What is powerline networking technology?
Powerline networking adds the ability to connect a device to the network using an adapter wherever there is an electrical outlet. The network uses existing electrical wiring to send data. It is not a replacement for physical cabling, but it can add functionality in places where wireless access points cannot be used or cannot reach devices.
IEEE 802.11b/g uses what RF Band?
802.11b/g/n/ad devices all operate at 2.4 GHz
802.11a/n/ac/ad devices operate at 5 GHz
802.11ad devices operate at 60 GHz
What is peer-to-peer networking and what are the disadvantages to peer-to-peer network model
The simplest peer-to-peer network consists of two computers that are directly connected to each other through the use of a wired or wireless connection.
The primary disadvantages of a peer-to-peer network are its lack of central administration, minimal security, and its lack of scalability.
What is tethering?
Many cell phones have the ability to connect to other devices through a feature called tethering. The connection can be made using Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or a USB cable. Once a device is connected, it is able to use the cellular connection of the phone to access the internet. When a cellular phone allows Wi-Fi devices to connect and use the mobile data network, this is called a hotspot.
What does the Internet layer of TCP/IP do?
The TCP/IP model consists of four layers: application, transport, internet, and network access. Of these four layers, it is the internet layer that is responsible for routing messages.
What is Encapsulation?
When a message is placed inside of another message, this is known as encapsulation. On networks, encapsulation takes place when one protocol data unit is carried inside of the data field of the next lower protocol data unit.
What are IPv4 addresses used for?
IPv4 addresses are used to uniquely identify a device on an IP network. The subnet mask identifies how many hosts can be on a network and the network number.
What are the characteristics of multicast transmission?
A multicast transmission is a single packet sent to a group of hosts and is used by routing protocols, such as OSPF and RIPv2, to exchange routes. The address range 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255 is reserved for link-local addresses to reach multicast groups on a local network.
What type of devices are End Devices?
What type of Devices are Intermediary Devices
Routers and switches are intermediary devices.
End devices consist of PCs, laptops, and servers. They also include printers, VoIP phones, security cameras, and hand-held devices.

What 3 bits of info do you need to connect to Wifi?
In order to connect an Android or IOS device to a Wi-Fi network manually, perform these steps:
Enter the network SSID of the wireless network.
Choose the security type used by the wireless network.
Input the password to authenticate successfully.
What are the advantages to a peer-to-peer network?
Because network devices and dedicated servers are not required, peer-to-peer networks are easy to create, less complex, and have lower costs.
Peer-to-peer networks also have no centralized administration. They are less secure, not scalable, and those devices acting as both client and server may perform slower.
What is NFC?
NFC, or Near Field Communications, is a wireless technology for communication between devices at extremenly short distances and is used in contactless payment systems.
What does the Network Layer do?
Logical addresses, also known as IP addresses, are added at the network layer.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using fiber-optic cabling?
Fiber-optic connectors have higher costs, technician installation skills required are higher, fiber bandwidth supported is higher, and fiber-optic cabling is immune to RFI and EMI, and can transmit signals with less attenuation.
How many bits are represented by each group of four hexadecimal values contained between the colons in an IPv6 address?

The four hexadecimal values contained in a hextet represent 16 bits. There are eight hextets in an IPv6 address that make up the total 128 bits of the address. (16 x 8 = 128).
What is DHCP?
DHCP provides automatic IP address configuration to hosts on a network. Hosts will be dynamically assigned an address when they connect to the network, although not necessarily the same address each time they connect. If there are static and dynamic addresses used together on the network there could still be the possibility of address conflicts. DNS can be used in conjunction with DHCP to allow users to communicate using names rather than IP addresses.
What is DSL?
DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line. It’s a type of internet connection that uses existing telephone lines to deliver high-speed internet service to homes and businesses.
How DSL Works:
DSL transmits digital data over the copper wires of standard telephone lines.
It splits the line into separate channels for voice and data:
You can use the phone and internet at the same time.
A DSL modem is used to decode and transmit the data.
Types of DSL:
ADSL (Asymmetric DSL) – More download speed than upload; common in homes.
SDSL (Symmetric DSL) – Equal upload/download speeds; used in businesses.
VDSL (Very-high-bit-rate DSL) – Faster than ADSL; can support video and streaming.
How do you hide your SSID?
Disabling SSID broadcast prevents the access point from announcing the name of the network.
What will a Switch do if it receives an incoming frame and the destination MAC address is not listed in the MAC address table?
When a switch receives an incoming frame with a destination MAC address that is not listed in the MAC address table, the switch forwards the frame out all ports except for the ingress port of the frame. When the destination device responds, the switch adds the source MAC address and the port on which it was received to the MAC address table.
When analog voice signals are converted for use on a computer network, in what format are they encapsulated?
When Voice over iP (VoIP) is being used, analog voice signals are translated into digital data in the form of IP packets. This translation allows the phone call to be carried through a computer network.
What does the Data Link Layer do?
Physical addresses are added at the data link layer.
How is Data is transmitted across a network on Copper Cable media.
Metal wires within cables (copper cable, such as twisted-pair and coaxial cable) – Data is encoded into electrical impulses.
How many bits are in an IPv4 address?
An IPv4 address is comprised of 4 octets of binary digits, each containing 8 bits, resulting in a 32-bit address.
Why would technician ping the default gateway from the employee laptop?
