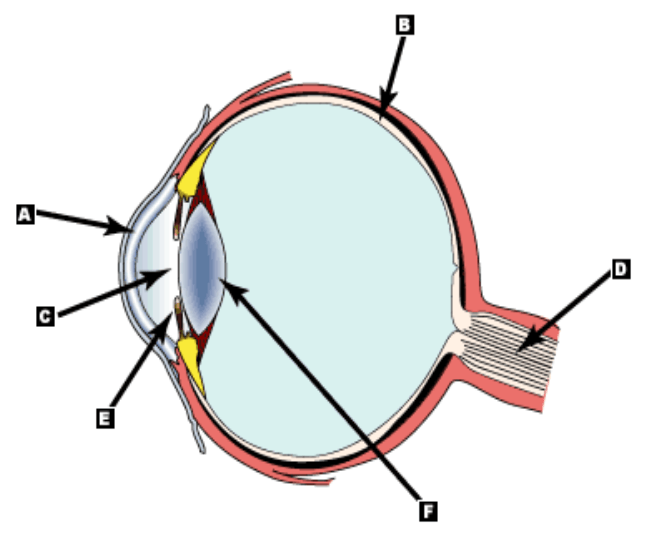
What is the optic nerve?
This vision disorder is characterized by increased internal eye pressure which damages the optic nerve.
What is glaucoma?
These two body structures make up the central nervous system.
What are the brain and spinal cord?
Also responsible for the formation and development of bone, this element signals vesicles to fuse into the presynaptic membrane and release neurotransmitters.
What is Ca2+?
What is Ca?
This "little brain" helps control movement, balance, and posture.
What is the cerebellum?
With the help of ciliary muscles, this structure changes shape to accommodate objects at various distances.
What is the lens?
This dense clouding of the lens causes the vision disorder shown below.
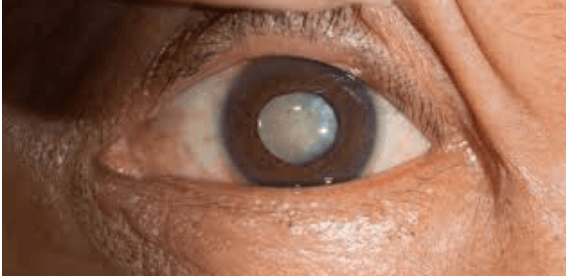
What are cataracts?
The Peripheral nervous system can be further broken down into these two divisions.
What are the autonomic and somatic nervous systems?
The buildup of this molecule in the postsynaptic neuron generates a new electrical impulse.
What is Na+?
What is sodium?
Lobe number 2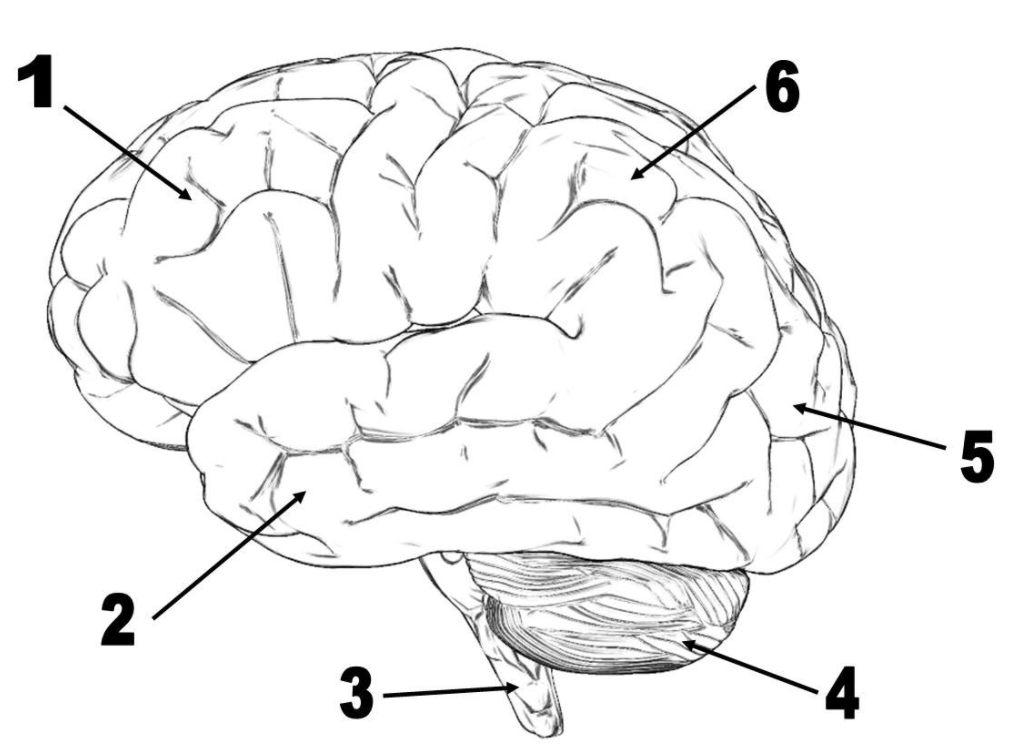
What is the temporal lobe?
What is the iris?
The medical term for farsightedness.
What is hyperopia?
This nervous system division is responsible for involuntary and unconscious impulses such as the heartbeat.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
The structures in red are reducing in number inside the brains of drug addicts.
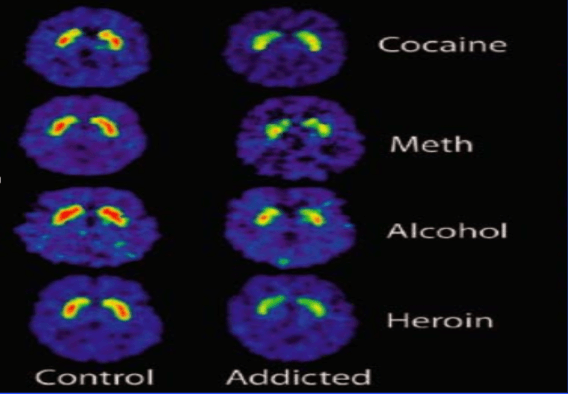
What are dopamine receptors?
This multi-layered tissue surrounds the cerebrum to provide an extra layer of protection, cushioning, and nourishment.
What is the meninges?
The innermost layer of the eye that's embedded with photoreceptors.
What is the retina?
Distorted or blurred vision at all distances.
What is astigmatism?