The long part of a neuron that transmits signals to the next neuron
AXON
Damage to this lobe would probably affect vision.
OCCIPITAL
What part of the brain is responsible for balance and coordinated movement?
CEREBELLUM
The P in PNS - what does it stand for and what does it include?
PERIPHERAL - NERVES
True or False? The right side of the brain controls the right side of the body.
FALSE !
The neuron extension that receives impulses from other neurons
DENDRITE
This is the ___ ___ lobe. (TWO words.)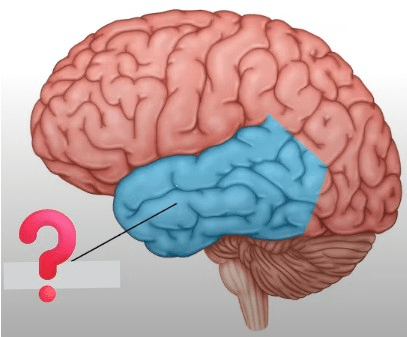
LEFT TEMPORAL
Damage to this brain part would be the most life-threatening
BRAINSTEM (MEDULLA OBLONGATA)
These always bring impulses toward the CNS (and are always unipolar)
SENSORY NEURONS aka afferent neurons
What do we call the numerous ridges and grooves on the surface of the cerebrum?
GYRI, SULCI
The empty space between 2 almost touching neurons
SYNAPSE
Which lobe is responsible for logic, problem solving, and other executive functions?
FRONTAL
The hub where the left and right hemispheres can communicate
CORPUS CALLOSUM
These always carry impulses away from the CNS to a muscle or gland.
MOTOR NEURONS aka efferent neurons
You know all the parts of a generic neuron. What part do multipolar neurons have that unipolar neurons lack?
DENDRITES
Myelin sheath - what is it made of and what is it for?
made of SCHWANN CELLS (ok to say LIPID)
INSULATES the axon (for conductivity)
What is the main responsibility of this lobe? 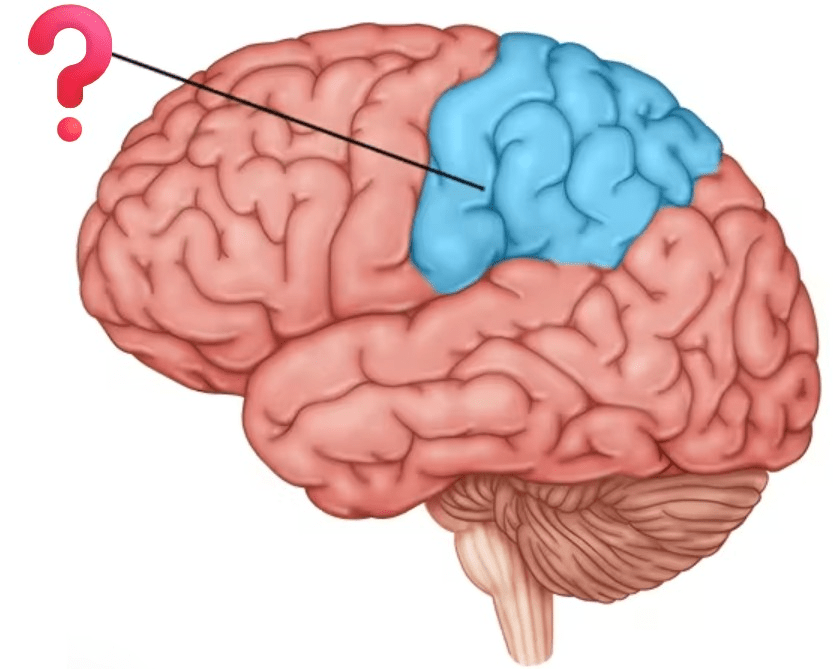
SENSE PERCEPTION
The "switchboard" where signals go to be redirected to the correct area of the brain for processing.
THALAMUS
What classification of neuron is never found in the PNS?
INTERNEURON (AKA association neuron)
CORPUS CALLOSUM
The short, uninsulated sections of a myelinated axon
NODES OF RANVIER
Contrast Wernicke's and Broca's areas.
Wernicke's is in the TEMPORAL and has to do with UNDERSTANDING LANGUAGE.
Broca's is in the FRONTAL and has to do with PRODUCING SPEECH.
Hypothalamus or Hippocampus - you choose one and tell its responsibility
Hypothalamus - hunger, thirst, hormones
Hippocampus - memories
What are the two classification categories of neurons?
STRUCTURAL, FUNCTIONAL
What is the purpose of all the ridges and grooves on the brain?
They increase SURFACE AREA to fit more neurons and make more neural connections.