The default gateway address is usually the address of the router interface. The router provides access to remote networks, so a successful ping to the default gateway would mean that the laptop is able to communicate with the router.
How does a Switch build it's MAC address Table?
A switch “learns” or builds the MAC address table based on the source MAC address as a frame comes into the switch. A switch forwards the frame onward based on the destination MAC address.
What is NAT?
A wireless router will perform Network Address Translation (NAT) whenever a private (local) source IPv4 address is translated to a public (global) address.
What type of network media would you most likely use to connect to a desktop computer?
Ethernet technology generally uses twisted-pair cables to interconnect devices. Because Ethernet is the foundation for most local networks, twisted-pair is the most commonly used type of network cabling for connecting office computers.
What does the netstat command do?
The netstat command is a network utility that can be used to display active TCP connections that are open and running on a networked host.
What does the Transport Layer do?
Port addresses are added at the transport layer.
How is Data is transmitted across a network on Glass or Plastic Fiber media.
Glass or plastic fibers within cables (fiber-optic cable) – Data is encoded into pulses of light.
When a host sends a packet, how does it determine if the destination of the packet is on the same local network or on a remote network?
When a host sends a packet, it uses the subnet mask to compare the source IPv4 address and the destination IPv4 address. If the network bits match, both the source and destination host are on the same local network. Otherwise, the destination host is on a remote network.
What does the ipconfig/renew command do?
The ipconfig/renew command requests an IP address from a DHCP server. Msconfig is not a network troubleshooting command.
What criteria do you use to choose a network medium?
Criteria for choosing a network medium include the following:
The distance the selected medium can successfully carry a signal in the environment in which the selected medium is to be installed
The amount of data and the speed at which the data must be transmitted
The cost of the medium and its installation
Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as two layers of the TCP/IP model?
The OSI transport layer is functionally equivalent to the TCP/IP transport layer, and the OSI network layer is equivalent to the TCP/IP internet layer.
What is a Broadcast Domain?
A Broadcast Domain is a logical network segment in which any broadcast packet sent by a device is received by all other devices within that same segment. Each port on a Router break the networks into separate LANs/broadcast domains. Each LAN is a broadcast domain.
What is a Reference Model?
Reference model – The primary purpose is to aid in a clearer understanding of the functions and processes necessary for network communications.This type of model does not specify exactly how a function should be accomplished. The OSI model is an example of a reference model.
How are port numbers used in the TCP/IP encapsulation process?
Both UDP and TCP use port numbers to provide a unique identifier for each conversation. Source port numbers are randomly generated and are used to track different conversations. Destination port numbers identify specific services by using either a default port number for the service or a port number that is assigned manually by a system administrator.
How is Data is transmitted across a network Wirelessly.
Wireless transmission – Data is encoded via modulation of specific frequencies of electromagnetic waves.
What are the IPv6 Rules?
An IPv6 address is made up of 128 bits represented in hexadecimal numbers.
There are two rules that help reduce the number of digits needed to represent an IPv6 address.
- Rule 1 – Omit leading zeros in any 16-bit section.
- Rule 2 – Replace any single group of consecutive zeros with a double colon (::). This can only be used once within an IPv6 address.
What does the ipconfig command do?
The ipconfig command displays the computer network configuration details.
How do you break up a Broadcast Domain?
All hosts within a single LAN belong to one broadcast domain. As the number of hosts increase, it could cause more traffic on the segment and may slow network performance. To solve the performance issue, a router would be the device used to segment the single LAN into multiple LANs.
What does the tracert command do?
The tracert utlility (also known as the tracert command or tracert tool) will enable the technician to locate the link to the server that is down.
Which Layer 2 and Layer 3 destination addresses will a Broadcast address be sent to?
The destination addresses of FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and 255.255.255.255.
Which types of nodes (devices) should be assigned static IP addresses on a network?
Servers, printers, and intermediary devices, such as routers, switches, and access points should have statically assigned IP addresses so that they are accessible to users and available for remote management.
What TCP header fields are used to confirm receipt of data?
Together the TCP sequence number and acknowledgment number fields are used by the receiver to inform the sender of the bytes of data that the receiver has accepted.
What would the default gateway be for devices connected to the R3 router? 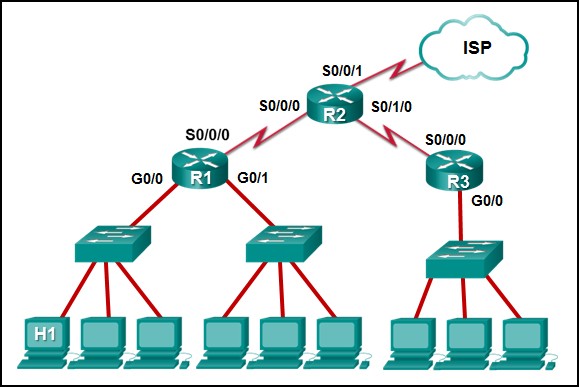
The default gateway for host devices on the the R3 router interface would be the G0/0 interface of R3. Any device on that network should be configured with the IP address of that interface in its addressing settings.
What are the ranges of private IPv4 addresses?
The ranges of private IPv4 addresses are as folllows:
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
What are the routing codes on a Cisco Router?
These codes tell you what type or route used to connect the two networks.
Some of the IPv4 routing table codes include the following:
C – directly connected
S – static
D – EIGRP
* – candidate default